Expl sw chapter_07_wireless rev.01
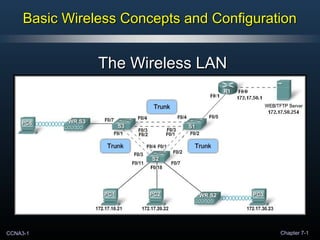
- 1. CCNA3-1 Chapter 7-1 Basic Wireless Concepts and ConfigurationBasic Wireless Concepts and Configuration The Wireless LANThe Wireless LAN
- 2. CCNA3-2 Chapter 7-1 • Perkembang Networking saat ini sudah dapat mendukung aktifitasPerkembang Networking saat ini sudah dapat mendukung aktifitas kita secara mobile/bergerak.kita secara mobile/bergerak. • Sehingga produktifitas kita saat iniSehingga produktifitas kita saat ini no longer restrictedno longer restricted lokasilokasi kerja yang tetap ataupun dibatasi oleh waktu.kerja yang tetap ataupun dibatasi oleh waktu. • Kita saat ini membutuhkan suatu network yang selaluKita saat ini membutuhkan suatu network yang selalu terkoneksi untuk dapat melakukan komunikasi dan aktifitasterkoneksi untuk dapat melakukan komunikasi dan aktifitas kita setiap saat dan setiap tempat atau dimana saja.kita setiap saat dan setiap tempat atau dimana saja. • Dengan networking yang dapat mendukung aktifitas kitaDengan networking yang dapat mendukung aktifitas kita secara mobile, maka saat ini kita dapat melakukan pekerjaansecara mobile, maka saat ini kita dapat melakukan pekerjaan seperti checkseperti check e-mail, voice mail, and the status of productse-mail, voice mail, and the status of products menggunakan personal digital assistants (PDAs) ataumenggunakan personal digital assistants (PDAs) atau handphone maupun pc tablet dari lokasi diluar kantor.handphone maupun pc tablet dari lokasi diluar kantor. • Access InternetAccess Internet dirumah-rumah saat ini sudah beralih daridirumah-rumah saat ini sudah beralih dari modem dial-up lama ke dedicated DSL atau cable servicemodem dial-up lama ke dedicated DSL atau cable service maupun handphone.maupun handphone. Why Use Wireless?Why Use Wireless?
- 3. CCNA3-3 Chapter 7-1 Why Use Wireless?Why Use Wireless? • Pada awalnya networks komunikasi terbatas hanya padaPada awalnya networks komunikasi terbatas hanya pada pertukaran informasi character based.pertukaran informasi character based. • Communications antar computers (cross) tidak mudahCommunications antar computers (cross) tidak mudah dilakukan dan memerlukan host/pc untuk keperluandilakukan dan memerlukan host/pc untuk keperluan komunikasi transfer data sederhana.komunikasi transfer data sederhana.
- 4. CCNA3-4 Chapter 7-1 Why Use Wireless?Why Use Wireless? • Saat ini networks dapat membawa berbagai jenis tipe dataSaat ini networks dapat membawa berbagai jenis tipe data information melalui banyak jenis device secarainformation melalui banyak jenis device secara SSIMULTANEOUSLY/bersamaanIMULTANEOUSLY/bersamaan.. • Kita mendapatkan response secara langsung dari lawanKita mendapatkan response secara langsung dari lawan komunikasi kita dimanapun kita berada.komunikasi kita dimanapun kita berada. Silver and Diamond Cell Phone $1.3Million Wind Energy Cell Phone Charger
- 5. CCNA3-5 Chapter 7-1 • Selain flexibility yang disediakan teknologi WLANs,Selain flexibility yang disediakan teknologi WLANs, keuntungan lainnya adalahkeuntungan lainnya adalah reduced costsreduced costs.. • Moving persons within a building with a wirelessMoving persons within a building with a wireless infrastructure.infrastructure. • Moving into a new building with no wired infrastructure.Moving into a new building with no wired infrastructure. Why Use Wireless?Why Use Wireless? Wired NetworkWired Network Wireless NetworkWireless Network ComponentComponent QtyQty CostCost TotalTotal QtyQty CostCost TotalTotal Switches,Switches, cabinets, etc.cabinets, etc. 167167 3,3503,350 559,450559,450 2525 4,4044,404 110,100110,100 CablingCabling 7,5007,500 4545 337,500337,500 430430 7575 61,92061,920 Network AdaptersNetwork Adapters 2,5002,500 5757 142,500142,500 2,5002,500 7777 192,500192,500 Wireless AccessWireless Access PointsPoints 250250 1,0341,034 258,500258,500 POE AdaptersPOE Adapters 4040 6767 2,6802,680 TotalTotal 1,039,4501,039,450 364,520364,520 Note: Values are estimates and do not reflect actual pricing.Note: Values are estimates and do not reflect actual pricing.Note: Values are estimates and do not reflect actual pricing.Note: Values are estimates and do not reflect actual pricing.
- 6. CCNA3-6 Chapter 7-1 • Kebanyakan network dalam suatu perusahaan menggunakan Switch-Kebanyakan network dalam suatu perusahaan menggunakan Switch- Based LANs untuk operasional sehari-hari didalam gedung kantor.Based LANs untuk operasional sehari-hari didalam gedung kantor. • Namun saat ini pekerja banyak melakukan pekerjaan secara mobile danNamun saat ini pekerja banyak melakukan pekerjaan secara mobile dan ingin dapat mengakses ke network perusahaan untuk melakukan aktifitasingin dapat mengakses ke network perusahaan untuk melakukan aktifitas kerja yang tidak hanya dapat dilakukan dari meja kerjanya saja.kerja yang tidak hanya dapat dilakukan dari meja kerjanya saja. Wireless LANsWireless LANs
- 7. CCNA3-7 Chapter 7-1 • Wireless LAN dapat menjadi pilihan yang efektif, sebagaiWireless LAN dapat menjadi pilihan yang efektif, sebagai perpanjangan/yang menghubungkan kita ke Ethernet LAN.perpanjangan/yang menghubungkan kita ke Ethernet LAN. Wireless LANsWireless LANs
- 8. CCNA3-8 Chapter 7-1 Comparing a WLAN to a LANComparing a WLAN to a LAN Network Architecture StandardsNetwork Architecture StandardsNetwork Architecture StandardsNetwork Architecture Standards Physical MediaPhysical MediaPhysical MediaPhysical Media
- 9. CCNA3-9 Chapter 7-1 Comparing a WLAN to a LANComparing a WLAN to a LAN Wireless Access Points (AP)Wireless Access Points (AP) instead of a switch.instead of a switch. Wireless Access Points (AP)Wireless Access Points (AP) instead of a switch.instead of a switch. PrivacyPrivacy IssuesIssues PrivacyPrivacy IssuesIssues
- 10. CCNA3-10 Chapter 7-1 Comparing a WLAN to a LANComparing a WLAN to a LAN • CSMA/CD (Collision Detection) • Proses awal, perangkat memantau media untuk keberadaan sinyal data. • Jika tidak ada sinyal data, atau media dalam kondisi bebas, maka perangkat dapat melakukan transmisi data. • Tetapi jika ada sinyal yang terdeteksi, ini menunjukkan perangkat lain sedang melakukan transmisi data dan semua perangkat lain harus menghentikan pengiriman dan akan mencoba lagi diwaktu berikutnya. • Metode ini digunakan oleh jaringan Ethernet 802.3 • CSMA/CA (Collision Avoidance) • Proses awal, melakukan pemeriksaan perangkat media, dan keberadaan dari sinyal data. • Kemudian perangkat mengirim pemberitahuan kepada semua node akan melakukan pengiriman data, permintaan untuk melakukan pengiriman, dengan maksud untuk menggunakan media penghantar • Setelah itu perangkat kemudian melakukan pengiriman data • Metode ini digunakan oleh jaringan Nirkabel/Wireless 802.11
- 11. CCNA3-11 Chapter 7-1 • Additional components and protocolsAdditional components and protocols yang digunakan pada 802.11yang digunakan pada 802.11 wireless connections sebagai extend dari 802.3 Ethernet LAN.wireless connections sebagai extend dari 802.3 Ethernet LAN. Wireless LAN ComponentsWireless LAN Components Wireless AccessWireless Access Point (AP)Point (AP) Wireless AccessWireless Access Point (AP)Point (AP)
- 12. CCNA3-12 Chapter 7-1 • 802.11 wireless LAN802.11 wireless LAN:: • IEEE standard menentukan radio frequency (RF) untukIEEE standard menentukan radio frequency (RF) untuk kebutuhan unlicensed Industrial, Scientific, and Medicalkebutuhan unlicensed Industrial, Scientific, and Medical (ISM)(ISM) berdasarkan frequency bands yang digunakan olehberdasarkan frequency bands yang digunakan oleh Physical layerPhysical layer dandan MAC sub-layerMAC sub-layer dari wireless links.dari wireless links. • Typically frequency bands ini, dipilih berdasarkanTypically frequency bands ini, dipilih berdasarkan standart daristandart dari data ratedata rate-nya.-nya. Wireless LAN StandardsWireless LAN Standards Final ratificationFinal ratification expected inexpected in November, 2009November, 2009 Final ratificationFinal ratification expected inexpected in November, 2009November, 2009
- 13. CCNA3-13 Chapter 7-1 • Data Rates dipengaruhi oleh teknik modulation yang digunakan: 1. Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS): Juga dikenal sebagai Direct Sequence Code Division Multiple Access (DS-CDMA), DSSS adalah salah satu jenis dari modulasi spread spectrum untuk pengiriman data digital kecepatan tinggi melalui radio. Umumnya peralatan IEEE 802.11b menggunakan DSSS untuk memancarkan data-nya yang memberikan kecepatan sekitar 11Mbps. Pada saat dikirim, seluruh data akan digabungkan dengan sebuah data berurut kecepatan tinggi (yang dikenal sebagai chipping code) yang akan mendefinisikan perbandingan spreading dari data. Chipping code akan menolong me-reduce interferensi dan juga merecover data menjadi data aslinya kembali jika terjadi kerusakan pada saat dikirim. • Simpler of the two methods. • Less expensive to implement. • 802.11b and 802.11g. Wireless LAN StandardsWireless LAN Standards
- 14. CCNA3-14 Chapter 7-1 2. Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM):2. Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM): Merupakan teknik mudulasi untuk komunikasi wireless broadbandMerupakan teknik mudulasi untuk komunikasi wireless broadband dimasa yang akan datang, karena OFDM ini tahan melawan frekuensidimasa yang akan datang, karena OFDM ini tahan melawan frekuensi selective fading dan interferensi narrowband dan efisien menghadapiselective fading dan interferensi narrowband dan efisien menghadapi multi-path delay spread. Untuk mencapai hal tersebut, OFDM membagimulti-path delay spread. Untuk mencapai hal tersebut, OFDM membagi aliran data high-rate menjadi aliran rate yang lebih rendah, yangaliran data high-rate menjadi aliran rate yang lebih rendah, yang kemudian dikirimkan secara bersama pada beberapa sub-carrier.kemudian dikirimkan secara bersama pada beberapa sub-carrier. Sub-carrier dimodulasikan sendiri dengan menggunakanSub-carrier dimodulasikan sendiri dengan menggunakan Phase ShiftPhase Shift Keying (PSK) atau Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM).Keying (PSK) atau Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM). • Data rates lebih cepat dibandingkan dengan DSSS.Data rates lebih cepat dibandingkan dengan DSSS. • 802.11a, 802.11g, 802.11n.802.11a, 802.11g, 802.11n. Wireless LAN StandardsWireless LAN Standards
- 15. CCNA3-15 Chapter 7-1 Wireless LAN StandardsWireless LAN Standards
- 16. CCNA3-16 Chapter 7-1 Wireless LAN StandardsWireless LAN Standards
- 17. CCNA3-17 Chapter 7-1 • 802.11a Standard:802.11a Standard: • OFDMOFDM modulation & menggunakan Frekusensimodulation & menggunakan Frekusensi 5 GHz5 GHz.. • Less likely to experience interferenceLess likely to experience interference than devicesthan devices that operate in the 2.4 GHz band because there arethat operate in the 2.4 GHz band because there are fewer consumer devices that use the 5 GHz band.fewer consumer devices that use the 5 GHz band. Wireless LAN StandardsWireless LAN Standards
- 18. CCNA3-18 Chapter 7-1 • 802.11a Standard:802.11a Standard: • Disadvantages/kerugianDisadvantages/kerugian menggunakan frekuensi 5GHz.menggunakan frekuensi 5GHz. • More easily absorbed by walls (obstructions).More easily absorbed by walls (obstructions). • Jangkauannya lebih pendek dibanding 802.11g.Jangkauannya lebih pendek dibanding 802.11g. • Dibeberapa negara dilarang digunakanDibeberapa negara dilarang digunakan Wireless LAN StandardsWireless LAN Standards
- 19. CCNA3-19 Chapter 7-1 • 802.11b and 802.11g Standard:802.11b and 802.11g Standard: • Both use the 2.4 GHz band.Both use the 2.4 GHz band. • 802.11b:802.11b: • Up toUp to 1111 Mb/s usingMb/s using DSSSDSSS.. • 802.11g:802.11g: • Up toUp to 5454 Mb/s usingMb/s using OFDMOFDM.. Wireless LAN StandardsWireless LAN Standards
- 20. CCNA3-20 Chapter 7-1 • 2.4 GHz band:2.4 GHz band: • Advantage:Advantage: • Jangkauan yang lebih baik dibanding band 5GHz karenaJangkauan yang lebih baik dibanding band 5GHz karena sinyalnya tidak mudah terhalang.sinyalnya tidak mudah terhalang. • Disadvantage:Disadvantage: • Banyak perangkat lain menggunakan band ini sehinggaBanyak perangkat lain menggunakan band ini sehingga sangat rentan terhadap gangguan (microwave oven,sangat rentan terhadap gangguan (microwave oven, monitor bayi, Bluetooth, telepon cordless).monitor bayi, Bluetooth, telepon cordless). Wireless LAN StandardsWireless LAN Standards
- 21. CCNA3-21 Chapter 7-1 • 802.11n: (November 2009)802.11n: (November 2009) • Didesign untuk meningkatkan kecepatan data WLAN dan jangkauanDidesign untuk meningkatkan kecepatan data WLAN dan jangkauan tanpa memerlukan daya tambahan atau alokasi RF band.tanpa memerlukan daya tambahan atau alokasi RF band. • MenggunakanMenggunakan multiple radios and antenna at endpointsmultiple radios and antenna at endpoints, dan, dan masing-masing melakukan broadcasting dengan frequency yangmasing-masing melakukan broadcasting dengan frequency yang sama untuk membentuk multiple streams.sama untuk membentuk multiple streams. • Multiple Input / Multiple OutputMultiple Input / Multiple Output (MIMO) and OFDM(MIMO) and OFDM.. • Theoretical maximum of 248 Mb/s.Theoretical maximum of 248 Mb/s. Wireless LAN StandardsWireless LAN Standards
- 22. CCNA3-22 Chapter 7-1 • Wireless NICs:Wireless NICs: • The device that makes a client station capable of sendingThe device that makes a client station capable of sending and receiving RF signals is the wireless NIC.and receiving RF signals is the wireless NIC. • Like an Ethernet NIC, the wireless NIC, using theLike an Ethernet NIC, the wireless NIC, using the modulation technique it is configured to use,modulation technique it is configured to use, encodes aencodes a data stream onto an RF signaldata stream onto an RF signal.. • Wireless NICs are most often associated with mobileWireless NICs are most often associated with mobile devices, such as laptop computers.devices, such as laptop computers. Wireless Infrastructure ComponentsWireless Infrastructure Components
- 23. CCNA3-23 Chapter 7-1 Wireless Infrastructure ComponentsWireless Infrastructure Components • Wireless Access Points:Wireless Access Points: • An access point is a Layer 2 device that functions like anAn access point is a Layer 2 device that functions like an 802.3 Ethernet hub.802.3 Ethernet hub. • Connects wireless clients (or stations) to the wired LAN.Connects wireless clients (or stations) to the wired LAN. • Client devices communicate with the AP – not each other.Client devices communicate with the AP – not each other. • Converts the TCP/IP data packets from their 802.11Converts the TCP/IP data packets from their 802.11 frame encapsulation to the 802.3 Ethernet frame format.frame encapsulation to the 802.3 Ethernet frame format. • Clients mustClients must associateassociate with an access point to obtainwith an access point to obtain network services.network services. • Association:Association: • Process wireless client join ke 802.11(AP) network,Process wireless client join ke 802.11(AP) network, ini sama dengan seperti mengkoneksikan host/pcini sama dengan seperti mengkoneksikan host/pc menggunakan kabel ke switch LAN.menggunakan kabel ke switch LAN.
- 24. CCNA3-24 Chapter 7-1 Wireless Infrastructure ComponentsWireless Infrastructure Components • Wireless Routers:Wireless Routers: • Wireless routers merupakan penggabungan fungsi dariWireless routers merupakan penggabungan fungsi dari access point, Ethernet switch, dan router.access point, Ethernet switch, dan router. • The Linksys WRT54GL is most commonly used as aThe Linksys WRT54GL is most commonly used as a small business or residential wireless access device.small business or residential wireless access device. • Beban pada perangkat diusahakan cukup rendahBeban pada perangkat diusahakan cukup rendah sehingga akan dapat mengelola penyediaan WLAN,sehingga akan dapat mengelola penyediaan WLAN, 802,3 Ethernet, dan terhubung ke ISP dengan baik .802,3 Ethernet, dan terhubung ke ISP dengan baik .
- 25. CCNA3-25 Chapter 7-1 Configurable Wireless ParametersConfigurable Wireless Parameters • Configurable Wireless Parameters:Configurable Wireless Parameters: 802.11g is802.11g is backwardbackward compatiblecompatible with 802.11.b.with 802.11.b. MixedMixed mode supports both.mode supports both. 802.11g is802.11g is backwardbackward compatiblecompatible with 802.11.b.with 802.11.b. MixedMixed mode supports both.mode supports both.
- 26. CCNA3-26 Chapter 7-1 Wireless OperationWireless Operation • Configurable Wireless Parameters:Configurable Wireless Parameters: AA shared service set identifier (SSID)shared service set identifier (SSID) is a uniqueis a unique identifier that client devices use to distinguish betweenidentifier that client devices use to distinguish between multiple wireless networks in the same vicinity.multiple wireless networks in the same vicinity. AA shared service set identifier (SSID)shared service set identifier (SSID) is a uniqueis a unique identifier that client devices use to distinguish betweenidentifier that client devices use to distinguish between multiple wireless networks in the same vicinity.multiple wireless networks in the same vicinity. Several access pointsSeveral access points can share an SSID.can share an SSID. Several access pointsSeveral access points can share an SSID.can share an SSID. Alphanumeric, case-sensitive,Alphanumeric, case-sensitive, from 2 to 32 characters.from 2 to 32 characters. Alphanumeric, case-sensitive,Alphanumeric, case-sensitive, from 2 to 32 characters.from 2 to 32 characters.
- 27. CCNA3-27 Chapter 7-1 Wireless OperationWireless Operation • Configurable Wireless Parameters:Configurable Wireless Parameters: The IEEE 802.11 standard establishes theThe IEEE 802.11 standard establishes the channelization schemechannelization scheme for the usefor the use of the unlicensedof the unlicensed ISM RF bandsISM RF bands in WLANs.in WLANs. TheThe 2.4 GHz2.4 GHz band is broken down intoband is broken down into 11 channels11 channels for North Americafor North America andand 13 channels13 channels for Europe.for Europe. The IEEE 802.11 standard establishes theThe IEEE 802.11 standard establishes the channelization schemechannelization scheme for the usefor the use of the unlicensedof the unlicensed ISM RF bandsISM RF bands in WLANs.in WLANs. TheThe 2.4 GHz2.4 GHz band is broken down intoband is broken down into 11 channels11 channels for North Americafor North America andand 13 channels13 channels for Europe.for Europe. Each arc represents 1 channel.Each arc represents 1 channel.Each arc represents 1 channel.Each arc represents 1 channel. 5 MHz overlap5 MHz overlap5 MHz overlap5 MHz overlap Best practices for WLANs that requireBest practices for WLANs that require multiple access points are set to usemultiple access points are set to use non-overlapping channelsnon-overlapping channels.. Best practices for WLANs that requireBest practices for WLANs that require multiple access points are set to usemultiple access points are set to use non-overlapping channelsnon-overlapping channels.. 3 Access Points3 Access Points3 Access Points3 Access Points Many access points can automatically select aMany access points can automatically select a channel based on adjacent channel use.channel based on adjacent channel use. Some products continuously monitor the radio spaceSome products continuously monitor the radio space to adjust the channel settings dynamically in responseto adjust the channel settings dynamically in response to environmental changes.to environmental changes. Many access points can automatically select aMany access points can automatically select a channel based on adjacent channel use.channel based on adjacent channel use. Some products continuously monitor the radio spaceSome products continuously monitor the radio space to adjust the channel settings dynamically in responseto adjust the channel settings dynamically in response to environmental changes.to environmental changes.
- 28. CCNA3-28 Chapter 7-1 Wireless TopologiesWireless Topologies • WLANsWLANs dapat mengakomodasi berbagai jaringan topologi.dapat mengakomodasi berbagai jaringan topologi. .. • When describing these topologies, theWhen describing these topologies, the fundamentalfundamental building blockbuilding block of the IEEE 802.11 WLAN architecture isof the IEEE 802.11 WLAN architecture is thethe basic service setbasic service set (BSS).(BSS). • BSS:BSS: • Sekelompok stations yang dapat salingSekelompok stations yang dapat saling berkomunikasi satu sama lainnya.berkomunikasi satu sama lainnya. • Three Types:Three Types: • Ad Hoc (Independent Basic Service Set –Ad Hoc (Independent Basic Service Set – IBSSIBSS)) • Basic Service Set (Basic Service Set (BSSBSS)) • Extended Service Set (Extended Service Set (ESSESS))
- 29. CCNA3-29 Chapter 7-1 Wireless TopologiesWireless Topologies • Ad Hoc:Ad Hoc: • Wireless networks can operate without access points.Wireless networks can operate without access points. • Client stations which are configured to operate in ad hocClient stations which are configured to operate in ad hoc modemode configure the wireless parameters betweenconfigure the wireless parameters between themselvesthemselves..
- 30. CCNA3-30 Chapter 7-1 Wireless TopologiesWireless Topologies • Basic Service Sets (BSS):Basic Service Sets (BSS): • Access points provide an infrastructure that adds servicesAccess points provide an infrastructure that adds services and improves the range for clients.and improves the range for clients. • A single access point in infrastructure mode manages theA single access point in infrastructure mode manages the wireless parameters and the topology is simply a BSS.wireless parameters and the topology is simply a BSS. • The coverage area forThe coverage area for both an IBSS or a BSSboth an IBSS or a BSS is theis the basic service area (BSA)basic service area (BSA).. Basic Service AreaBasic Service AreaBasic Service AreaBasic Service Area
- 31. CCNA3-31 Chapter 7-1 Wireless TopologiesWireless Topologies • Extended Service Sets (ESS):Extended Service Sets (ESS): • When a single BSS provides insufficient RF coverage,When a single BSS provides insufficient RF coverage, one or more can be joined through a common distributionone or more can be joined through a common distribution system into an extended service set (ESS).system into an extended service set (ESS). • One BSS is differentiated from another by theOne BSS is differentiated from another by the BSSBSS identifier (BSSID)identifier (BSSID).. • The MAC address of the access point.The MAC address of the access point. • The coverage area is theThe coverage area is the extended service area (ESA)extended service area (ESA).. Different MAC AddressesDifferent MAC Addresses = different BSSIDs.= different BSSIDs. Different MAC AddressesDifferent MAC Addresses = different BSSIDs.= different BSSIDs.
- 32. CCNA3-32 Chapter 7-1 Wireless TopologiesWireless Topologies • Common Distribution System:Common Distribution System: • AllowsAllows multiple access pointsmultiple access points dalam ESS untuk menjadidalam ESS untuk menjadi single BSSsingle BSS.. • An ESS generally includes aAn ESS generally includes a common SSIDcommon SSID to allow ato allow a user touser to roamroam from access point to access point.from access point to access point. • CellsCells represent the coverage area provided by a singlerepresent the coverage area provided by a single channel.channel. • An ESS should have 10 to 15 percent overlapAn ESS should have 10 to 15 percent overlap between cells.between cells. • Roaming capability created by using non-overlappingRoaming capability created by using non-overlapping channels (e.g. one cell on channel 1 and the other onchannels (e.g. one cell on channel 1 and the other on channel 6).channel 6).
- 33. CCNA3-33 Chapter 7-1 Wireless AssociationWireless Association • Bagian terpenting dari proses 802.11 adalah process discovering WLAN & melakukan koneksi ke WLAN tersebut. • Primary componentsnya adalah: • Beacons: Frame yang digunakan oleh jaringan WLAN untuk mengiklankan keberadaannya. • Probes: Frame yang digunakan oleh klien WLAN untuk menemukan jaringan mereka. • Authentication: Left over from the original 802.11 standard, but still required. • Association: Membangun data link antara jalur akses WLAN dan klien/user.
- 34. CCNA3-34 Chapter 7-1 Wireless AssociationWireless Association • Beacons:Beacons: • Frames used by the WLAN network to advertise itsFrames used by the WLAN network to advertise its presence.presence. Satu-satunya bagian dari prosesSatu-satunya bagian dari proses yang dapat disiarkan secarayang dapat disiarkan secara teratur.teratur. Not necessarily enabled.Not necessarily enabled. Satu-satunya bagian dari prosesSatu-satunya bagian dari proses yang dapat disiarkan secarayang dapat disiarkan secara teratur.teratur. Not necessarily enabled.Not necessarily enabled.
- 35. CCNA3-35 Chapter 7-1 Wireless AssociationWireless Association • Before an 802.11 client can send data over a WLAN network,Before an 802.11 client can send data over a WLAN network, it goes through the followingit goes through the following three-stagethree-stage process:process: • Step 1:Step 1: 802.11 Probing.802.11 Probing. • Step 2:Step 2: Authentication.Authentication. • Step 3:Step 3: Association.Association.
- 36. CCNA3-36 Chapter 7-1 Wireless AssociationWireless Association • Step 1:Step 1: 802.11 Probing802.11 Probing • Clients search for aClients search for a specificspecific network by:network by: • Sending aSending a probe request out on multiple channelsprobe request out on multiple channels.. • Specifies the network nameSpecifies the network name (SSID)(SSID) and bit rates.and bit rates. • A typical WLAN client is configured with a desiredA typical WLAN client is configured with a desired SSID.SSID. • Client is simply trying toClient is simply trying to discoverdiscover available WLANs:available WLANs: • Sends out a probe request withSends out a probe request with no SSIDno SSID.. • All access points that areAll access points that are configured to respondconfigured to respond to thisto this type of query respond.type of query respond. • WLANs denganWLANs dengan broadcast SSID feature disabledbroadcast SSID feature disabled tidaktidak akan meresponakan merespon
- 37. CCNA3-37 Chapter 7-1 Wireless AssociationWireless Association • Step 2:Step 2: AuthenticationAuthentication • 802.11 was originally developed with 2 authentication802.11 was originally developed with 2 authentication mechanisms.mechanisms. 1.1. Open Authentication:Open Authentication: • A NULL authenticationA NULL authentication • The client says "authenticate me“.The client says "authenticate me“. • The access point responds with "yes“.The access point responds with "yes“. • Ini merupakan mechanism yang digunakanIni merupakan mechanism yang digunakan secara umum oleh 802.11 deployments.secara umum oleh 802.11 deployments.
- 38. CCNA3-38 Chapter 7-1 Wireless AssociationWireless Association 2.2. Shared Key Authentication:Shared Key Authentication: • Based on a key that is shared between the clientBased on a key that is shared between the client station and the access point called the Wiredstation and the access point called the Wired Equivalency ProtectionEquivalency Protection (WEP)(WEP) key.key. • Bentuk perlindungan ini pada dasarnya menggunakanBentuk perlindungan ini pada dasarnya menggunakan kunci enkripsi untuk melindungi data yang dikirim darikunci enkripsi untuk melindungi data yang dikirim dari dan ke jaringan WLAN untuk mencegah penggunadan ke jaringan WLAN untuk mencegah pengguna tanpa izin dapat mengakses jaringan.tanpa izin dapat mengakses jaringan. • WEP needs to be included in client and access pointWEP needs to be included in client and access point implementations for standards compliance but it isimplementations for standards compliance but it is notnot used or recommendedused or recommended..
- 39. CCNA3-39 Chapter 7-1 Wireless AssociationWireless Association • Step 3:Step 3: 802.11 Association802.11 Association • Finalizes theFinalizes the security and bit rate optionssecurity and bit rate options.. • Establishes the data linkEstablishes the data link between the WLAN client andbetween the WLAN client and the access point.the access point. • The client learns theThe client learns the BSSID (MAC Address)BSSID (MAC Address) of the accessof the access point.point. • Access point maps a logical port known as theAccess point maps a logical port known as the association identifier (AID)association identifier (AID) to the WLAN client.to the WLAN client. • AID is equivalent to a port on a switch.AID is equivalent to a port on a switch. • Association identifier (AID)Association identifier (AID) allows the infrastructureallows the infrastructure switch to keep track of frames destined for the WLANswitch to keep track of frames destined for the WLAN client so that they can be forwarded.client so that they can be forwarded.
- 40. CCNA3-40 Chapter 7-1 Wireless AssociationWireless Association
- 41. CCNA3-41 Chapter 7-1 Planning the Wireless LANPlanning the Wireless LAN Perlu ada rencana yang terdokumentasi dengan baikPerlu ada rencana yang terdokumentasi dengan baik sebelum jaringan nirkabel dapat diimplementasikan. .sebelum jaringan nirkabel dapat diimplementasikan. . 1.1. Number of Users:Number of Users: • Ini bukanlah perhitungan jumlah user secara sederhana.Ini bukanlah perhitungan jumlah user secara sederhana. • Karena akan dipengaruhi lokasi geographical layoutKarena akan dipengaruhi lokasi geographical layout dimana user berada.dimana user berada. 1.1. Data Rates:Data Rates: • RF merupakan shared medium dan jika semakinRF merupakan shared medium dan jika semakin banyak pengguna maka akan mempengaruhi RFbanyak pengguna maka akan mempengaruhi RF tersebut.tersebut. • Untuk itu “Untuk itu “Use non-overlapping channelsUse non-overlapping channels” in an ESS.” in an ESS. 1.1. Rencanakan jaringan Anda untuk cakupan RF yang tepatRencanakan jaringan Anda untuk cakupan RF yang tepat dalam sebuah network ESS .dalam sebuah network ESS .
- 42. CCNA3-42 Chapter 7-1 Planning the Wireless LANPlanning the Wireless LAN 4.4. Location of Access Points:Location of Access Points: • You may not be able to simply draw coverage areaYou may not be able to simply draw coverage area circles and drop them over a plan.circles and drop them over a plan. • Do access points use existing wiring?Do access points use existing wiring? • Position access points:Position access points: • Above obstructions.Above obstructions. • Vertically near the ceiling in the center of eachVertically near the ceiling in the center of each coverage area, if possible.coverage area, if possible. • Lokasi dimana user akan bekerja. For example,Lokasi dimana user akan bekerja. For example, conference rooms are typically a better location forconference rooms are typically a better location for access points than a hallway.access points than a hallway.
- 43. CCNA3-43 Chapter 7-1 Planning the Wireless LANPlanning the Wireless LAN 5.5. Coverage Area of Access Points:Coverage Area of Access Points: • Memperkirakan cakupan area access point yangMemperkirakan cakupan area access point yang diharapkan.diharapkan. • This value varies depending on:This value varies depending on: • The WLAN standard or mix of standards that you areThe WLAN standard or mix of standards that you are deploying.deploying. • The nature of the facility.The nature of the facility. • The transmit power that the access point.The transmit power that the access point. 6.6. Based on your plan, tempatkan access points agar coverageBased on your plan, tempatkan access points agar coverage circles tidak terdapat banyak overlapping.circles tidak terdapat banyak overlapping.
- 45. CCNA3-45 Chapter 7-1 Number of Access PointsNumber of Access PointsNumber of Access PointsNumber of Access Points Planning the Wireless LANPlanning the Wireless LAN 20,000 Sq. Ft.20,000 Sq. Ft. (1860 Sq. Meters)(1860 Sq. Meters) 20,000 Sq. Ft.20,000 Sq. Ft. (1860 Sq. Meters)(1860 Sq. Meters) Minimum ofMinimum of 6 Mbps6 Mbps 802.11b throughput802.11b throughput forfor each Basic Serviceeach Basic Service Area (BSA)Area (BSA) Minimum ofMinimum of 6 Mbps6 Mbps 802.11b throughput802.11b throughput forfor each Basic Serviceeach Basic Service Area (BSA)Area (BSA) Can be achieved with aCan be achieved with a coverage area ofcoverage area of 5,000 Sq. Ft.5,000 Sq. Ft. (465 Sq. Meters)(465 Sq. Meters) Can be achieved with aCan be achieved with a coverage area ofcoverage area of 5,000 Sq. Ft.5,000 Sq. Ft. (465 Sq. Meters)(465 Sq. Meters) 20,000 Sq. Ft. with a20,000 Sq. Ft. with a coverage of 5,000 Sq. Ft.coverage of 5,000 Sq. Ft. results inresults in 4 Access4 Access PointsPoints.. 20,000 Sq. Ft. with a20,000 Sq. Ft. with a coverage of 5,000 Sq. Ft.coverage of 5,000 Sq. Ft. results inresults in 4 Access4 Access PointsPoints..
- 46. CCNA3-46 Chapter 7-1 Planning the Wireless LANPlanning the Wireless LAN 50 foot (15 Meter) Radius50 foot (15 Meter) Radius50 foot (15 Meter) Radius50 foot (15 Meter) Radius 71 foot (22 Meter) Square71 foot (22 Meter) Square71 foot (22 Meter) Square71 foot (22 Meter) Square Dimension of Coverage AreaDimension of Coverage AreaDimension of Coverage AreaDimension of Coverage Area
- 47. CCNA3-47 Chapter 7-1 Planning the Wireless LANPlanning the Wireless LAN Location of Access PointsLocation of Access PointsLocation of Access PointsLocation of Access Points