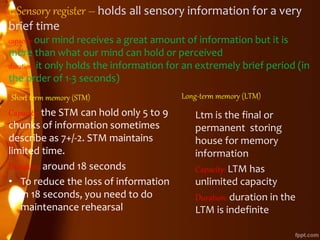
The information processing theory focuses on how knowledge enters and is stored in memory and retrieved. It involves three main stages: encoding, where information is perceived and attended to; storage, where information is kept for brief or extended periods; and retrieval, where stored information is reactivated. There are different types of knowledge like general/specific, declarative, procedural, and episodic. Memory involves three stages - sensory register (holds info <3 sec), short-term memory (holds 5-9 chunks for 18 sec), and long-term memory (unlimited capacity, indefinite duration). Forgetting occurs through decay or interference, while retrieval is increased through rehearsal, meaningful learning, organization, elaboration, imagery, generation, context,