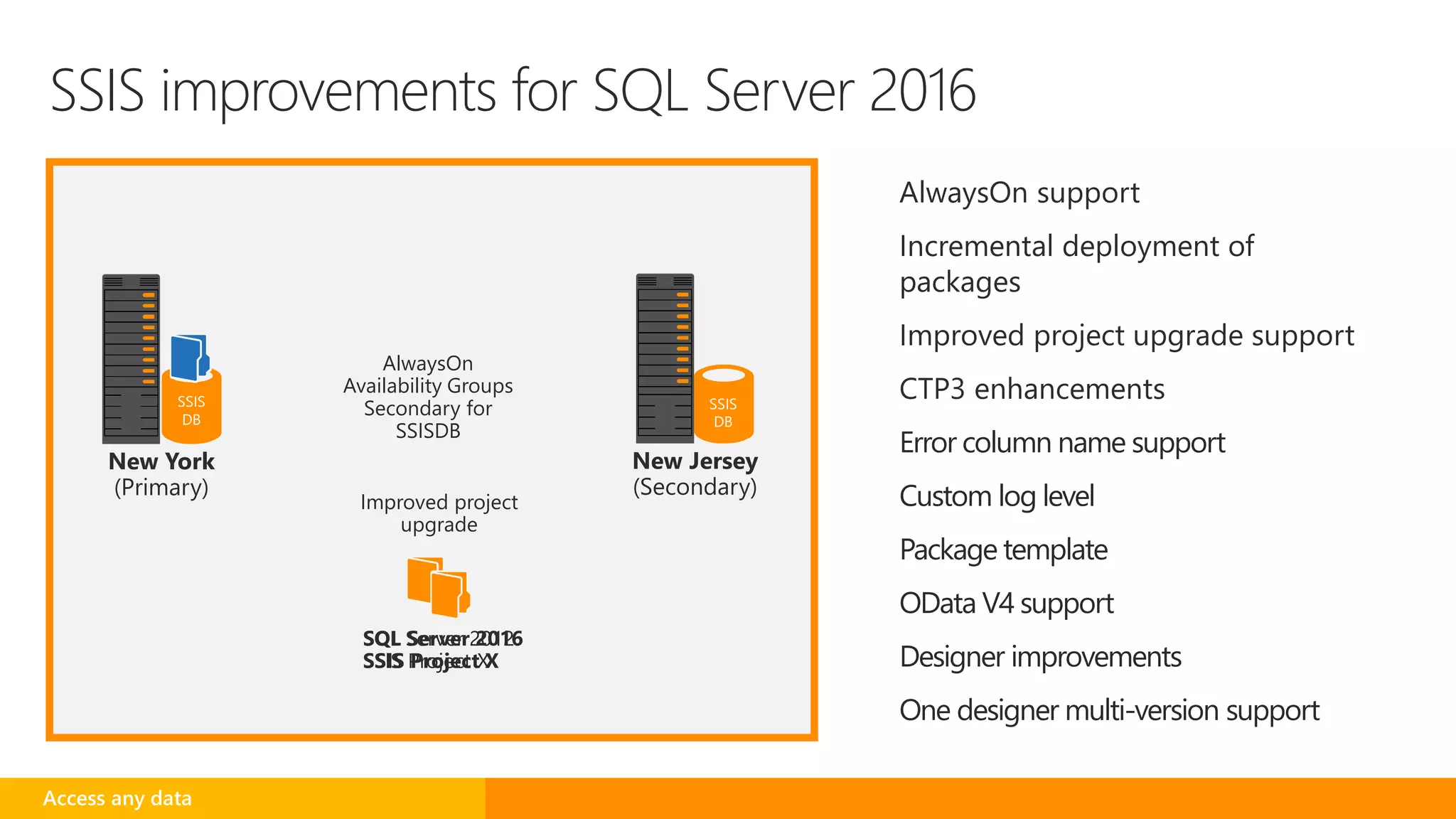
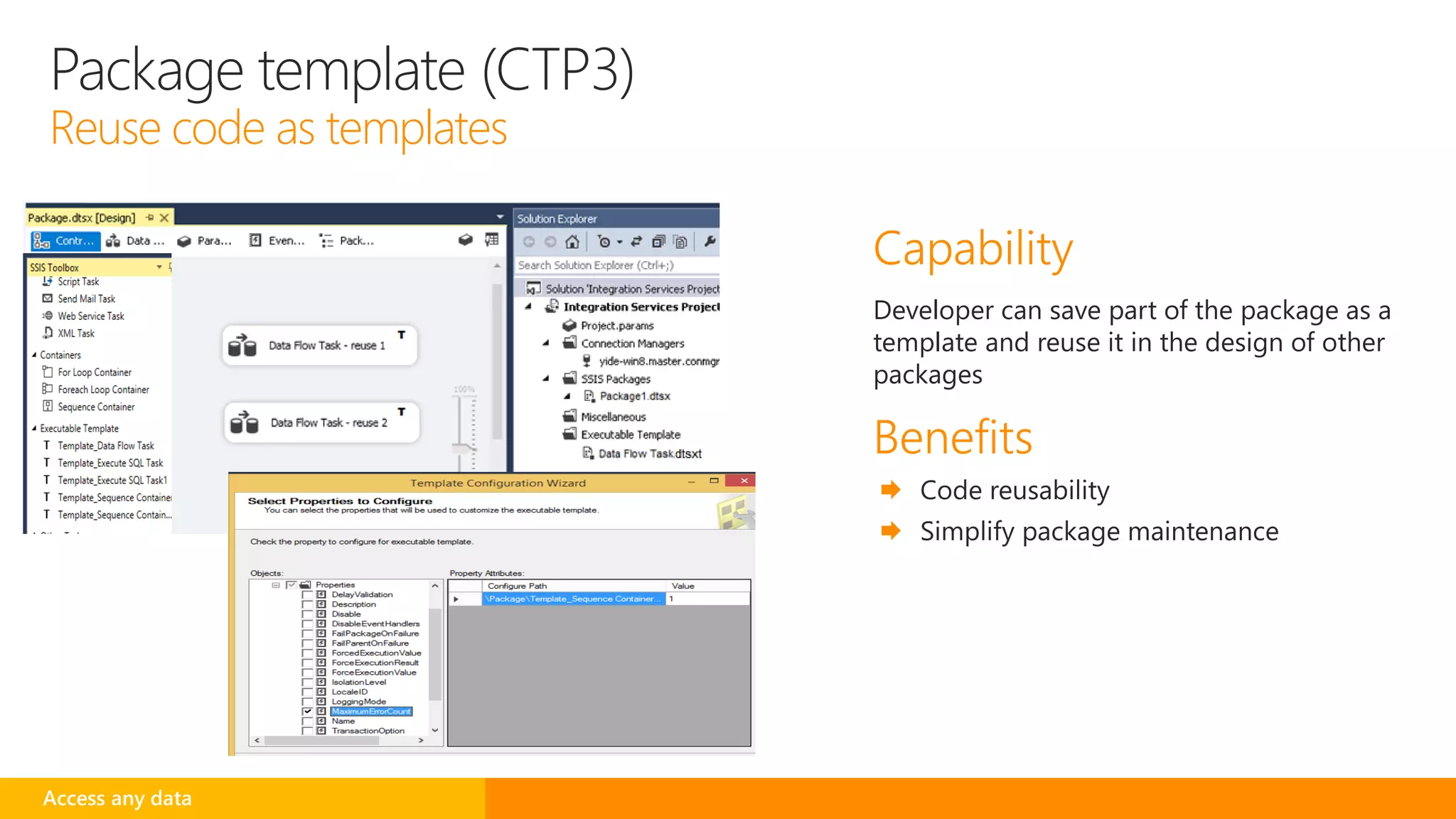
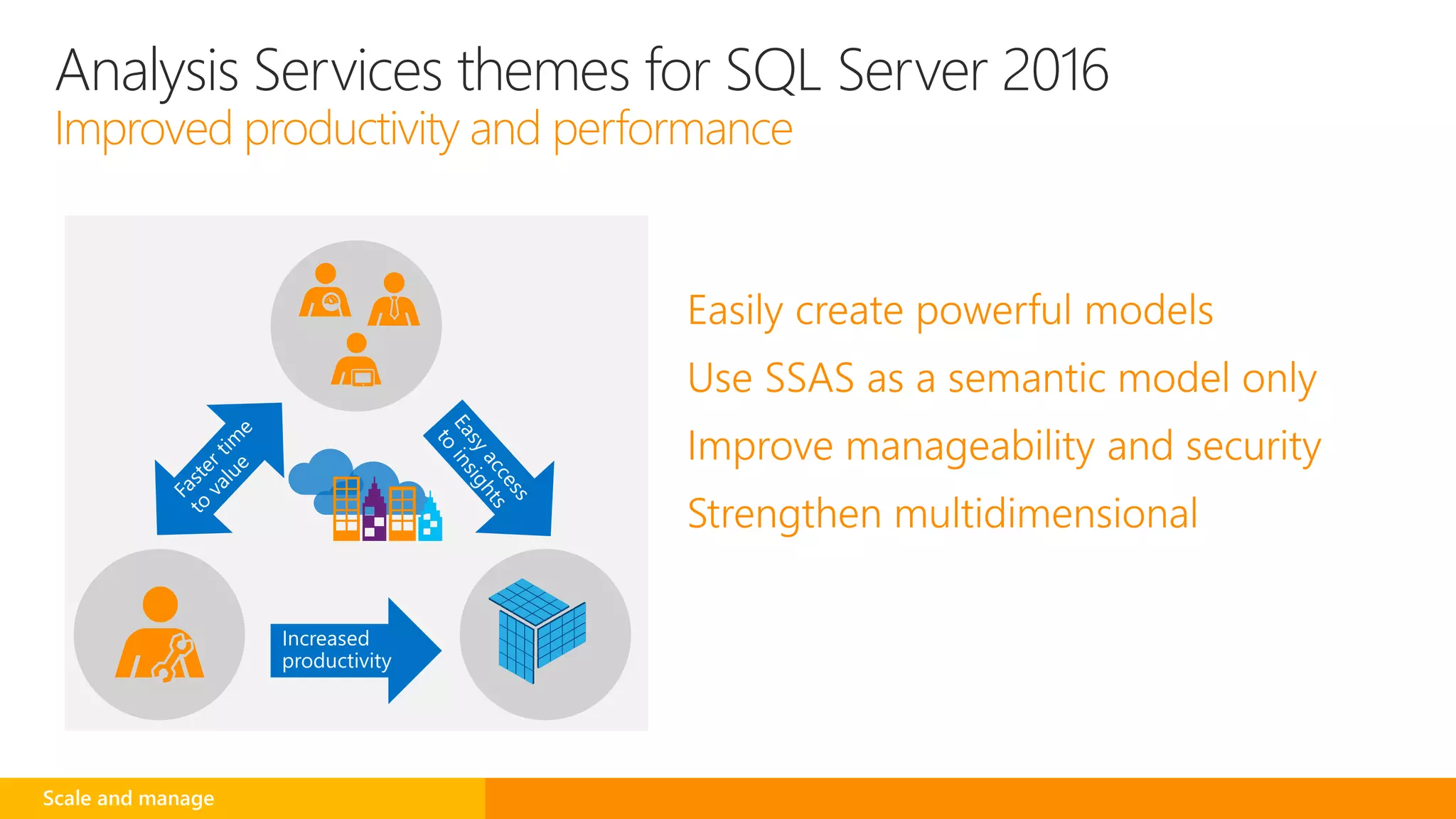
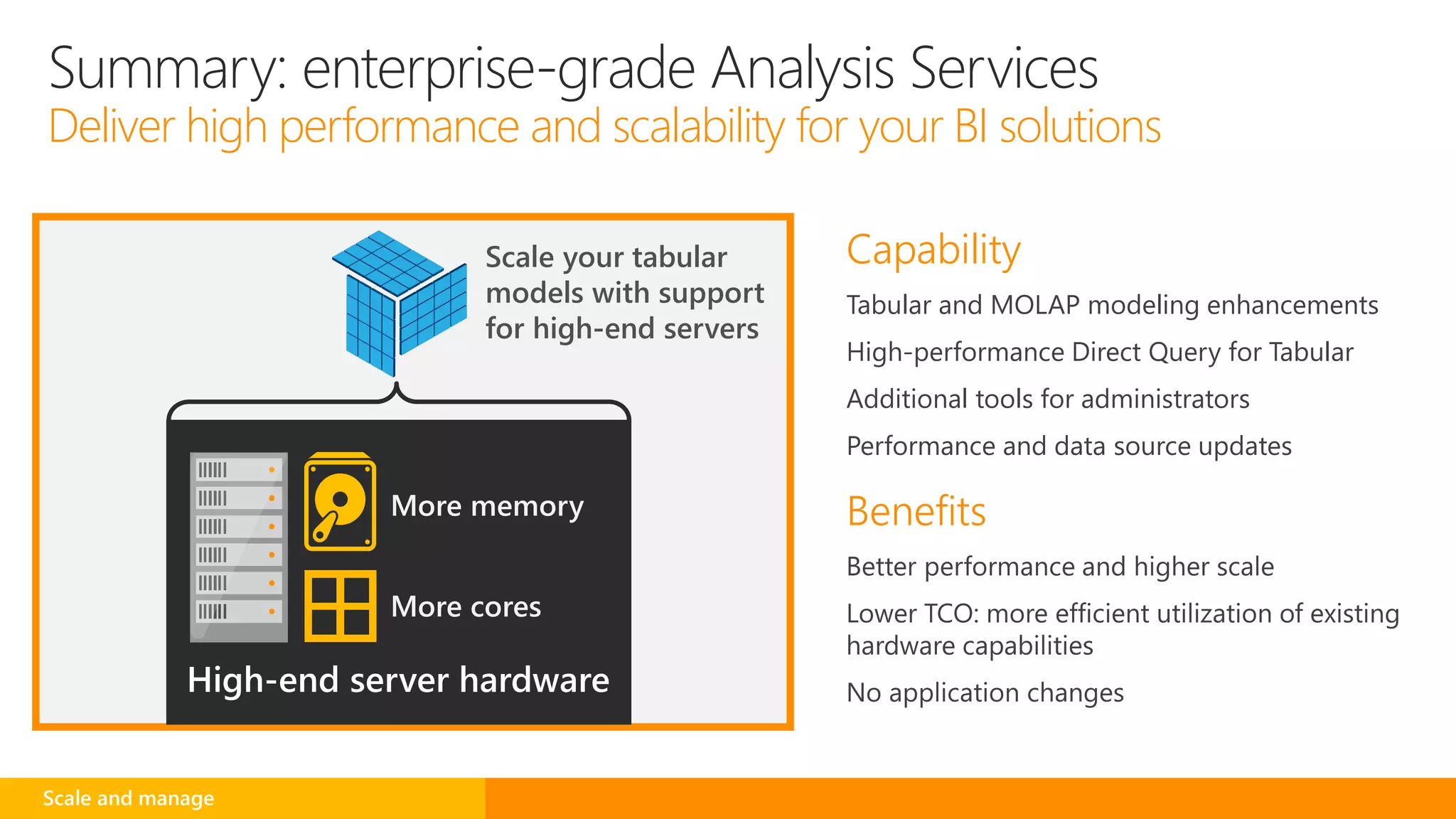
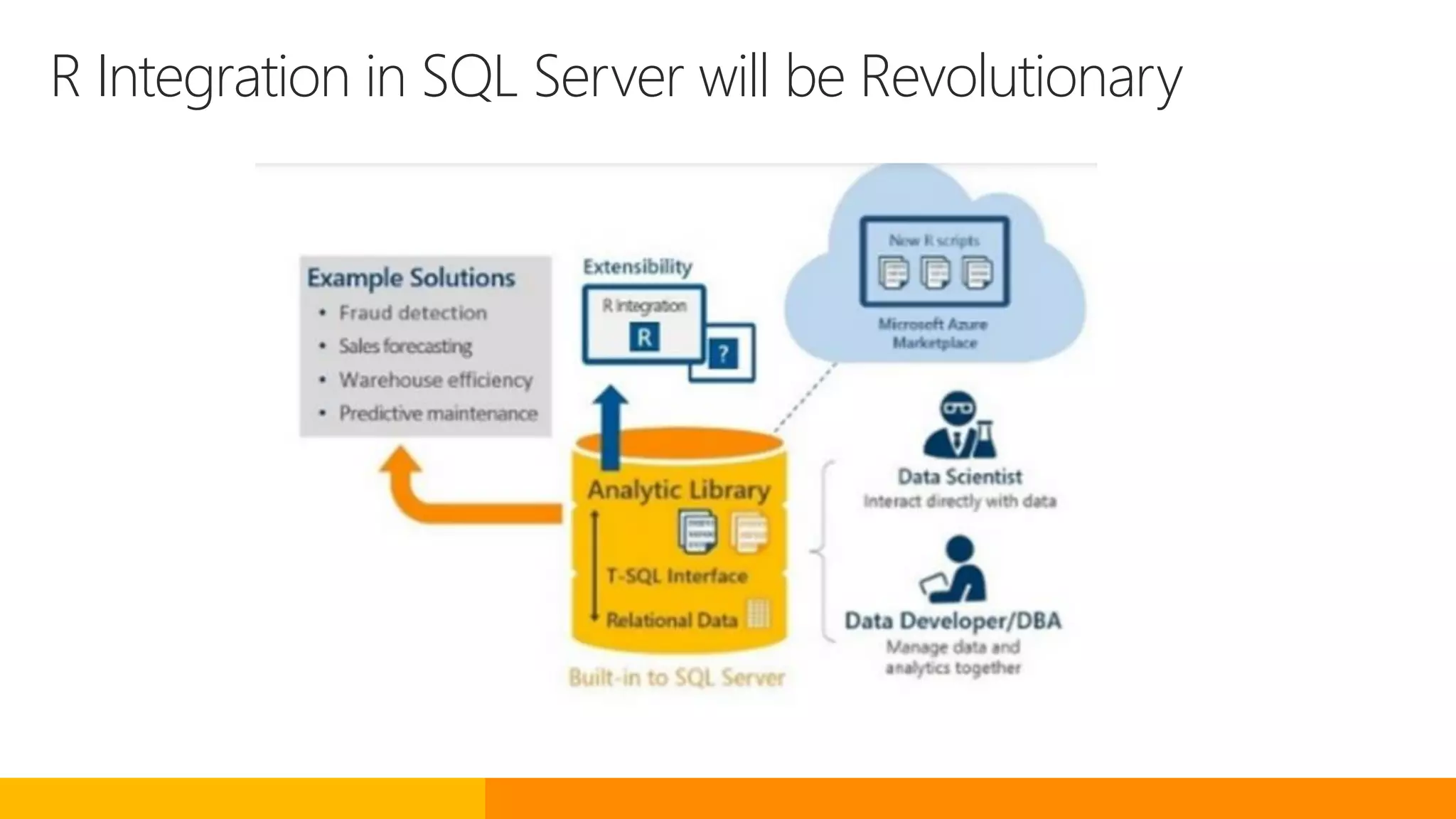
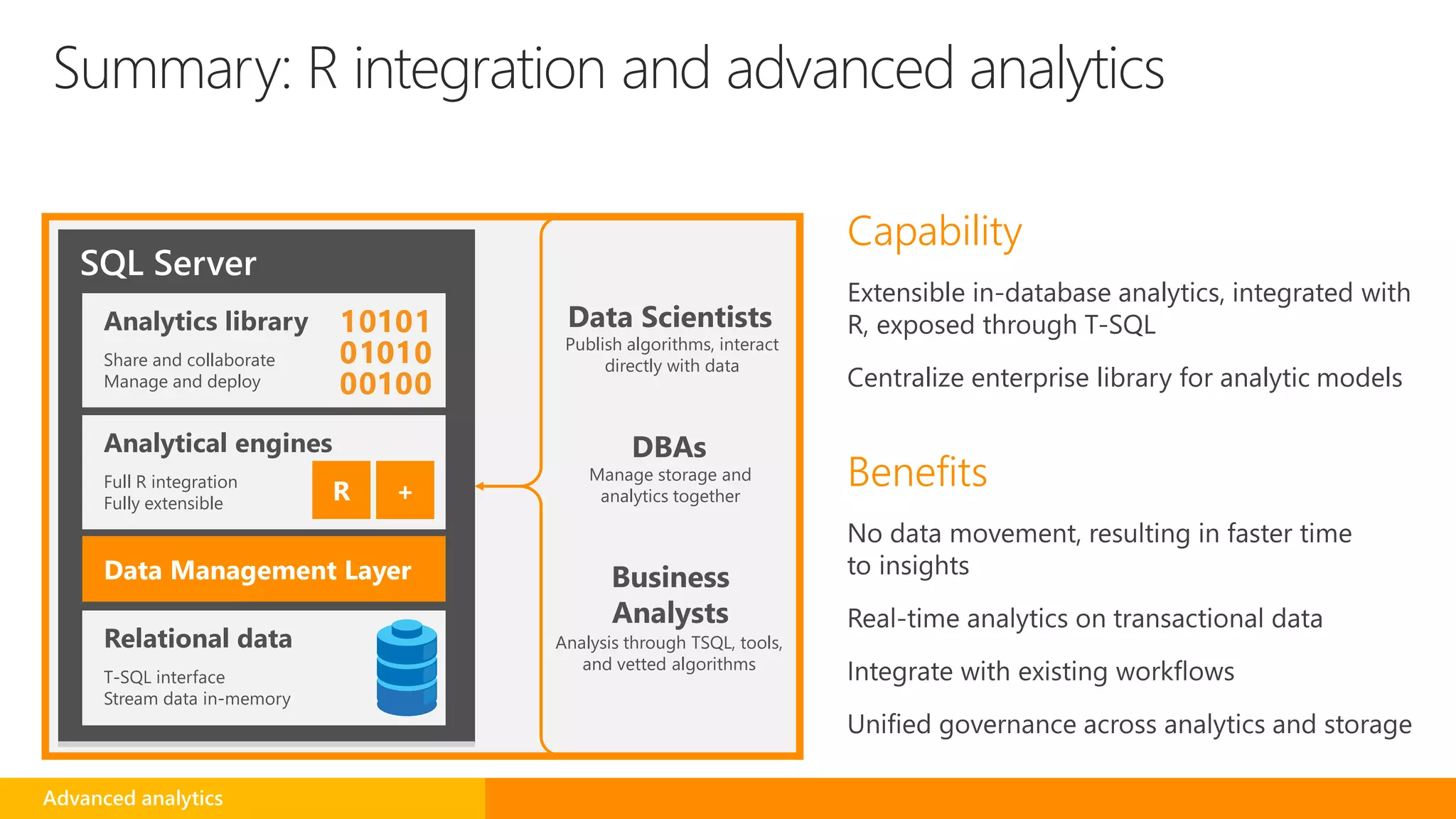
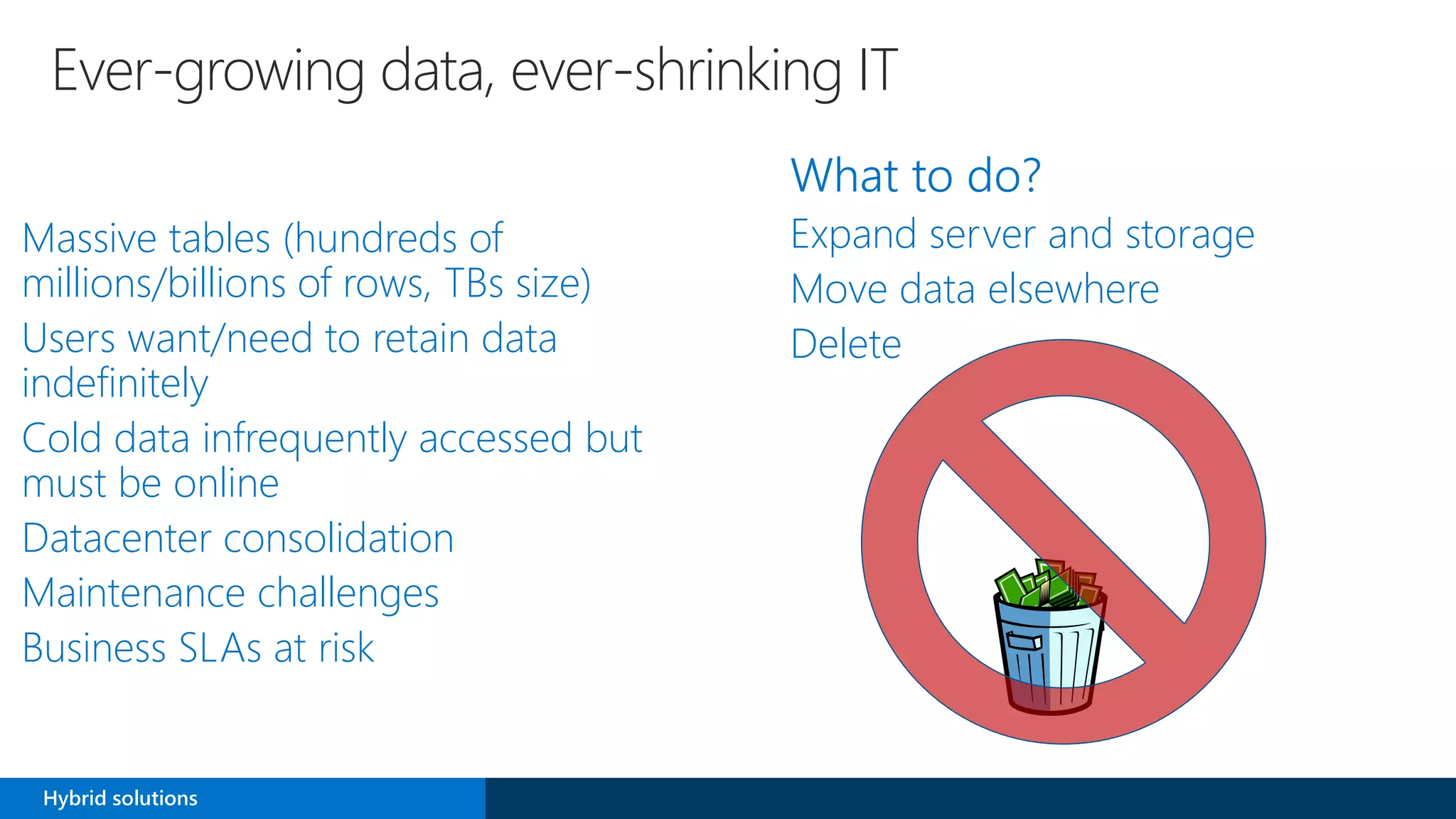
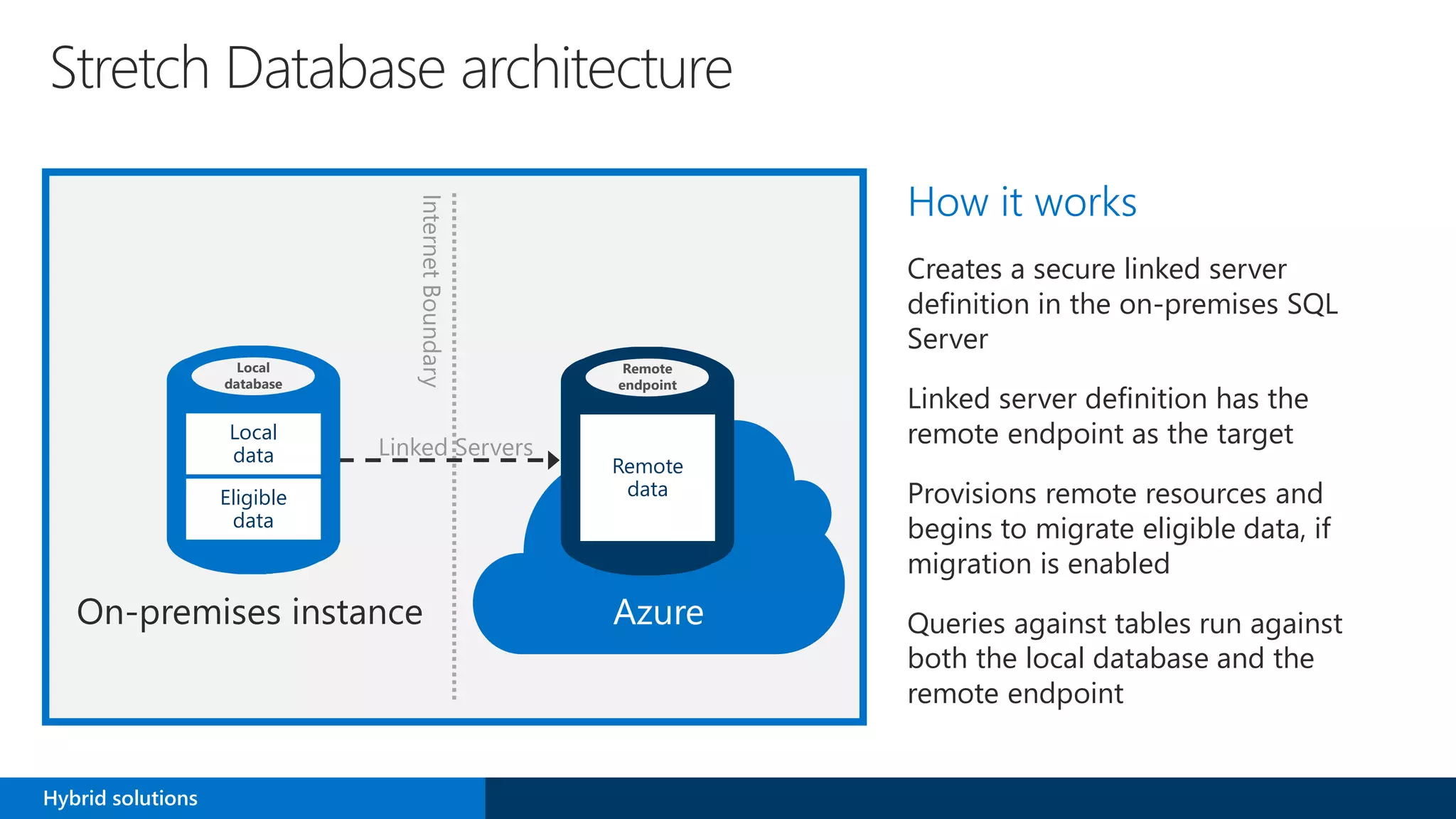
SQL Server 2016 introduces new capabilities to help improve performance, security, and analytics:
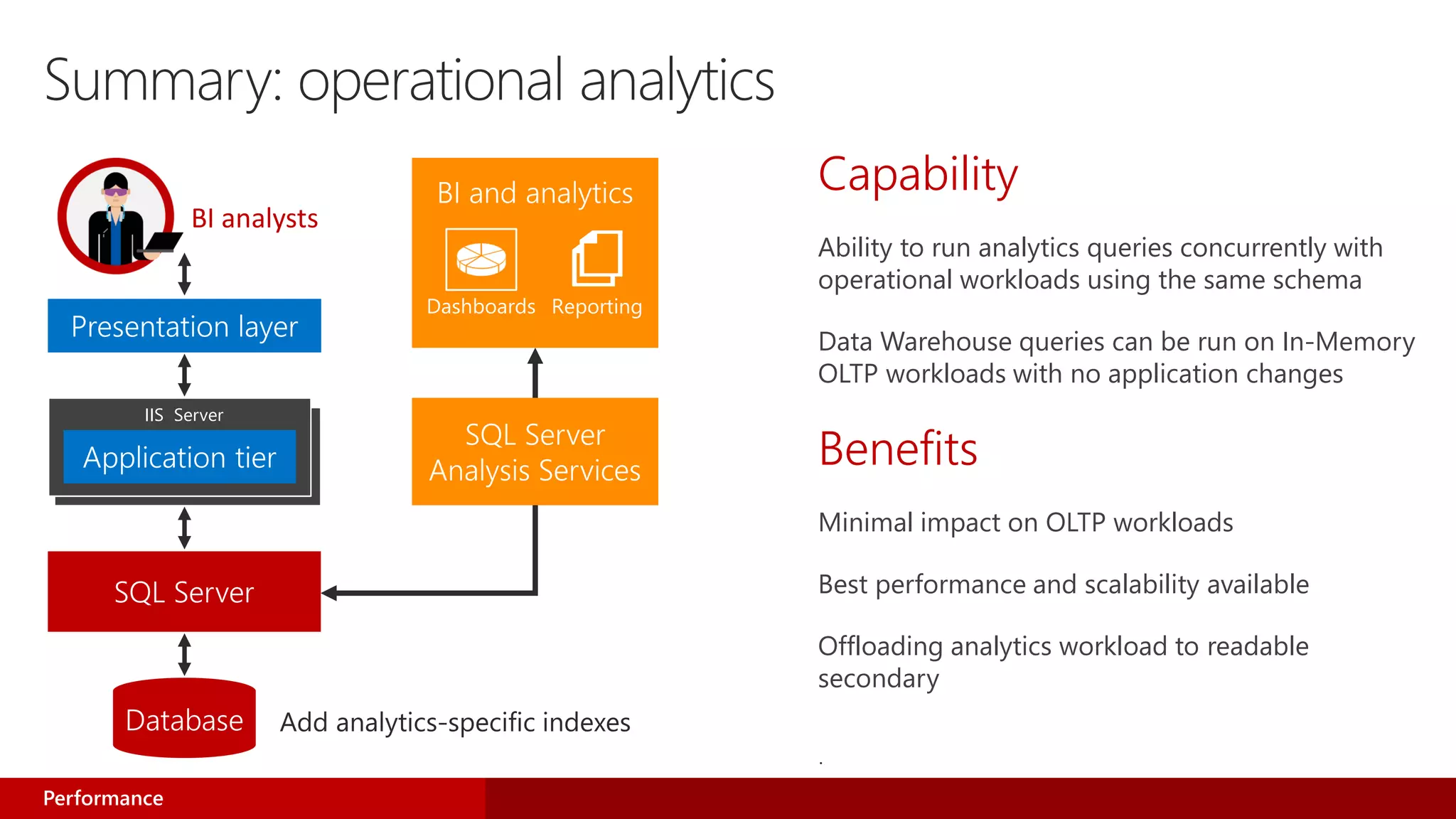
- Operational analytics allows running analytics queries concurrently with OLTP workloads using the same schema. This provides minimal impact on OLTP and best performance.
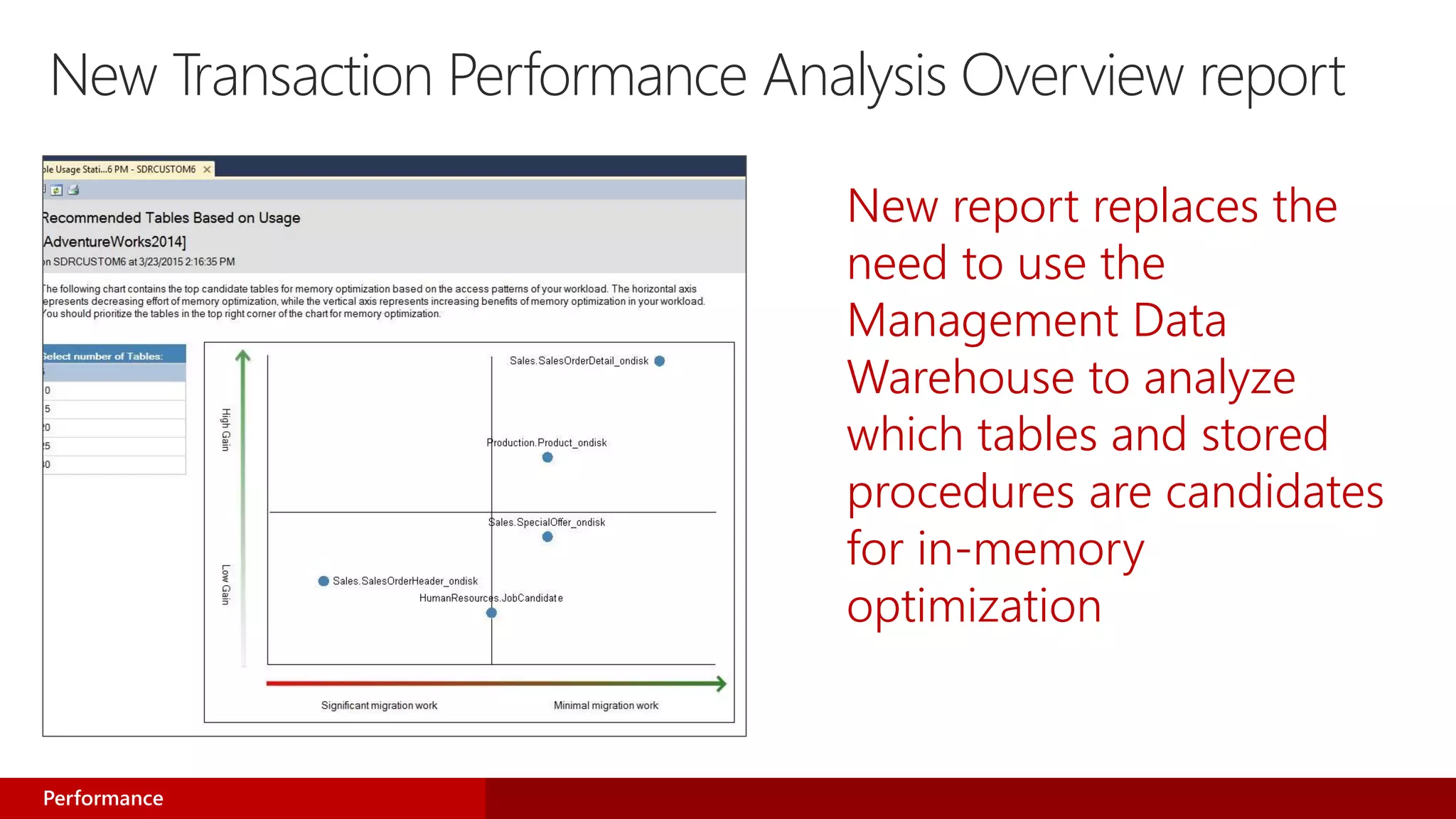
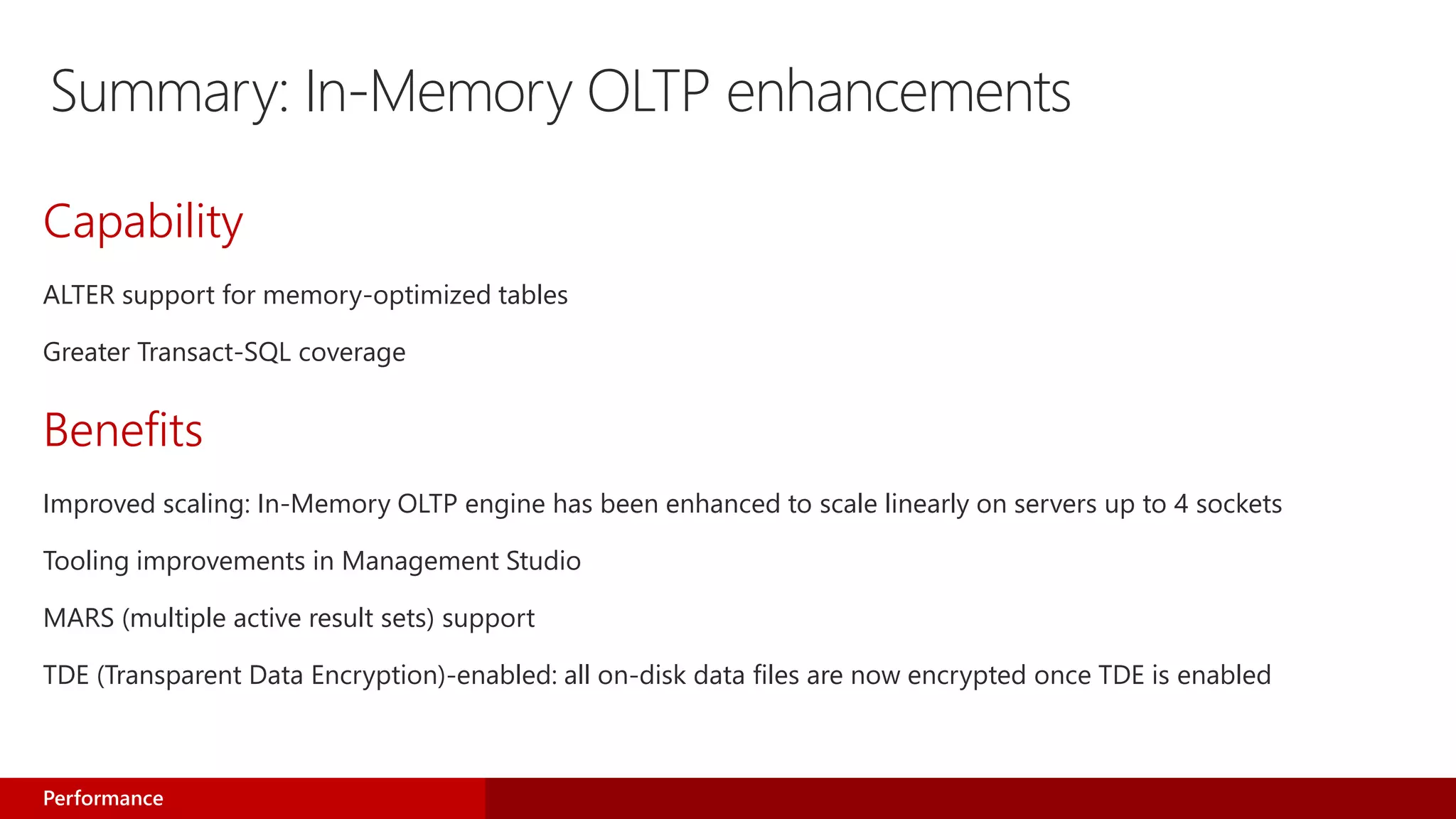
- In-Memory OLTP enhancements include greater Transact-SQL coverage, improved scaling, and tooling improvements.
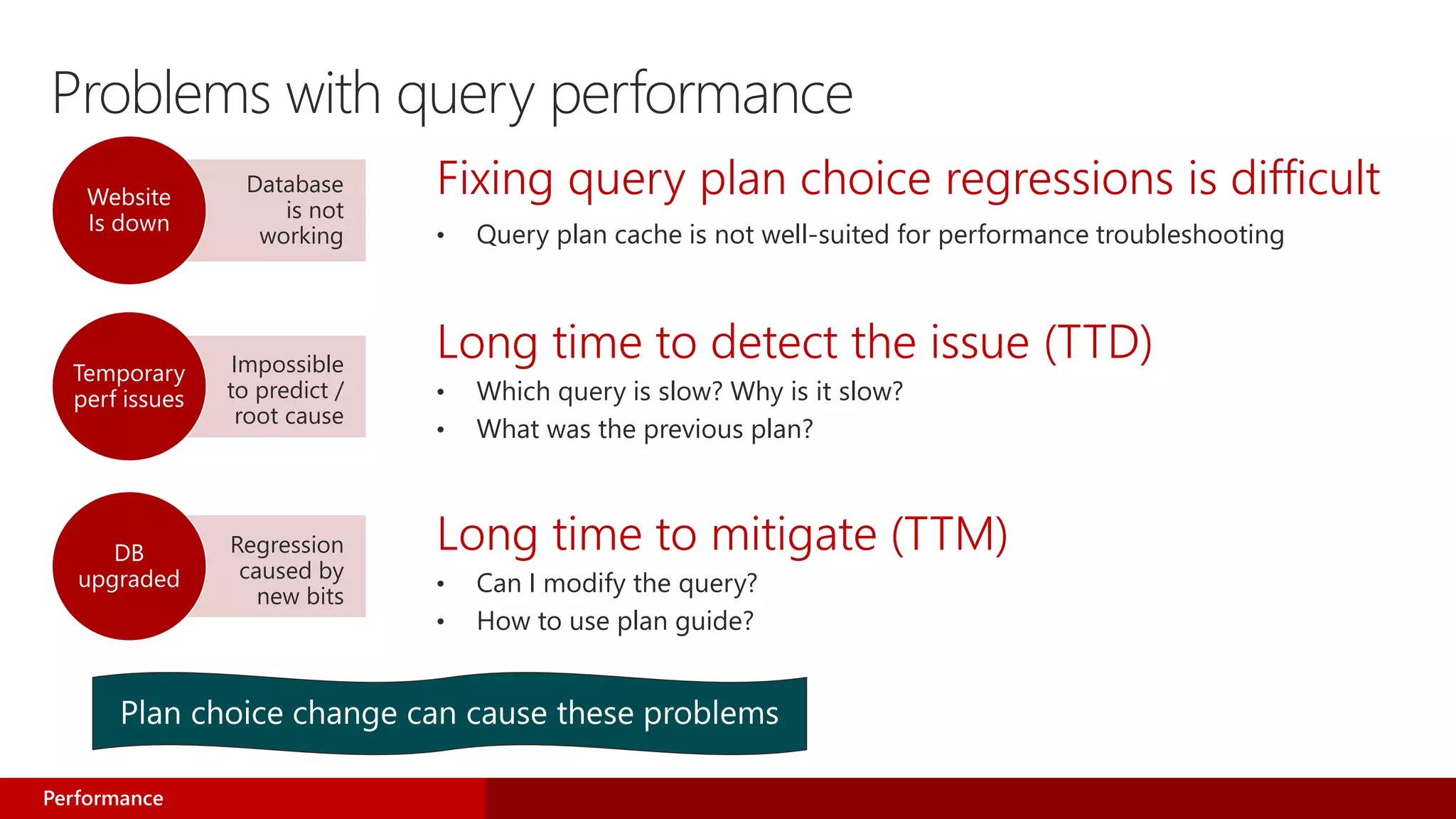
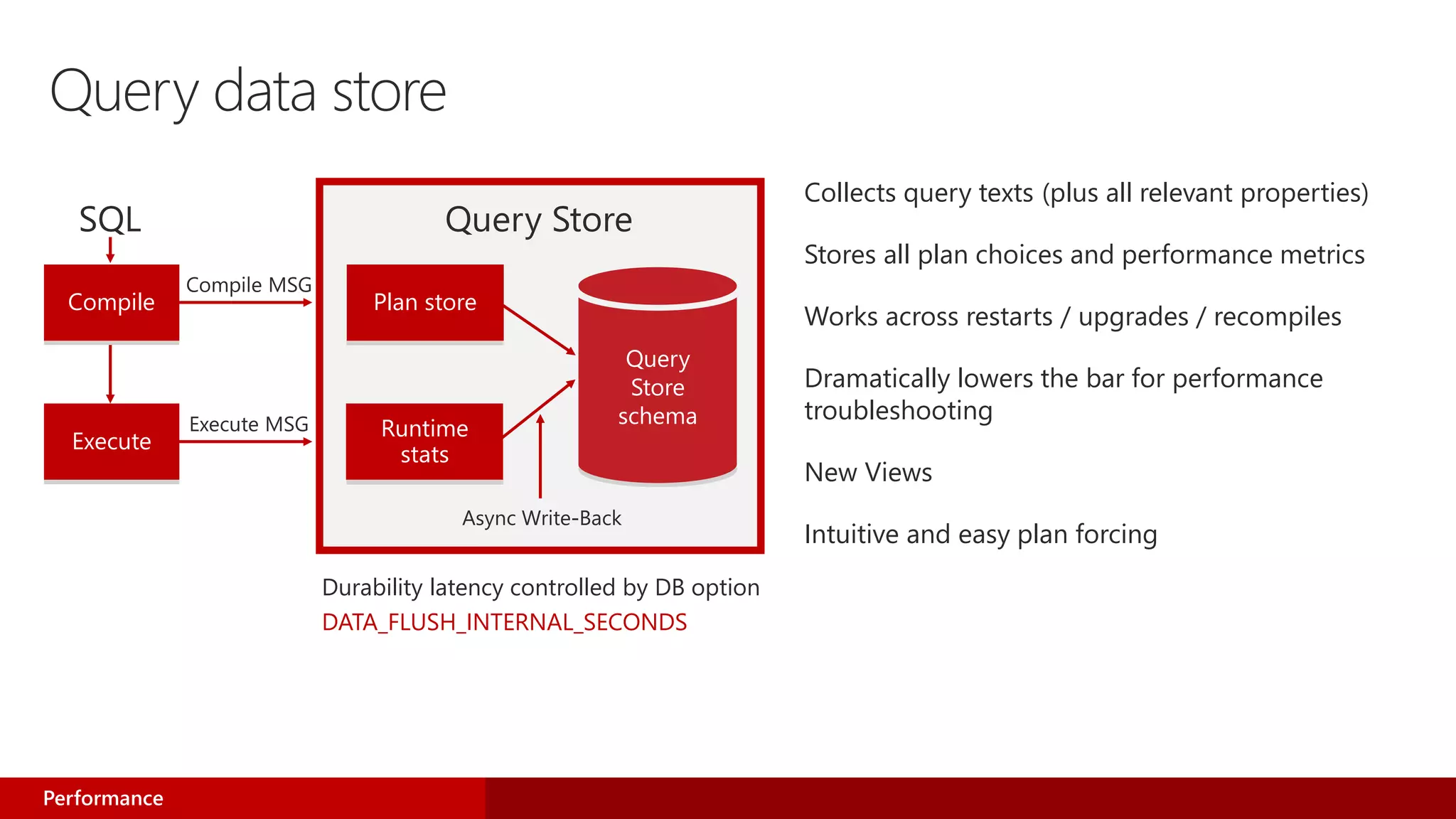
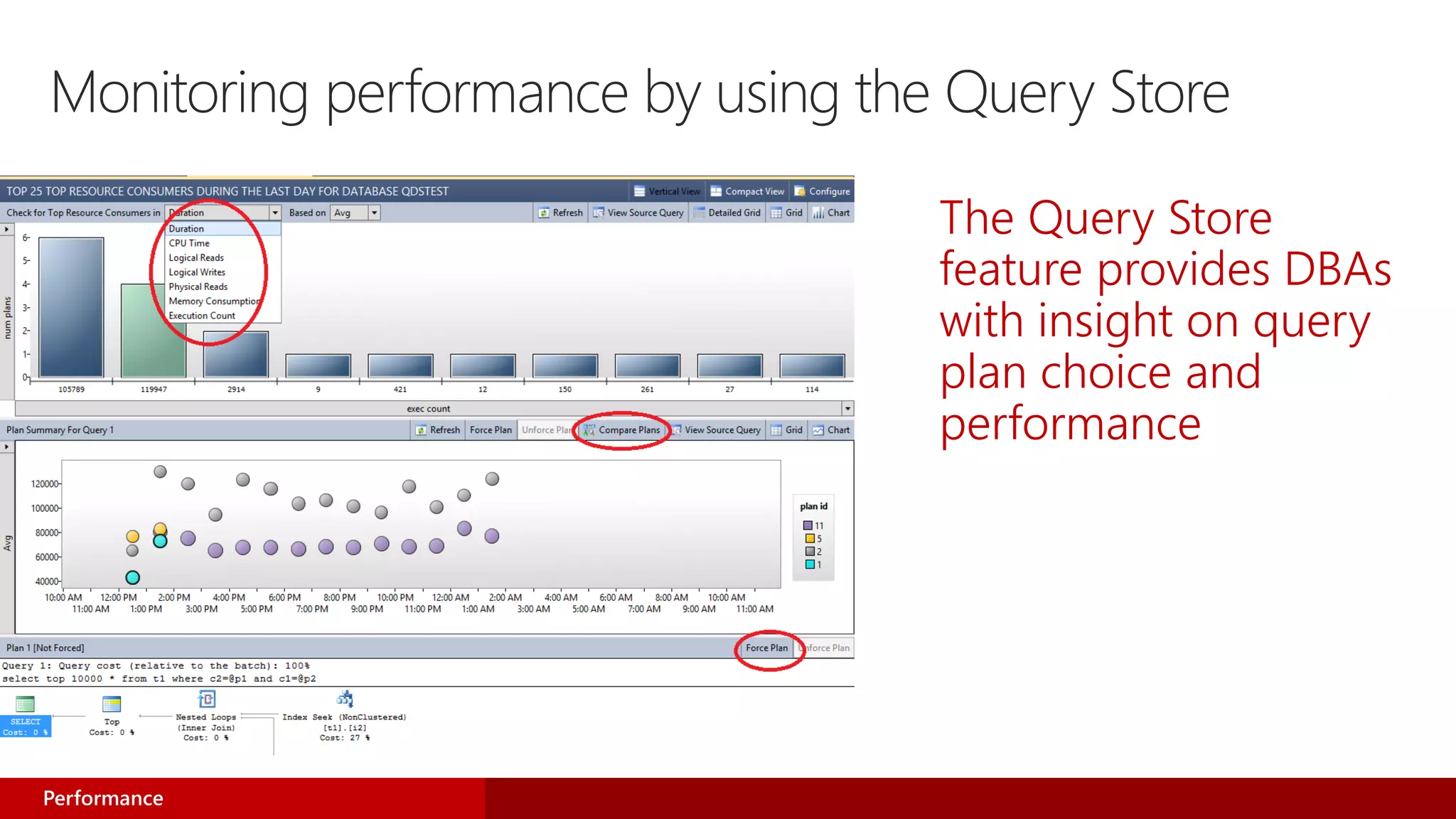
- The new Query Store feature acts as a "flight data recorder" for databases, enabling quick performance issue identification and resolution.


![| ADD
{
<column_definition>
| <table_constraint>
| <table_index>
} [ ,...n ]
| DROP
{
[ CONSTRAINT ]
{
constraint_name
} [ ,...n ]
| COLUMN
{
column_name
} [ ,...n ]
| INDEX
{
index_name
} [ ,...n ]
} [ ,...n ]
| ALTER INDEX index_name
{
REBUILD (WITH <rebuild_index_option>)
}
}
The ALTER TABLE syntax is
used for making changes to the
table schema, as well as for
adding, deleting, and rebuilding
indexes
Indexes are considered part of
the table definition
Key advantage is the ability to
change the BUCKET_COUNT with
an ALTER INDEX statement
Altering memory-optimized tables
Performance](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlserver2016ctp3technicaldeck-hoc-160502200610/75/SQL-Server-2016-novelties-6-2048.jpg)
![CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[usp_1]
WITH NATIVE_COMPILATION, SCHEMABINDING, EXECUTE AS OWNER
AS BEGIN ATOMIC WITH
(
TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL = SNAPSHOT, LANGUAGE =
N'us_english'
)
SELECT c1, c2 from dbo.T1
END
GO
ALTER PROCEDURE [dbo].[usp_1]
WITH NATIVE_COMPILATION, SCHEMABINDING, EXECUTE AS OWNER
AS BEGIN ATOMIC WITH
(
TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL = SNAPSHOT, LANGUAGE =
N'us_english'
)
SELECT c1 from dbo.T1
END
GO
You can now perform ALTER
operations on natively compiled
stored procedures using the
ALTER PROCEDURE statement
Use sp_recompile to
recompile stored procedures on
the next execution
Altering natively compiled stored procedures
Performance](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlserver2016ctp3technicaldeck-hoc-160502200610/75/SQL-Server-2016-novelties-7-2048.jpg)


![JSON in SQL Server
[
{
"Number":"SO43659",
"Date":"2011-05-31T00:00:00"
"AccountNumber":"AW29825",
"Price":59.99,
"Quantity":1
},
{
"Number":"SO43661",
"Date":"2011-06-01T00:00:00“
"AccountNumber":"AW73565“,
"Price":24.99,
"Quantity":3
}
]
SO43659 2011-05-31T00:00:00 MSFT 59.99 1
SO43661 2011-06-01T00:00:00 Nokia 24.99 3
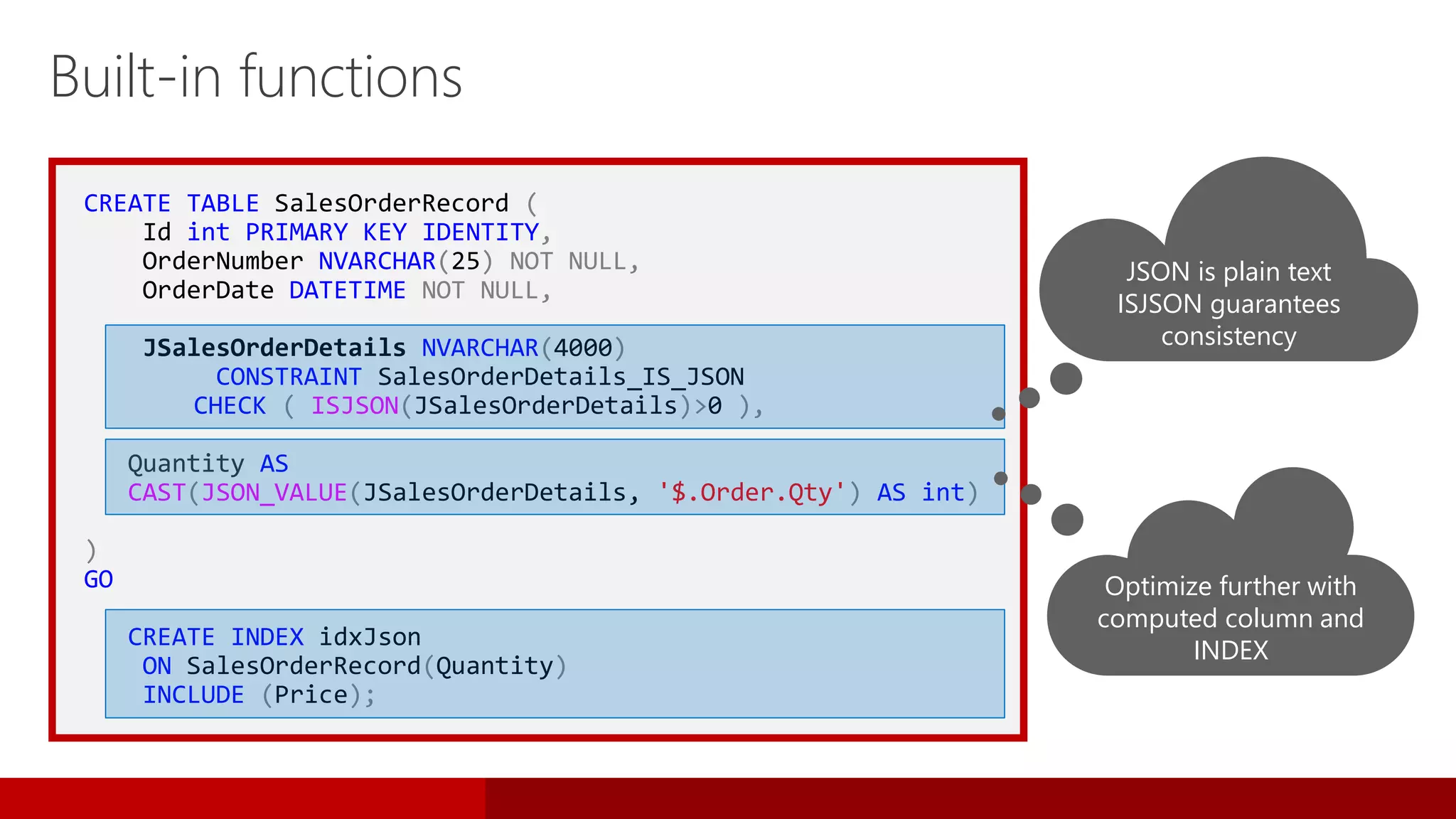
Table 2 JSON
Formats result set
as JSON text.
JSON 2 table
Migrates JSON
text to table
Built-in functions
ISJSON
JSON_VALUE
JSON_MODIFY
Performance](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlserver2016ctp3technicaldeck-hoc-160502200610/75/SQL-Server-2016-novelties-17-2048.jpg)

![Table to JSON
JSON output:
SO43659 2011-05-31T00:00:00 MSFT 59.99 1
SO43661 2011-06-01T00:00:00 Nokia 24.99 3
SELECT Number AS [Order.Number], Date AS [Order.Date],
Customer AS Account,
Price AS 'Item.UnitPrice', Quantity AS 'Item.Qty'
FROM SalesOrder
FOR JSON PATH
Performance](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlserver2016ctp3technicaldeck-hoc-160502200610/75/SQL-Server-2016-novelties-19-2048.jpg)










![Security
CREATE FUNCTION dbo.fn_securitypredicate(@wing int)
RETURNS TABLE WITH SCHEMABINDING AS
return SELECT 1 as [fn_securitypredicate_result]
FROM
StaffDuties d INNER JOIN Employees e
ON (d.EmpId = e.EmpId)
WHERE e.UserSID = SUSER_SID()
AND @wing = d.Wing;
CREATE SECURITY POLICY dbo.SecPol
ADD FILTER PREDICATE dbo.fn_securitypredicate(Wing)
ON Patients
WITH (STATE = ON)
Fine-grained access control over
rows in a table based on one or
more pre-defined filtering
criteria, such as user’s role or
clearance level in organization
Concepts:
Predicate function
Security policy
Example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlserver2016ctp3technicaldeck-hoc-160502200610/75/SQL-Server-2016-novelties-35-2048.jpg)
![Two
App user (e.g., nurse) selects from Patients table
Three
Security Policy transparently rewrites query to apply filter predicate
Database Policy Manager
CREATE FUNCTION dbo.fn_securitypredicate(@wing int)
RETURNS TABLE WITH SCHEMABINDING AS
return SELECT 1 as [fn_securitypredicate_result] FROM
StaffDuties d INNER JOIN Employees e
ON (d.EmpId = e.EmpId)
WHERE e.UserSID = SUSER_SID() AND @wing = d.Wing;
CREATE SECURITY POLICY dbo.SecPol
ADD FILTER PREDICATE dbo.fn_securitypredicate(Wing) ON Patients
WITH (STATE = ON)
Filter
Predicate:
INNER
JOIN…
Security
Policy
Application
Patients
Nurse
SELECT * FROM Patients
SELECT * FROM Patients
SEMIJOIN APPLY dbo.fn_securitypredicate(patients.Wing);
SELECT Patients.* FROM Patients,
StaffDuties d INNER JOIN Employees e ON (d.EmpId = e.EmpId)
WHERE e.UserSID = SUSER_SID() AND Patients.wing = d.Wing;
RLS in three steps
Security](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlserver2016ctp3technicaldeck-hoc-160502200610/75/SQL-Server-2016-novelties-36-2048.jpg)


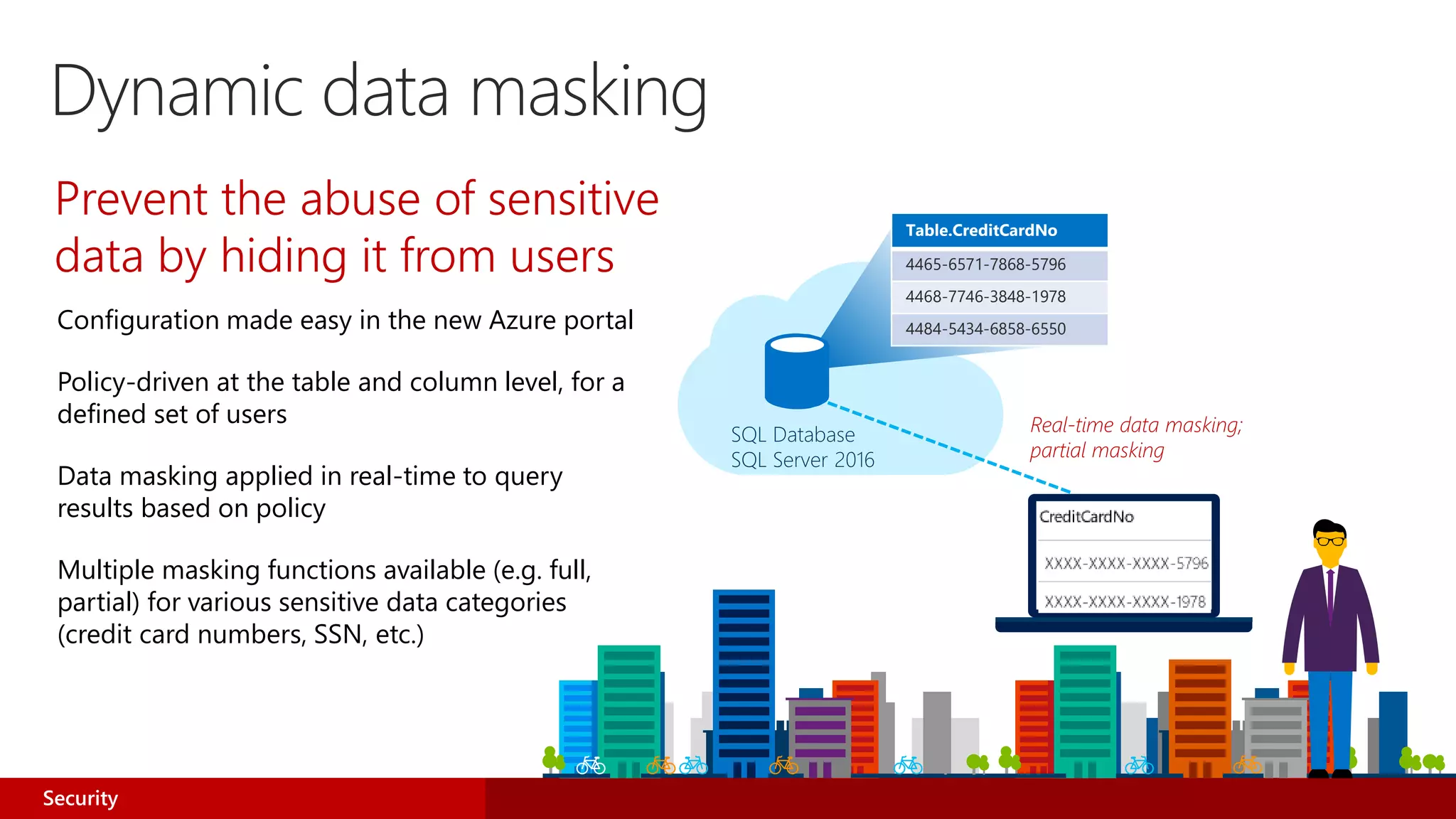
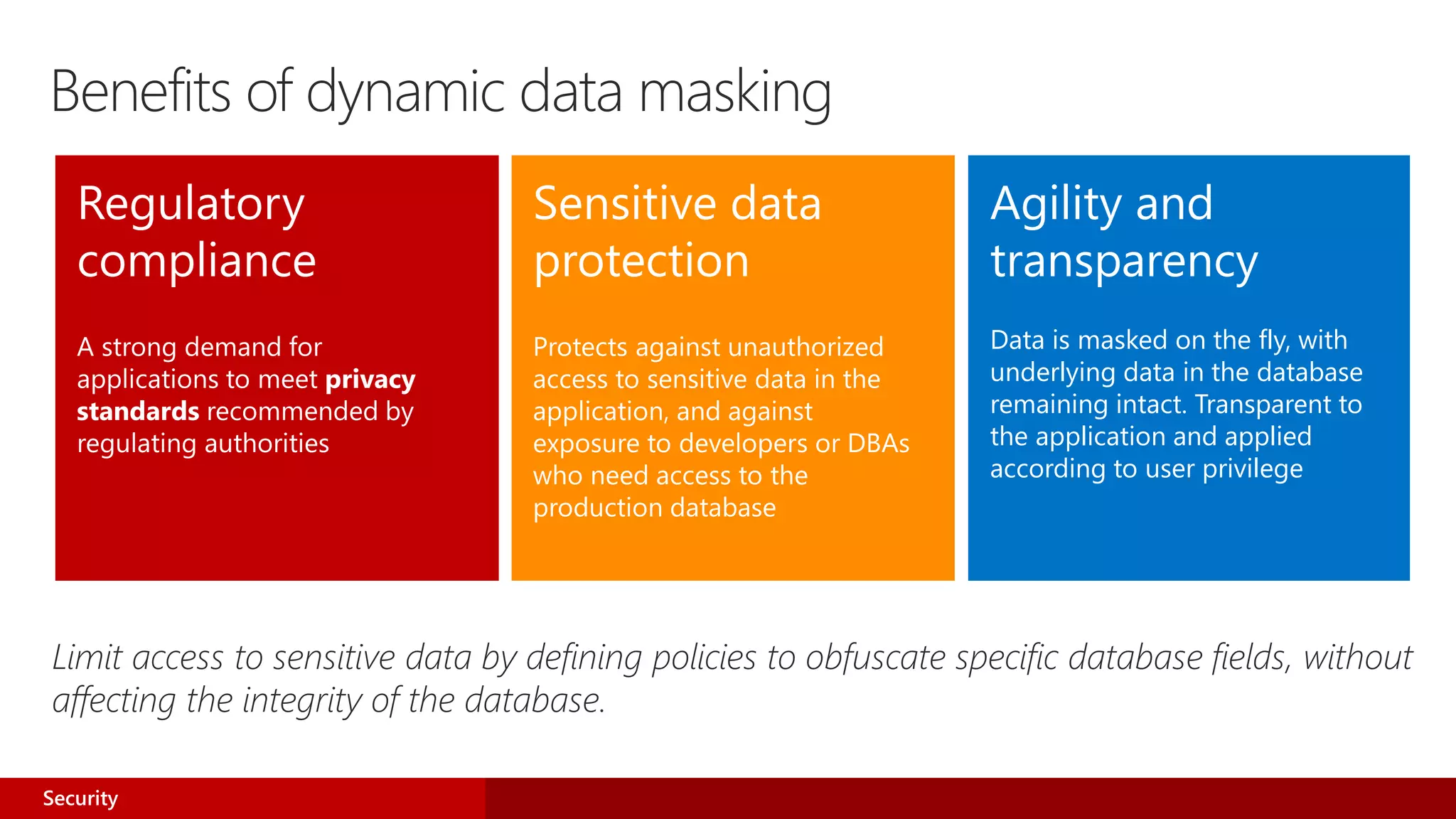
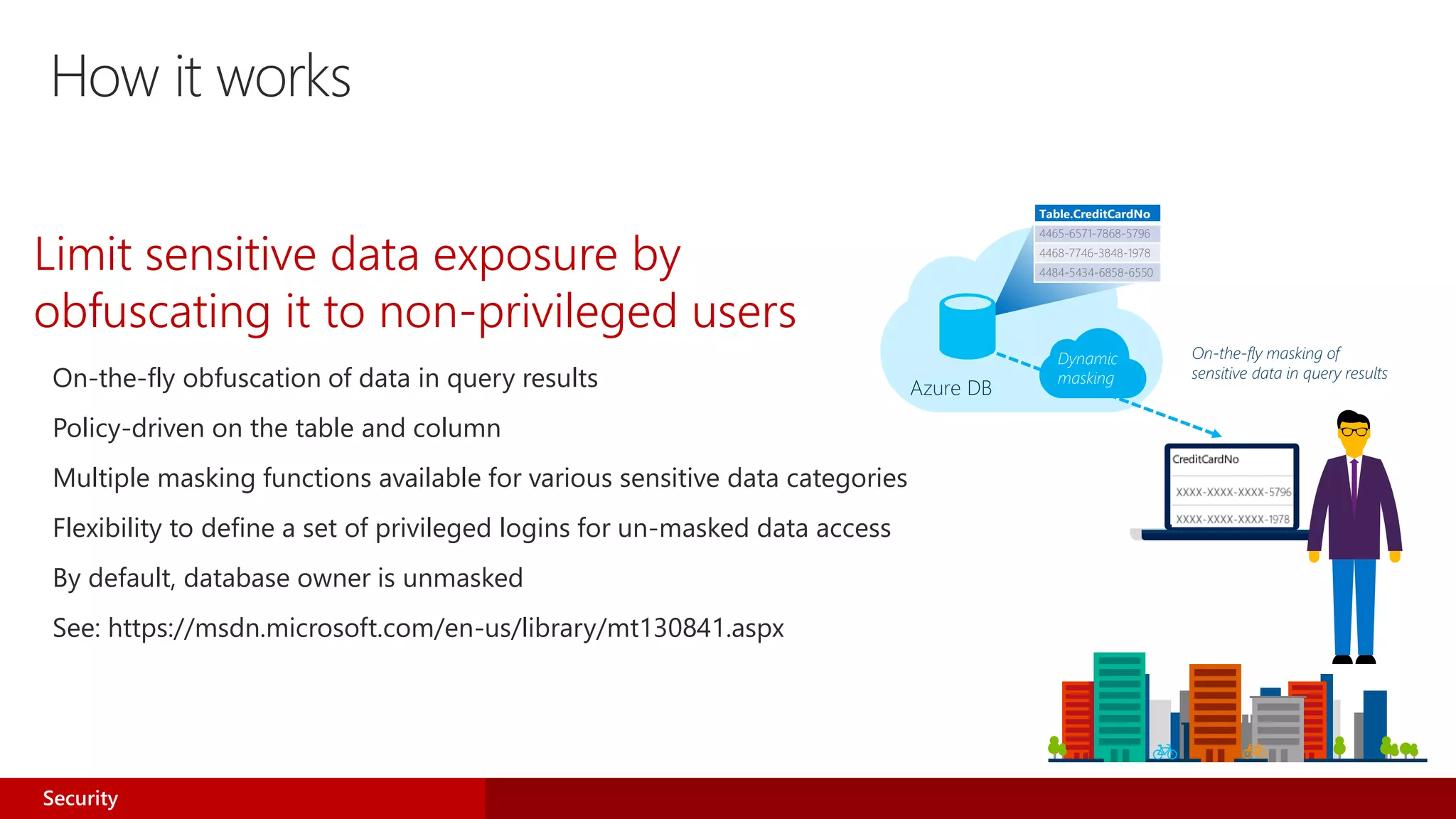
![Dynamic data masking walkthrough
ALTER TABLE [Employee] ALTER COLUMN [SocialSecurityNumber]
ADD MASKED WITH (FUNCTION = ‘SSN()’)
ALTER TABLE [Employee] ALTER COLUMN [Email]
ADD MASKED WITH (FUNCTION = ‘EMAIL()’)
ALTER TABLE [Employee] ALTER COLUMN [Salary]
ADD MASKED WITH (FUNCTION = ‘RANDOM(1,20000)’)
GRANT UNMASK to admin1
1) Security officer defines dynamic data masking policy in T-SQL over sensitive data in Employee table2) Application user selects from Employee table3) Dynamic data masking policy obfuscates the sensitive data in the query results
SELECT [Name],
[SocialSecurityNumber],
[Email],
[Salary]
FROM [Employee]
Security](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlserver2016ctp3technicaldeck-hoc-160502200610/75/SQL-Server-2016-novelties-42-2048.jpg)