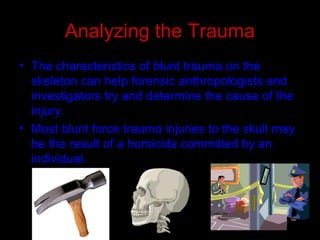
Blunt force trauma refers to injuries caused by impacts over a wide area rather than a puncture or penetration. It can affect many bones and cause fractures. Common weapons that cause blunt force trauma include bats, clubs, and other handheld objects. Analyzing the size, shape, weight of the object and pattern of fractures can provide clues about the nature and severity of the trauma. Blunt force to the skull can result in depressed fractures and LeFort fractures of the face indicate significant impact.