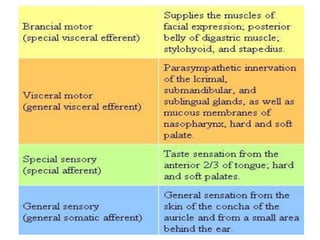
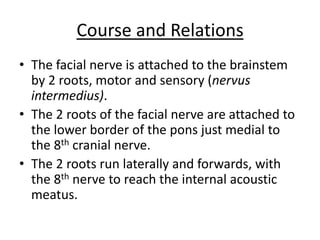
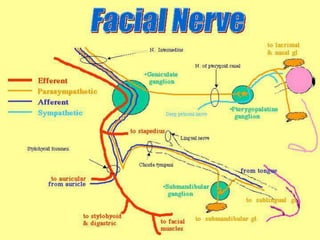
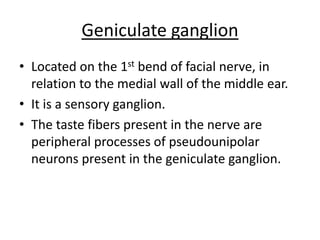
The facial nerve emerges from the brainstem and travels through the facial canal in the temporal bone. It has motor, parasympathetic, and sensory components. The motor component innervates the muscles of facial expression. The parasympathetic component innervates salivary and lacrimal glands. The sensory component provides taste sensation to the tongue and palate. The facial nerve exits the skull through the stylomastoid foramen and divides into 5 branches that innervate muscles of the face. Lesions can occur at different points along the nerve's course, resulting in varying symptoms such as facial paralysis, loss of taste, or impaired lacrimation or salivation.