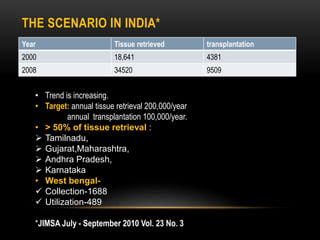
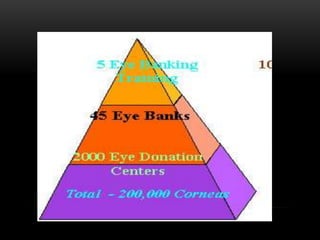
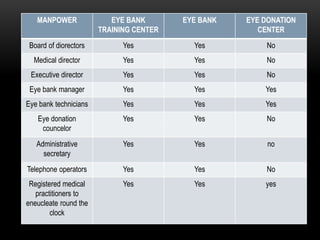
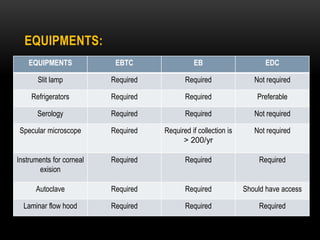
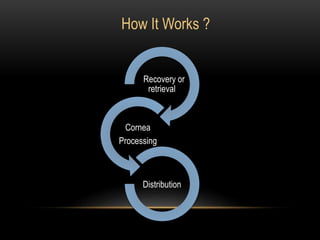
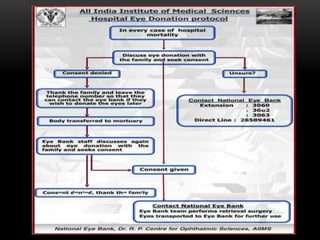
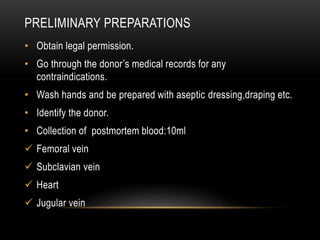
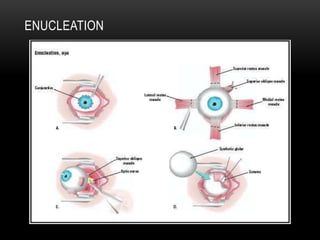
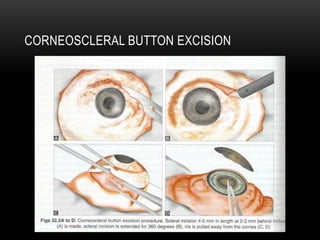
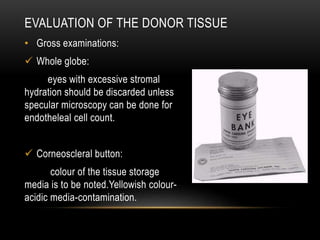
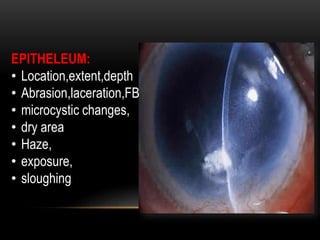
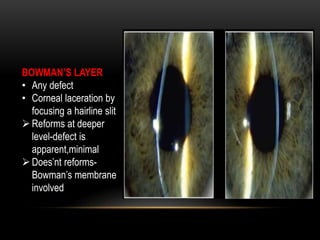
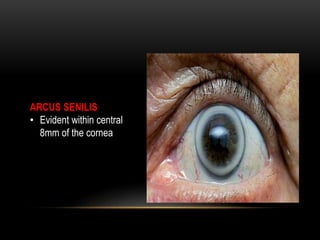
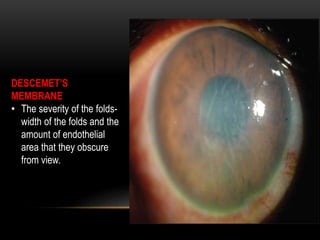
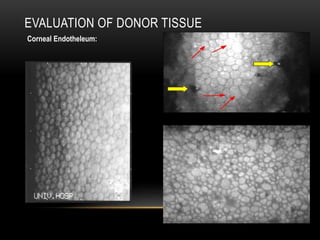
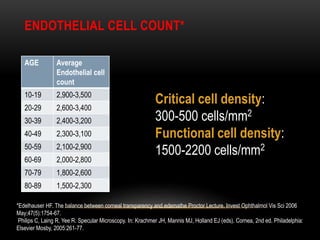
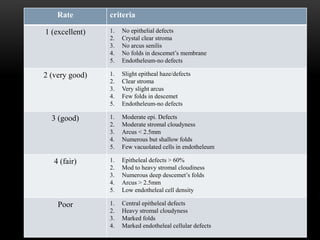
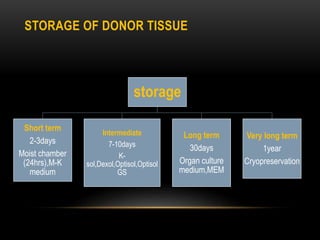
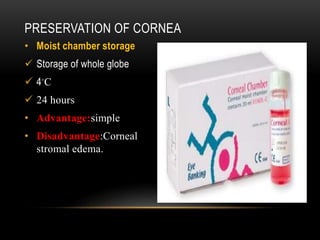
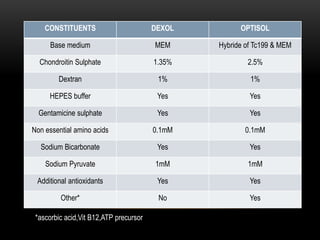
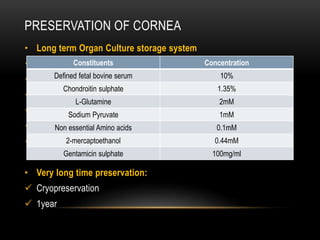
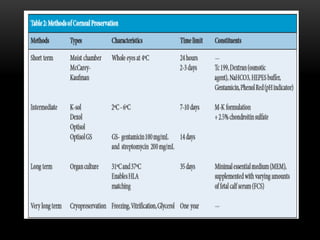
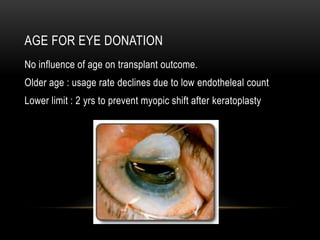
An eye bank is a nonprofit organization that retrieves, processes, stores and distributes donor corneal tissue for transplantation. Corneal blindness is a major problem in developing countries that can often be addressed through corneal transplantation, which has a high success rate. In India, the number of corneal transplants has been increasing but still does not meet the need, with over 50% of tissue coming from a few states. Eye banks are responsible for properly evaluating donor tissue through testing, examination and microscopy before distributing it to ensure safe and effective transplantation. Tissue is stored short or long-term in special nutrient media depending on preservation needs.