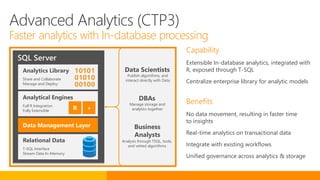
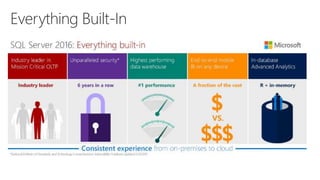
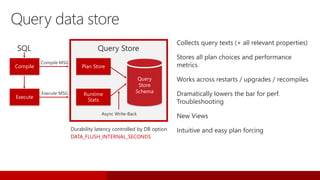
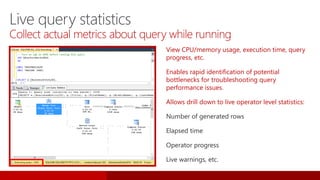
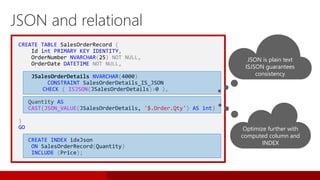
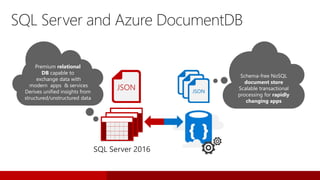
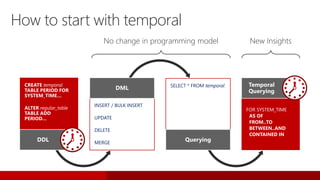
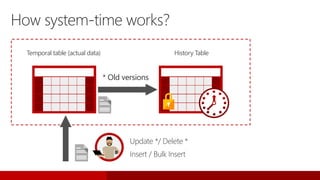
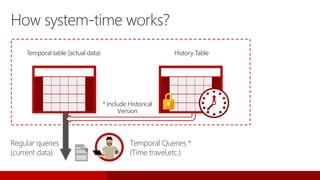
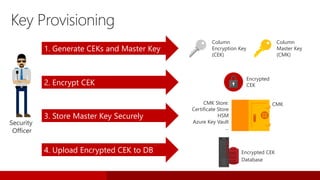
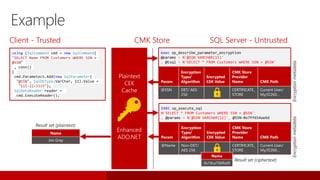
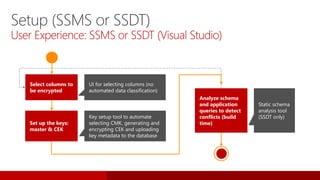
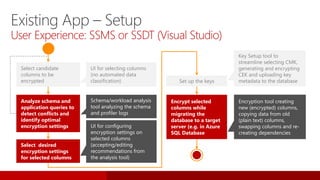
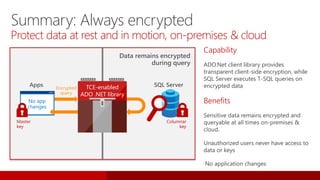
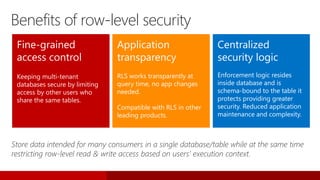
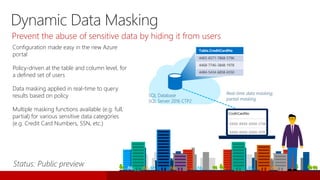
SQL Server 2016 introduces significant innovations in operational database management, including enhanced performance, security, and support for in-memory OLTP and temporal databases. Key features include integrated JSON support, query performance optimization via the Query Store, and advanced encryption capabilities for sensitive data. These improvements facilitate more effective analytics and operational insights, as well as streamlined handling of both structured and unstructured data.






![ALTER TABLE Sales.SalesOrderDetail
ALTER INDEX PK_SalesOrderID
REBUILD
WITH (BUCKET_COUNT=100000000)
T-SQL surface area: New
{LEFT|RIGHT} OUTER JOIN
Disjunction (OR, NOT)
UNION [ALL]
SELECT DISTINCT
Subqueries (EXISTS, IN, scalar)
ALTER support
Full schema change support: add/alter/drop
column/constraint
Add/drop index supported
Surface area improvements
Almost full T-SQL coverage including scaler user-defined
functions
Improved scaling
Increased size allowed for durable tables; more sockets
Other improvements
MARS support
Lightweight migration reports](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expertsummit-sqlserver2016-151209130556-lva1-app6891/85/Expert-summit-SQL-Server-2016-15-320.jpg)









![[
{
"Number":"SO43659",
"Date":"2011-05-31T00:00:00"
"AccountNumber":"AW29825",
"Price":59.99,
"Quantity":1
},
{
"Number":"SO43661",
"Date":"2011-06-01T00:00:00“
"AccountNumber":"AW73565“,
"Price":24.99,
"Quantity":3
}
]
Number Date Customer Price Quantity
SO43659 2011-05-31T00:00:00 AW29825 59.99 1
SO43661 2011-06-01T00:00:00 AW73565 24.99 3
SELECT * FROM myTable
FOR JSON AUTO
SELECT * FROM
OPENJSON(@json)
Data exchange with JSON](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expertsummit-sqlserver2016-151209130556-lva1-app6891/85/Expert-summit-SQL-Server-2016-28-320.jpg)


![SELECT
OrderNumber AS 'Order.Number',
OrderDate AS 'Order.Date'
FROM SalesOrder
FOR JSON PATH
For JSON path
[
{
"Order":{
"Number":"SO43659",
"Date":"2011-05 31T00:00:00“
},
},
{
"Order":{
"Number":"SO43660",
"Date":"2011-06-01T00:00:00“
},
}
]
Query Result (JSON array)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expertsummit-sqlserver2016-151209130556-lva1-app6891/85/Expert-summit-SQL-Server-2016-32-320.jpg)
![SELECT SalesOrderNumber,
OrderDate,
UnitPrice,
OrderQty
FROM Sales.SalesOrderHeader H
INNER JOIN Sales.SalesOrderDetail D
ON H.SalesOrderID = D.SalesOrderID
FOR JSON AUTO
For JSON AUTO
[
{
"SalesOrderNumber":"SO43659",
"OrderDate":"2011-05-31T00:00:00",
"D":[
{"UnitPrice":24.99, "OrderQty":1
}
]
},
{
"SalesOrderNumber":"SO43659" ,
"D":[
{ "UnitPrice":34.40 },
{ "UnitPrice":134.24, "OrderQty":5
}
]
}
]
Query Result](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expertsummit-sqlserver2016-151209130556-lva1-app6891/85/Expert-summit-SQL-Server-2016-33-320.jpg)

![OPENJSON
OPENJSON (@json, N'$.Orders.OrdersArray')
WITH (
Number varchar(200) N'$.Order.Number',
Date datetime N'$.Order.Date',
Customer varchar(200) N'$.AccountNumber',
Quantity int N'$.Item.Quantity'
)
{"Orders": { "OrdersArray":
[
{
"Order": {
"Number":"SO43659",
"Date":"2011-05-31T00:00:00“
},
"AccountNumber":"AW29825“,
"Item": {
"Price":2024.9940,
"Quantity":1
}
},
{
"Order":{
“Number":"SO43661",
"Date":"2011-06-01T00:00:00“
},
"AccountNumber":"AW73565“,
"Item": {
"Price":2024.9940,
"Quantity":3
}
}
]} }
Number Date Customer Quantity
SO43659 2011-05-31T00:00:00 AW29825 1
SO43661 2011-06-01T00:00:00 AW73565 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expertsummit-sqlserver2016-151209130556-lva1-app6891/85/Expert-summit-SQL-Server-2016-35-320.jpg)
























![-- Run sp_configure ‘hadoop connectivity’
-- and set an appropriate value
sp_configure
@configname = 'hadoop connectivity',
@configvalue = 7;
GO
RECONFIGURE
GO
-- List the configuration settings for
-- one configuration name
sp_configure @configname='hadoop connectivity';
GO
Option values
0: Disable Hadoop connectivity
1: Hortonworks HDP 1.3 on Windows Server
Azure blob storage (WASB[S])
2: Hortonworks HDP 1.3 on Linux
3: Cloudera CDH 4.3 on Linux
4: Hortonworks HDP 2.0 on Windows Server
Azure blob storage (WASB[S])
5: Hortonworks HDP 2.0 on Linux
6: Cloudera 5.1 on Linux
7: Hortonworks 2.1 and 2.2 on Linux
Hortonworks 2.2 on Windows Server
Azure blob storage (WASB[S])
Choose Hadoop data source with sp_configure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expertsummit-sqlserver2016-151209130556-lva1-app6891/85/Expert-summit-SQL-Server-2016-79-320.jpg)

![-- Using credentials on database requires enabling
-- traceflag
DBCC TRACEON(4631,-1)
-- Create a master key
CREATE MASTER KEY ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD = 'S0me!nfo';
CREATE CREDENTIAL WASBSecret ON DATABASE WITH
IDENTITY = 'pdw_user', Secret = 'mykey==';
-- Create an external data source (Azure Blob Storage)
-- with the credential
CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE Azure_Storage WITH
( TYPE = HADOOP,
LOCATION
='wasb[s]://mycontainer@test.blob.core.windows.net/pat
h’,
CREDENTIAL = WASBSecret
)
Type methods for providing
credentials
Core-site.xml in installation path of
SQL Server -
<SqlBinRoot>PolybaseHadoopConf
Credential object in SQL Server for
higher security
NOTE: The syntax for a database-scoped
credential (CREATE CREDENTIAL … ON
DATABASE) is temporary and will change
in the next release. This new feature is
documented only in the examples in the
CTP2 content, and will be fully
documented in the next release.
Configure PolyBase for Azure blob storage](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expertsummit-sqlserver2016-151209130556-lva1-app6891/85/Expert-summit-SQL-Server-2016-81-320.jpg)

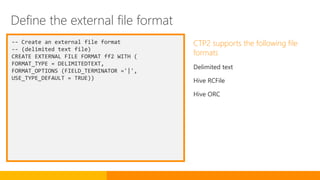
![-- Create an external table pointing to file
stored in Hadoop
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE [dbo].[CarSensor_Data] (
[SensorKey] int NOT NULL,
[CustomerKey] int NOT NULL,
[GeographyKey] int NULL,
[Speed] float NOT NULL,
[YearMeasured] int NOT NULL
)
WITH (LOCATION='/Demo/car_sensordata.tbl',
DATA_SOURCE = hdp2,
FILE_FORMAT = ff2,
REJECT_TYPE = VALUE,
REJECT_VALUE = 0
The external table provides a T-
SQL reference to the data source
used to:
Query Hadoop or Azure blob storage
data with Transact-SQL statements
Import and store data from Hadoop
or Azure blob storage into your SQL
Server database
Create an external table to the data source](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expertsummit-sqlserver2016-151209130556-lva1-app6891/85/Expert-summit-SQL-Server-2016-84-320.jpg)




![private static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Connection string to SSISDB
var connectionString = "Data Source=.;Initial Catalog=SSISDB;Integrated
Security=True;MultipleActiveResultSets=false";
using (var sqlConnection = new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
sqlConnection.Open();
var sqlCommand = new SqlCommand
{
Connection = sqlConnection,
CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure,
CommandText = "[catalog].[deploy_packages]"
};
var packageData = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(File.ReadAllText(@"C:TestPackage.dtsx"));
// DataTable: name is the package name without extension and package_data is byte
array of package.
var packageTable = new DataTable();
packageTable.Columns.Add("name", typeof(string));
packageTable.Columns.Add("package_data", typeof(byte[]));
packageTable.Rows.Add("Package", packageData);
// Set the destination project and folder which is named Folder and Project.
sqlCommand.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@folder_name", SqlDbType.NVarChar,
ParameterDirection.Input, "Folder", -1));
sqlCommand.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@project_name", SqlDbType.NVarChar,
ParameterDirection.Input, "Project", -1));
sqlCommand.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@packages_table", SqlDbType.Structured,
ParameterDirection.Input, packageTable, -1));
var result = sqlCommand.Parameters.Add("RetVal", SqlDbType.Int);
result.Direction = ParameterDirection.ReturnValue;
sqlCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
Deployment options in CTP2
Integration Services Deployment
Wizard
SQL Server Management Studio
deploy_packages stored procedure
Object model API
Deployment options in CTP3
SQL Server Data Tools for Business
Intelligence
Deploy packages to Integration Services server](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expertsummit-sqlserver2016-151209130556-lva1-app6891/85/Expert-summit-SQL-Server-2016-91-320.jpg)