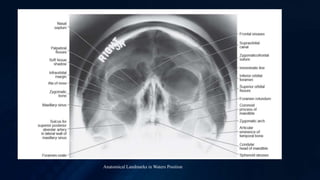
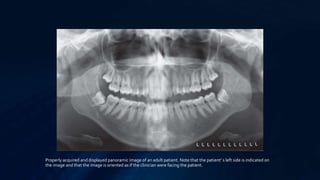
This document describes various extraoral imaging techniques used in dentistry including lateral skull, submentovertex, Waters, posteroanterior skull, and reverse-Towne projections. For each technique, it provides details on positioning of the image receptor and patient, direction of the central x-ray beam, and anatomical structures visible in the resultant image. Common indications for each technique are also listed. Extraoral radiographs provide important diagnostic information for evaluating facial bones, sinuses, and temporomandibular joints. Proper patient positioning is essential for obtaining high quality images.