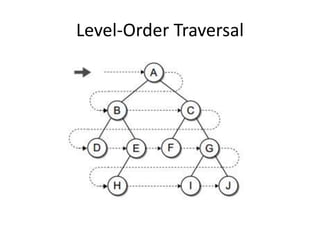
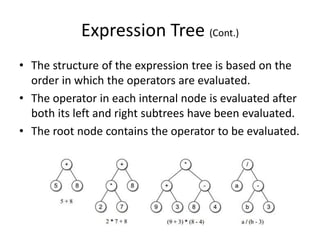
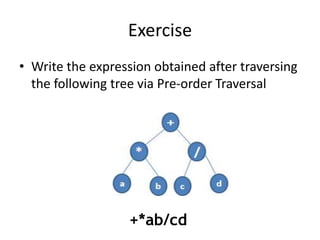
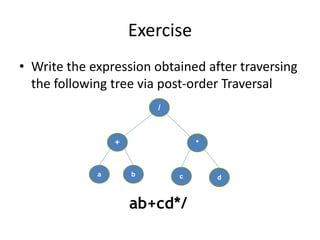
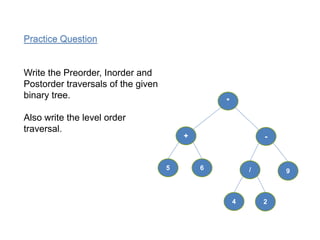
This document discusses different types of tree traversals including preorder, inorder, postorder, and breadth-first traversals. It explains that preorder, inorder, and postorder traversals are examples of depth-first traversals as they traverse nodes deeper in the tree before moving to higher levels, while breadth-first traversal visits nodes by level from left to right. The document also covers expression trees, which represent arithmetic expressions as binary trees with operators in interior nodes and operands in leaves.