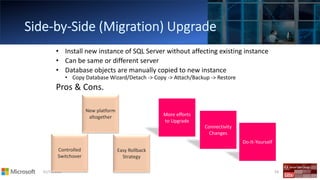
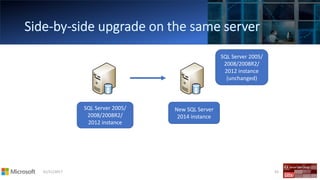
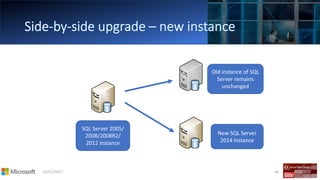
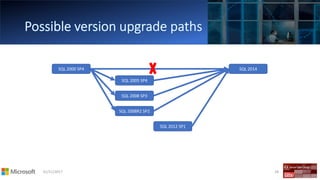
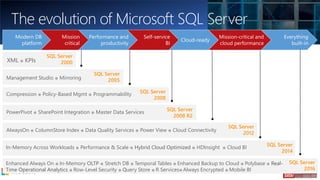
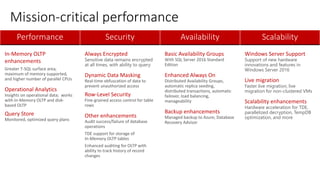
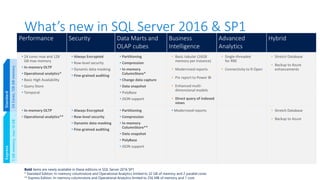
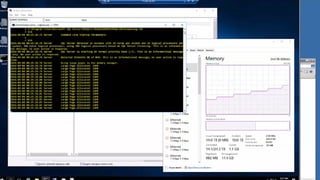
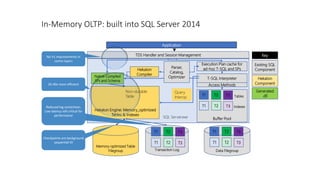
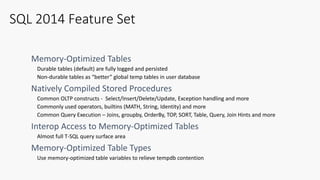
The document outlines the agenda and content covered during a SQL Server modernization event, focusing on SQL Server 2016, its features, improvements, and benefits. Key topics include enhanced performance, security, and availability features, along with detailed discussions on in-memory OLTP, upgrade strategies, and hybrid IT capabilities. It emphasizes the need for upgrading from older SQL Server versions for better scalability and efficiency in data handling.

















,
[Name] NVARCHAR(250) NOT NULL,
[CustomerSince] DATETIME NULL
INDEX [ICustomerSince] NONCLUSTERED
)
WITH (MEMORY_OPTIMIZED = ON, DURABILITY = SCHEMA_AND_DATA);
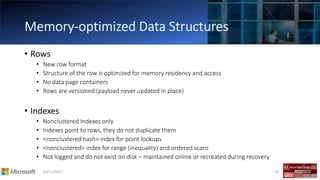
This table is memory
optimized
This table is durable
Non-durable tables:
DURABILITY=SCHEMA_ONLY
Indexes are specified inline
NONCLUSTERED indexes are
supported
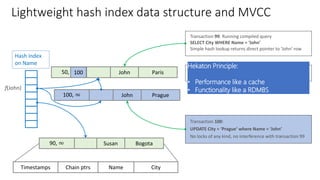
Hash Index
BUCKET_COUNT 1-2X nr of
unique index key values](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modernization-sqlserver2016-180526032341/85/Modernization-sql-server-2016-28-320.jpg)