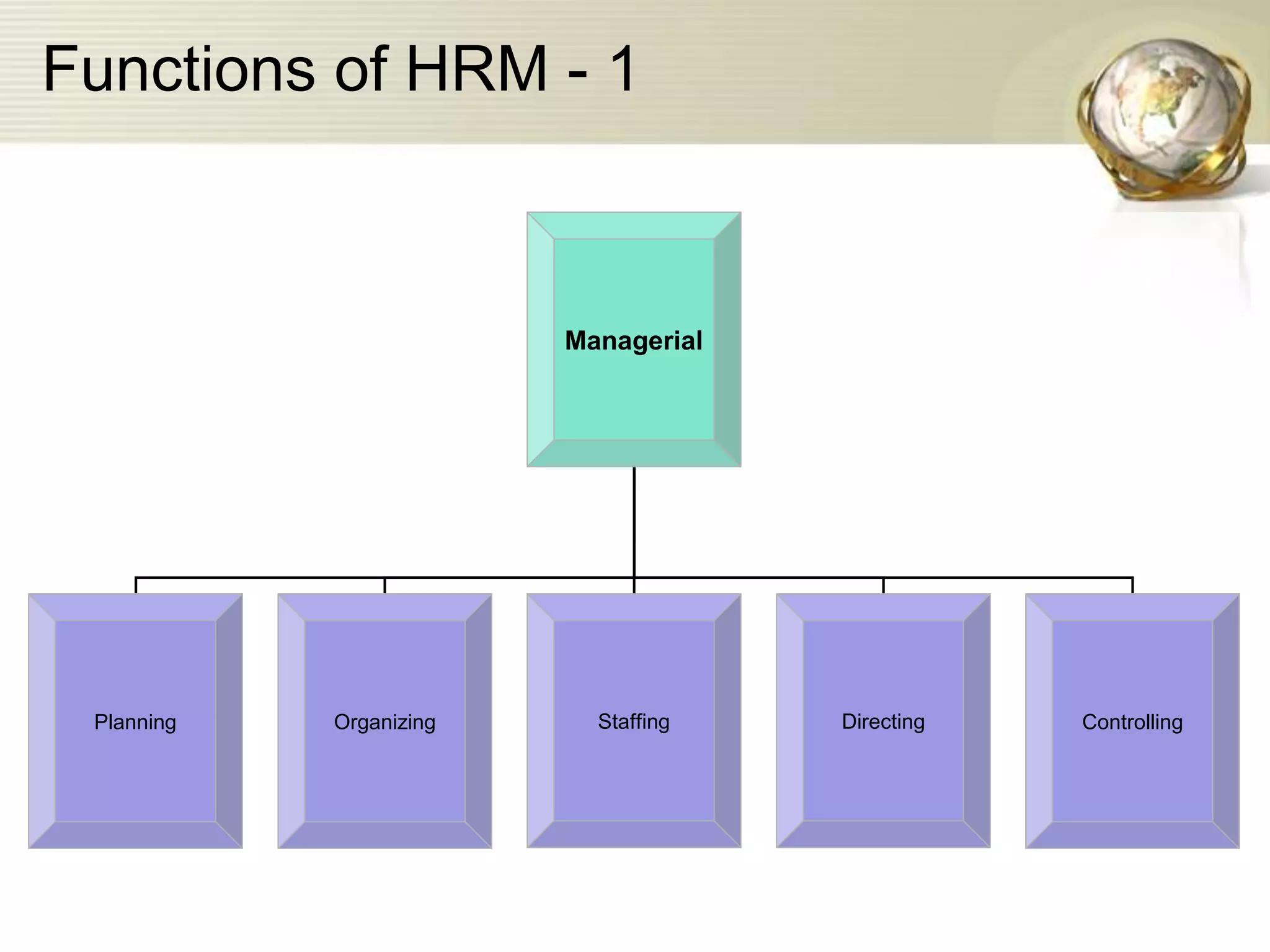
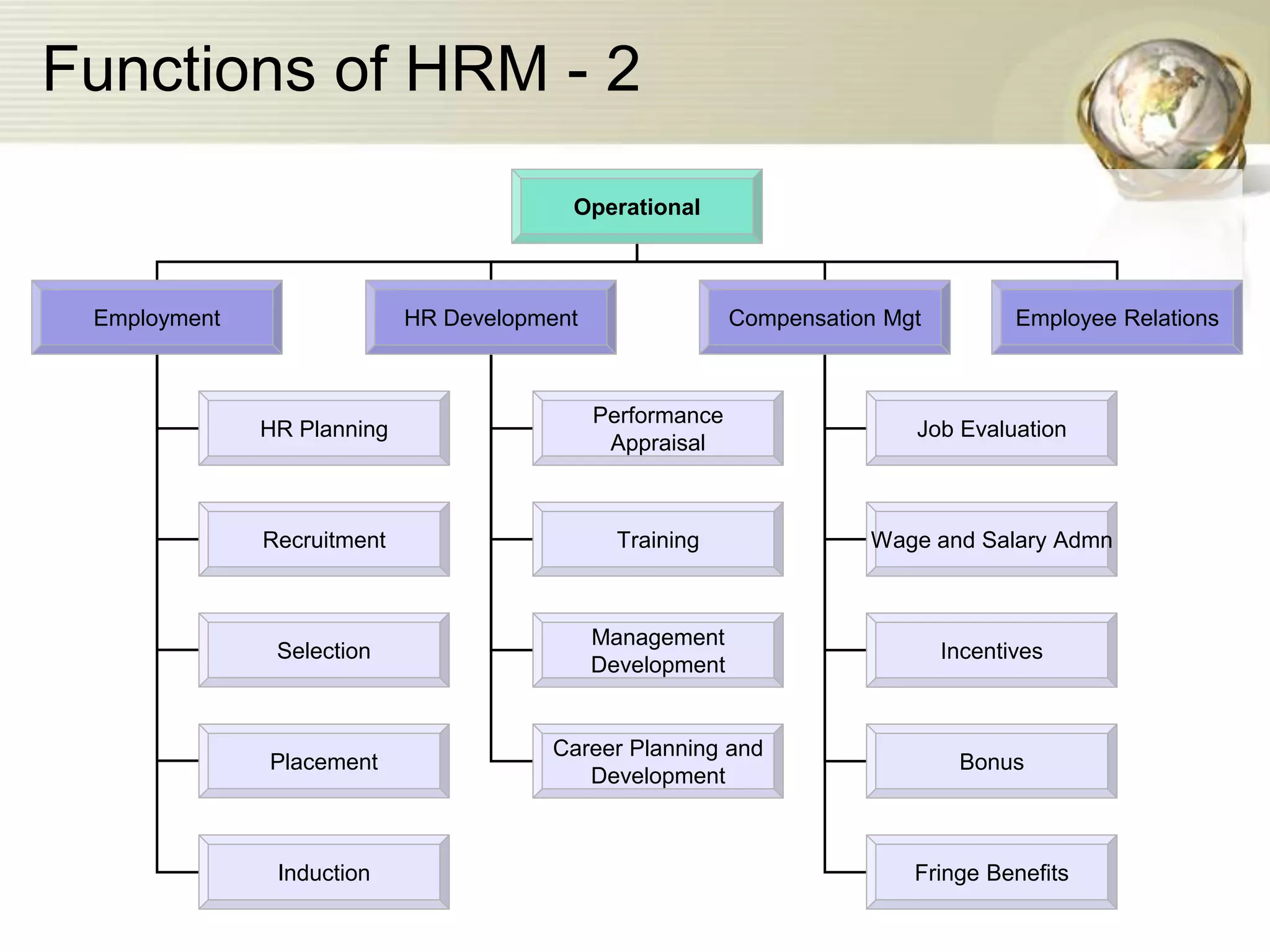
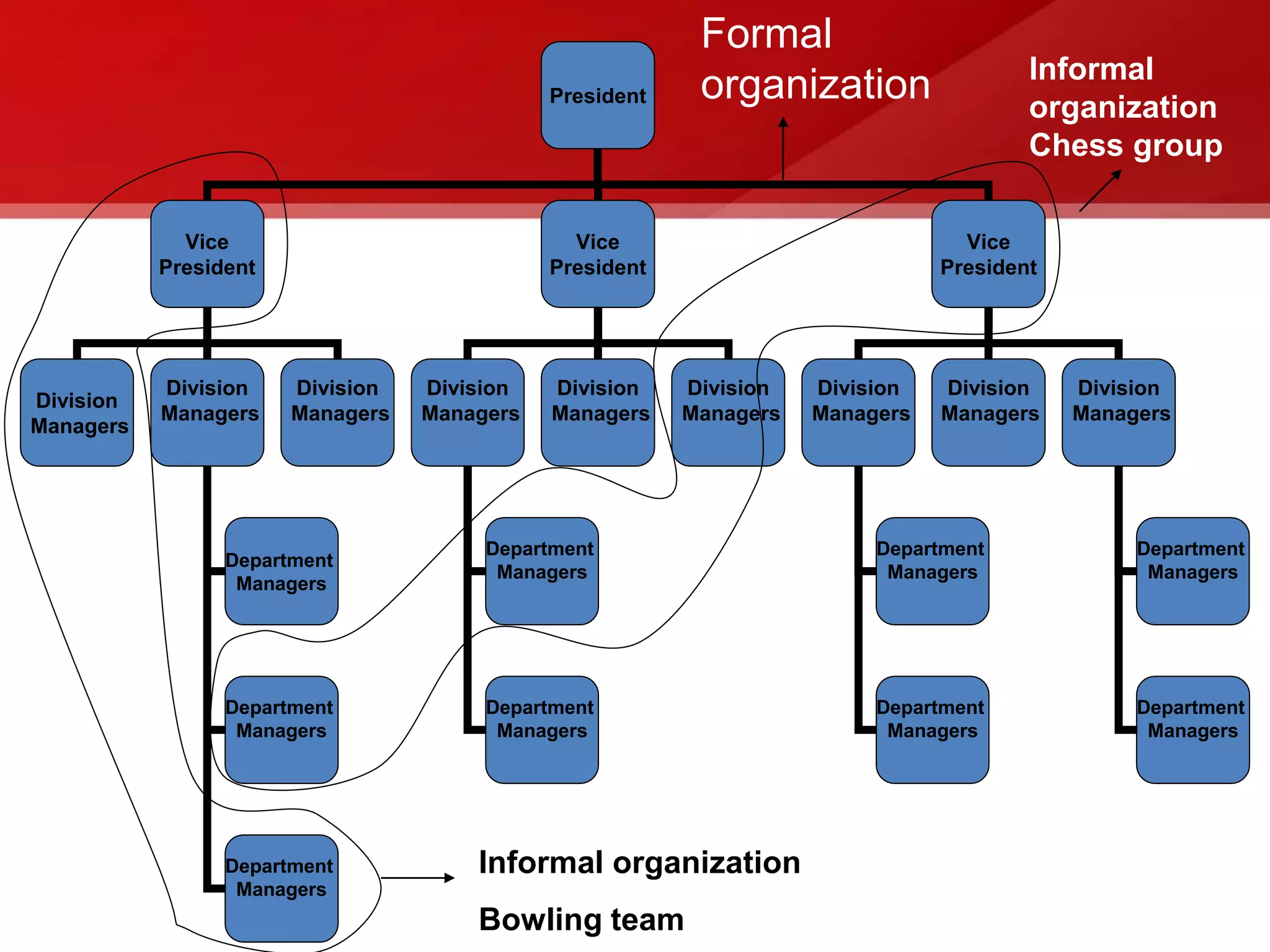
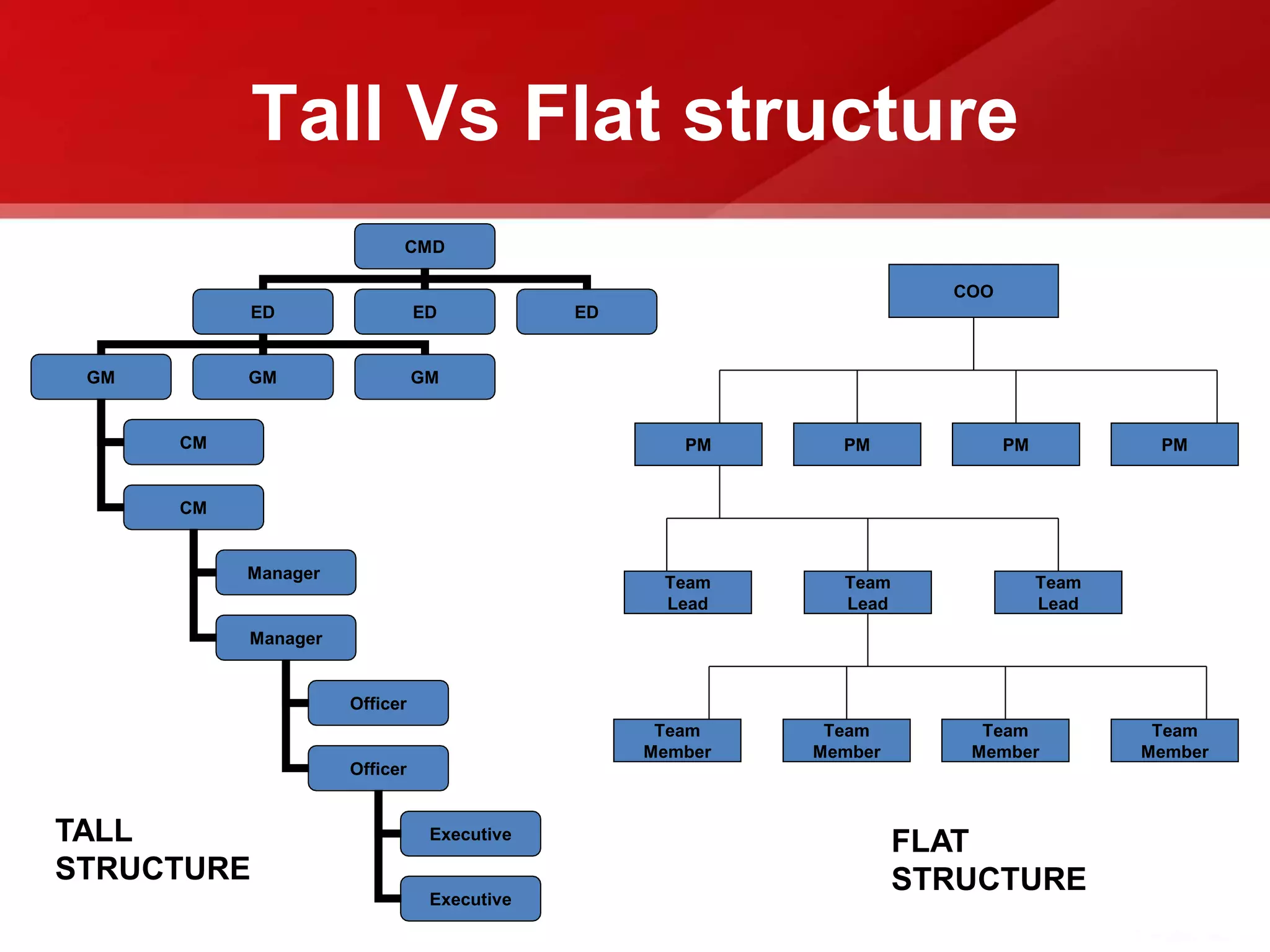
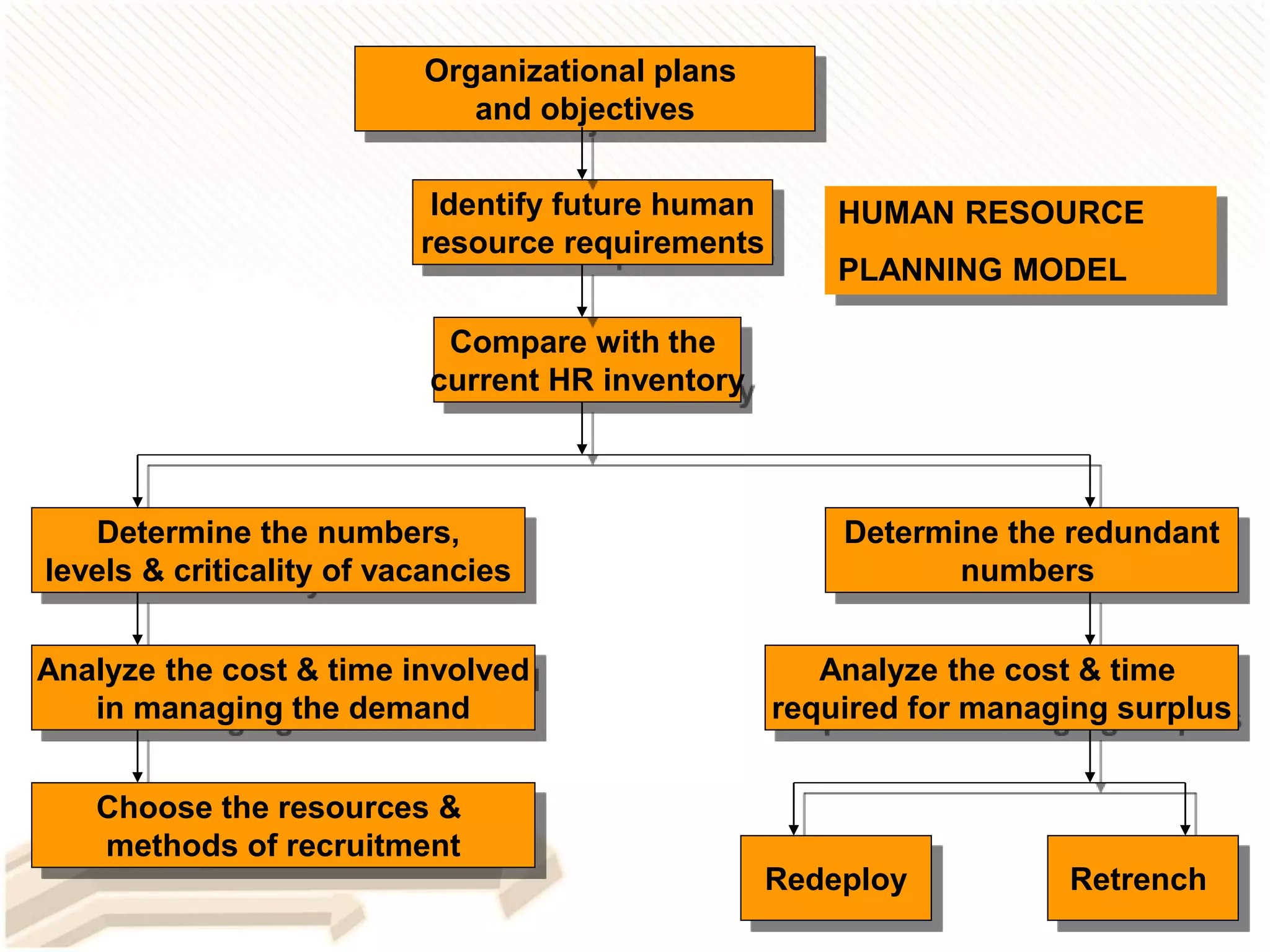
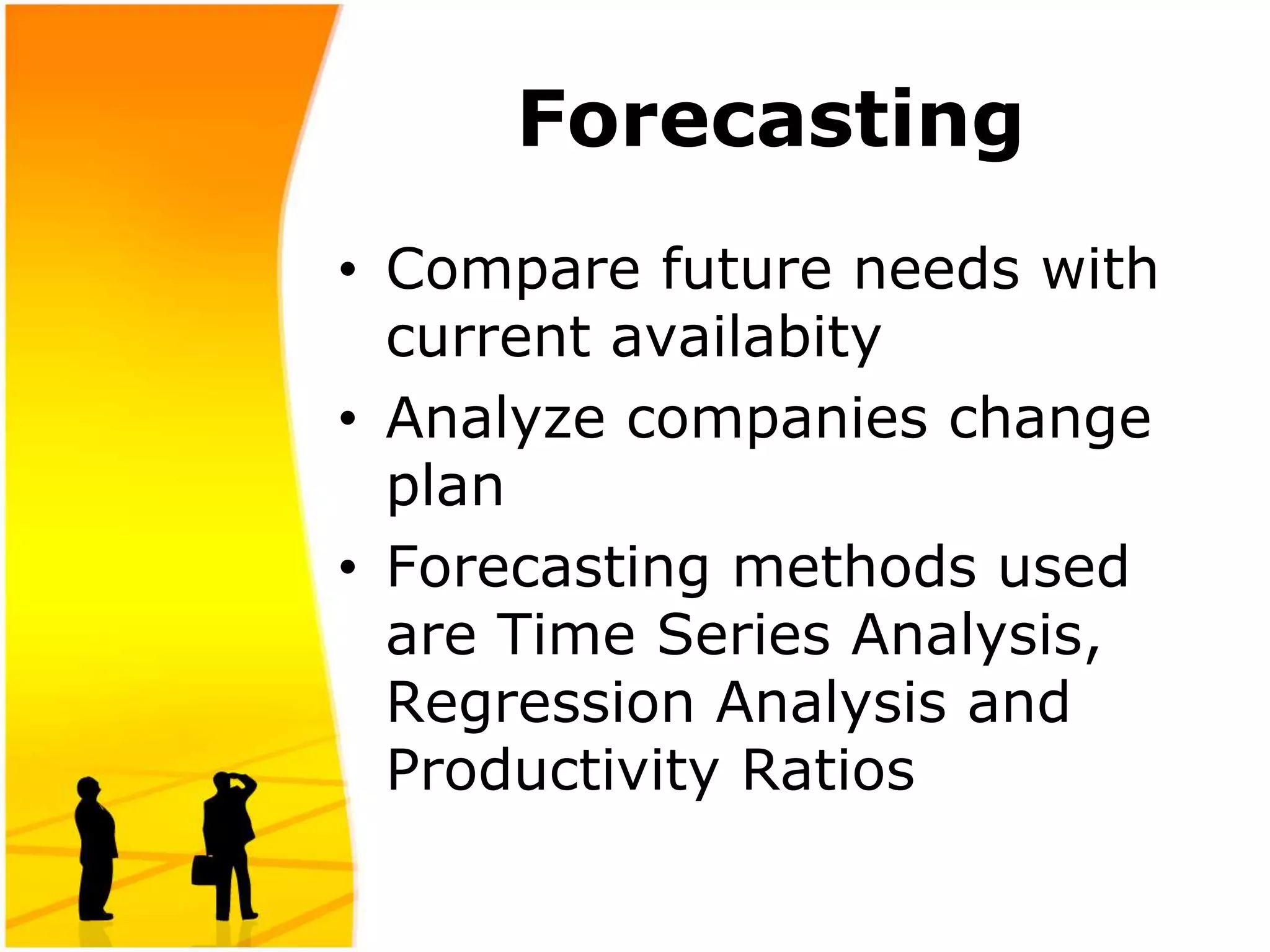
The document provides an introduction to human resource planning. It discusses key points such as the definition of human resource planning as anticipating and making provision for the movement of people into, within and out of an organization. The objectives of HRP are to maintain, forecast, optimize and utilize the right number of people with the right skills at the right time and cost. The process of HRP involves identifying future requirements, comparing them to current resources, determining surpluses or vacancies, and managing demand and surplus. Effective HRP is increasingly important for organizations.