Sanrich Restaurant, a market leader in Moratuwa with three branches, focuses on reward management to recognize employee contributions and align with business goals. The document outlines various reward types, principles, and motivation theories relevant to enhancing employee performance. It emphasizes that strategic reward management is essential for employee satisfaction and retention.














![List of Reference
1. Armstrong, M., 2007. Motivation and Reward. In Improving
performance through reward. 2nd ed. p.133.
2. HR WALE, 2010. HR WALE. [Online] HR WALE Productions
Available at: http://www.hrwale.com [Accessed 11 May 2016].
3. Jaques, E., 1961. In Equitable Payment.
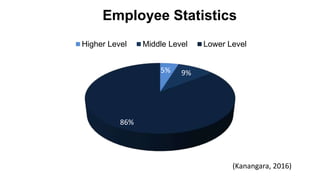
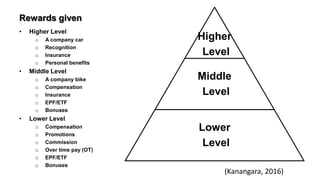
4. Kanangara, C., 2016. About Sanrich Restaurant. Moratuwa, Sri
Lanka, 11 May 2016.
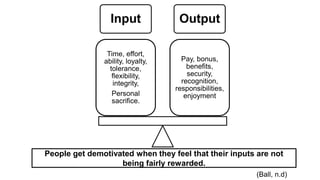
5. Ball, B., n.d. In Summary of motivation theories. P. 15.
6. Zingeim, P.K..J.R.S., 2000. Pay People Right. [Online] Schuster-
Zingeim and Associates, Inc. Available at:
http://www.paypeopleright.com [Accessed 7 May 2016].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rewardmangement-160630113628/85/Reward-mangement-19-320.jpg)
