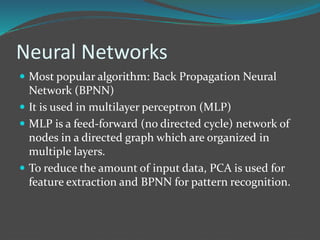
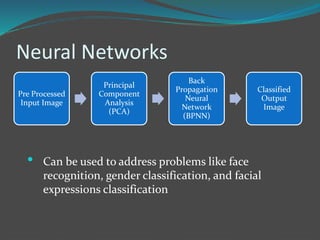
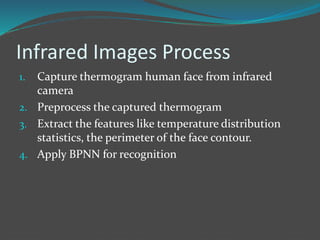
Face recognition is a technique for identifying or verifying individuals using their facial features. It involves extracting features from images, selecting subsets of important features, and matching feature sets to identify faces. 2D recognition uses image features while 3D recognition uses geometric facial features, improving accuracy over 2D. Face recognition has applications in security, biometrics, law enforcement, and advertising. Key algorithms include PCA, LDA, neural networks, and recently deep learning methods.