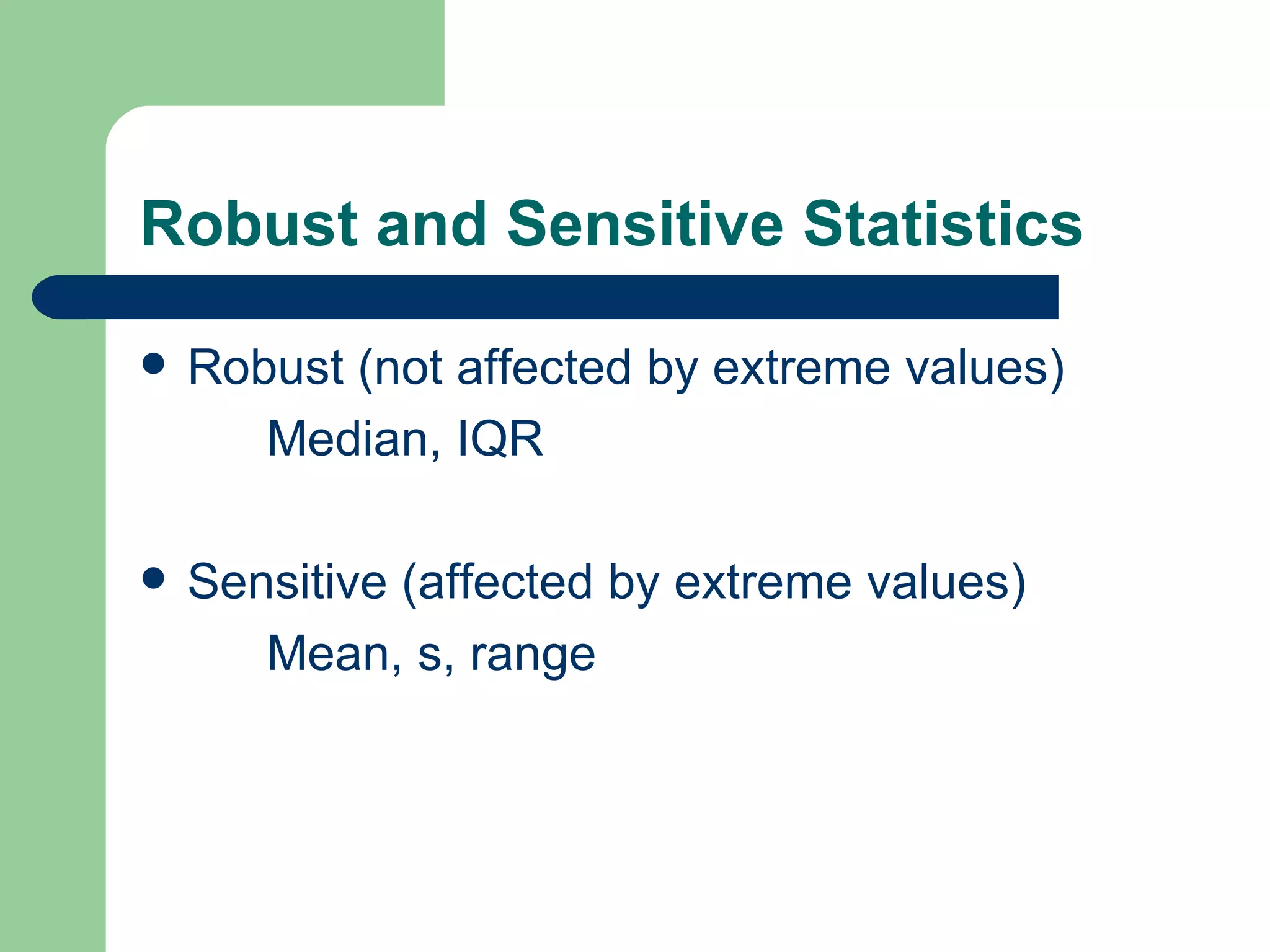
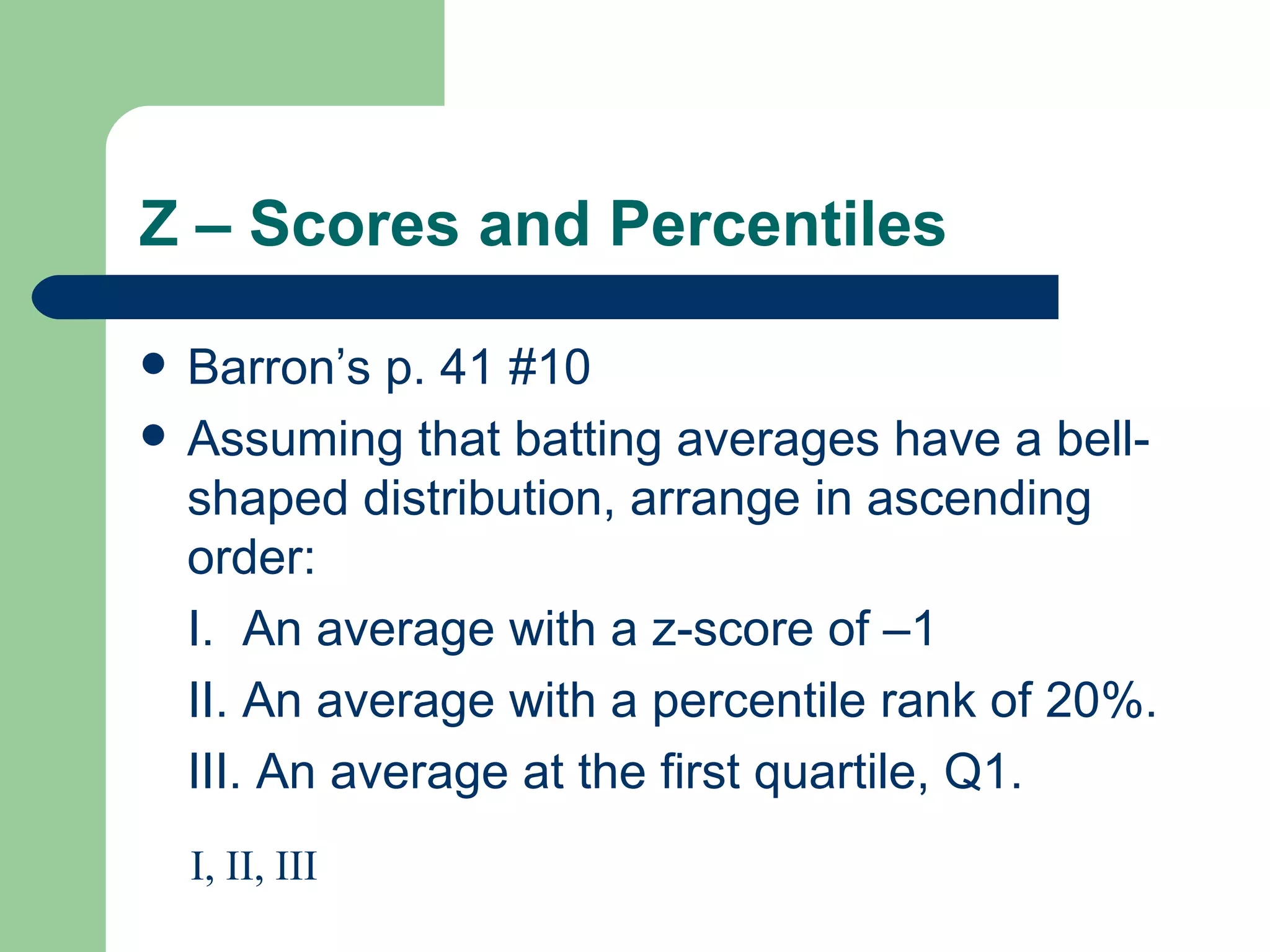
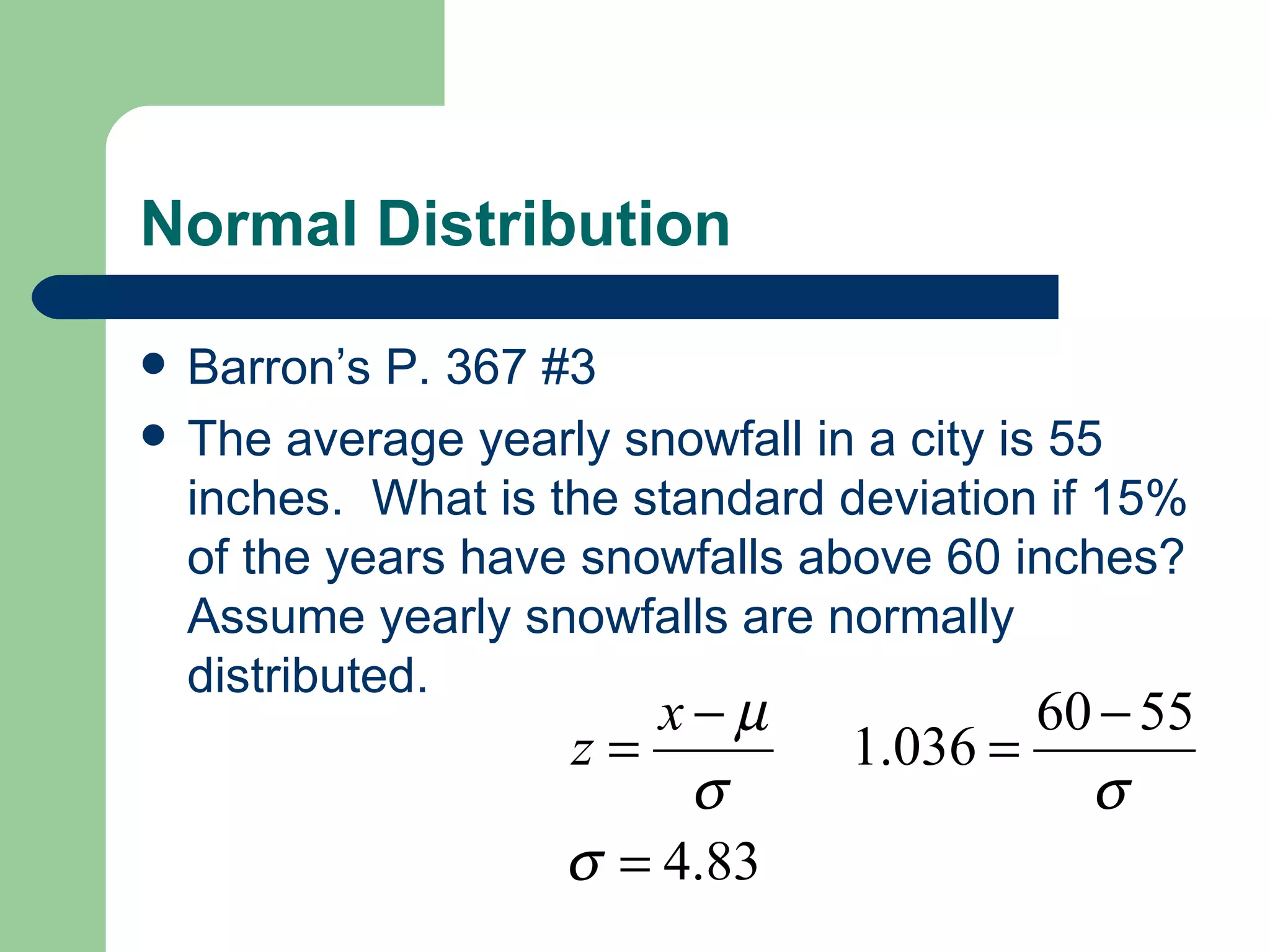
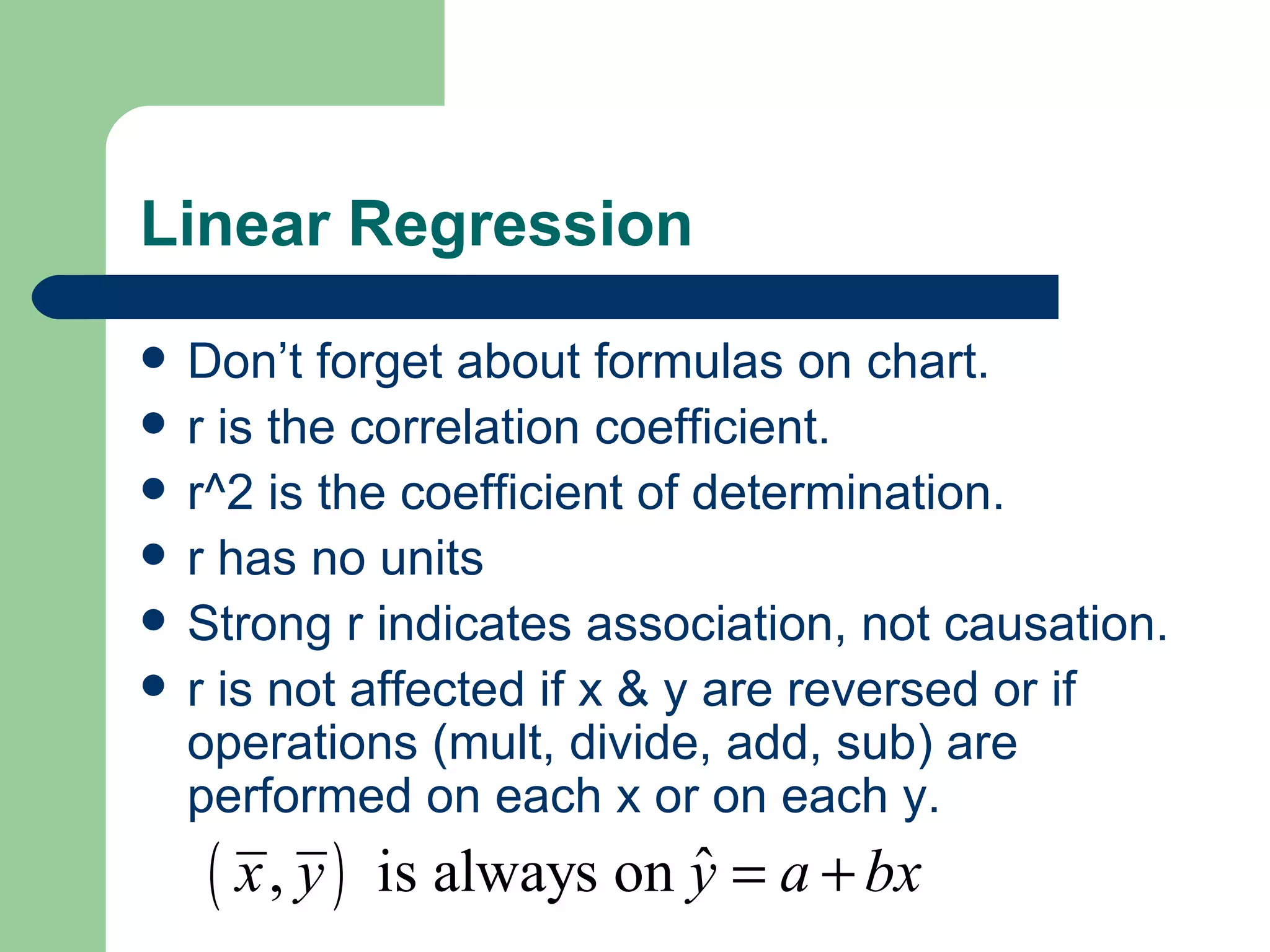
The document provides an overview of key statistical concepts for describing and analyzing data distributions, including measures of center, spread, and outliers. It also covers z-scores, percentiles, normal distributions, linear regression, and influential points. Specific topics summarized are checking for outliers in restaurant quality ratings data, comparing robust and sensitive statistics, the difference between parameters and statistics, and guidance for Barron's practice problems.