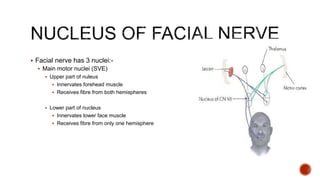
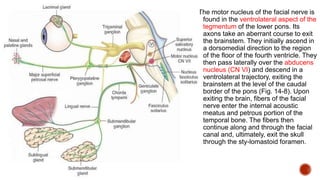
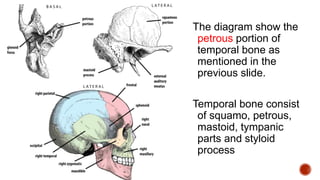
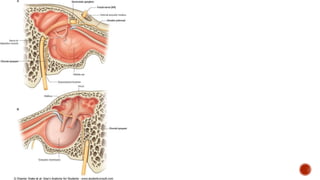
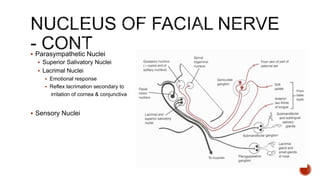
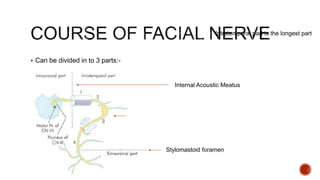
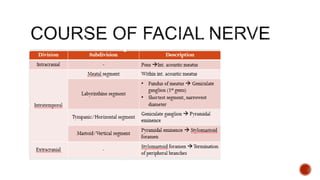
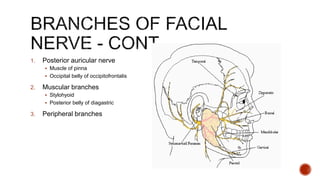
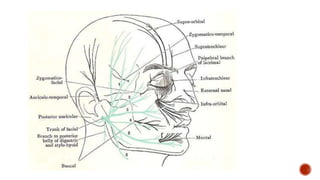
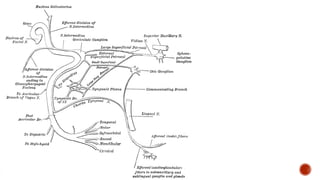
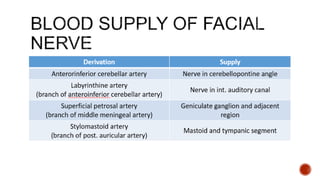
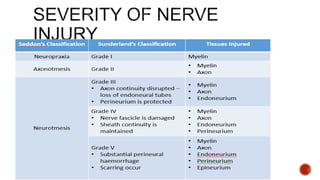
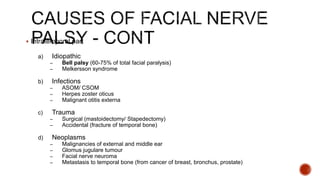
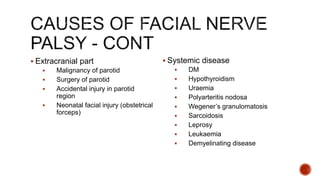
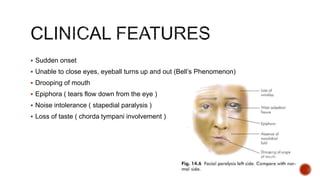
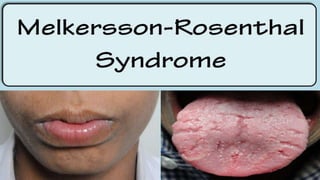
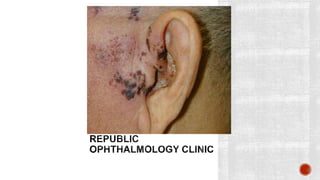
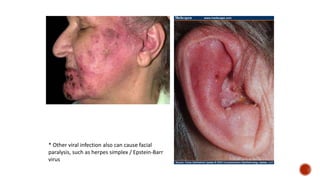
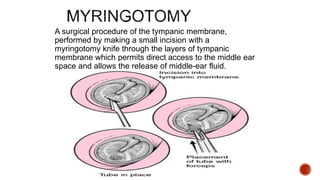
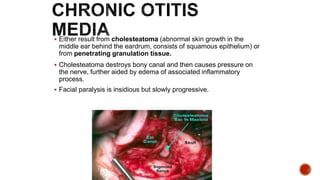
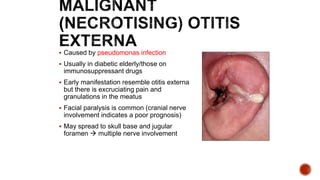
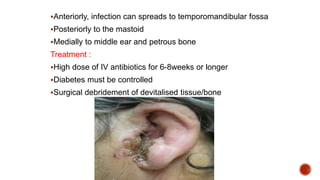
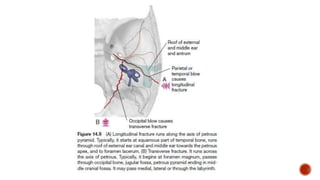
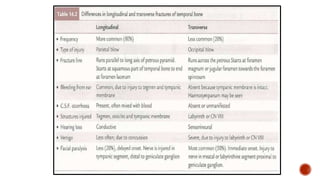
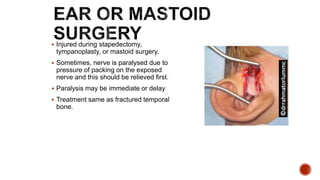
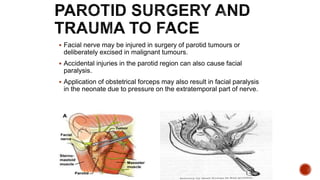
The facial nerve has motor and sensory components. It exits the brainstem at the caudal pons border and travels through the internal acoustic meatus, facial canal, and stylomastoid foramen to innervate muscles of the face. Facial nerve paralysis can result from central, intratemporal, or extracranial causes such as Bell's palsy, Ramsay Hunt syndrome, fractures of the temporal bone, ear infections, tumors, and complications of ear/parotid surgery. Treatment depends on the cause but may include antibiotics, antivirals, steroids, nerve decompression, or reconstructive surgery.