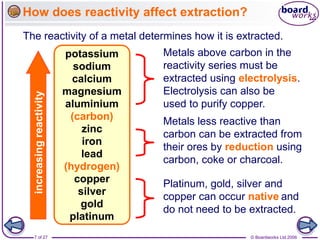
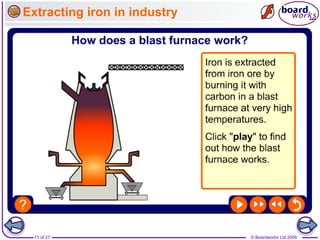
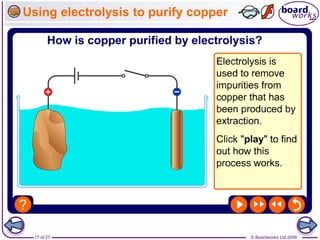
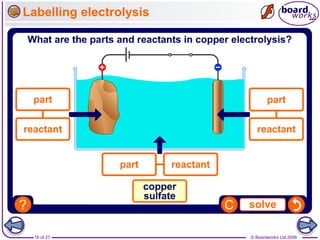
The document discusses the process of metal extraction from ores. Metals are found combined with other elements in rocks known as ores and require extraction to be separated before use. There are two main methods: reduction using carbon or electrolysis using electricity. The reactivity of the metal determines which method is suitable. Extraction has environmental impacts but these can be reduced through techniques like recycling and leaching.