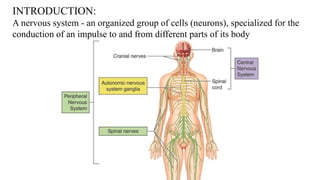
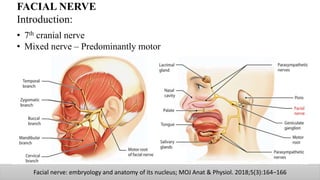
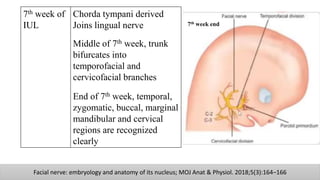
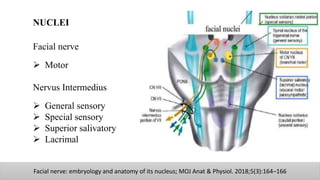
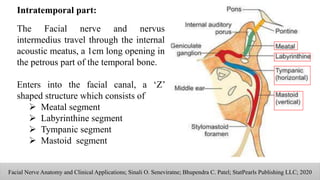
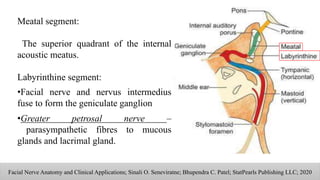
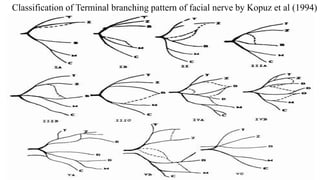
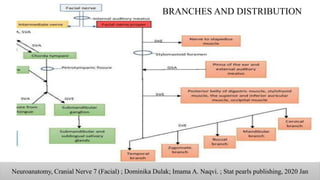
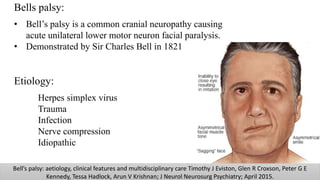
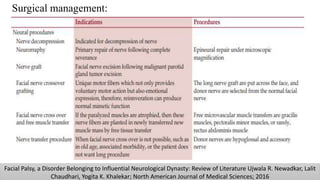
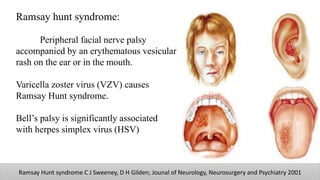
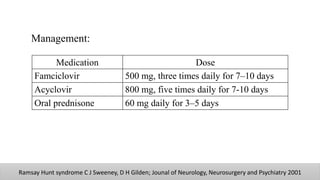
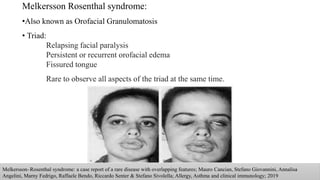
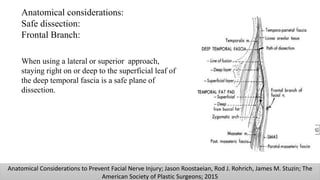
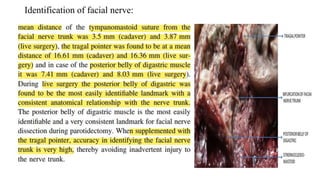
The document discusses the anatomy and embryology of the facial nerve, its various components, functions, and clinical implications of lesions and disorders. It describes the nerve's development, branching patterns, sensory and motor innervations, common conditions affecting it like Bell's palsy and Ramsay Hunt syndrome, and management strategies. Key anatomical landmarks and clinical tests for assessing facial nerve function are also highlighted.