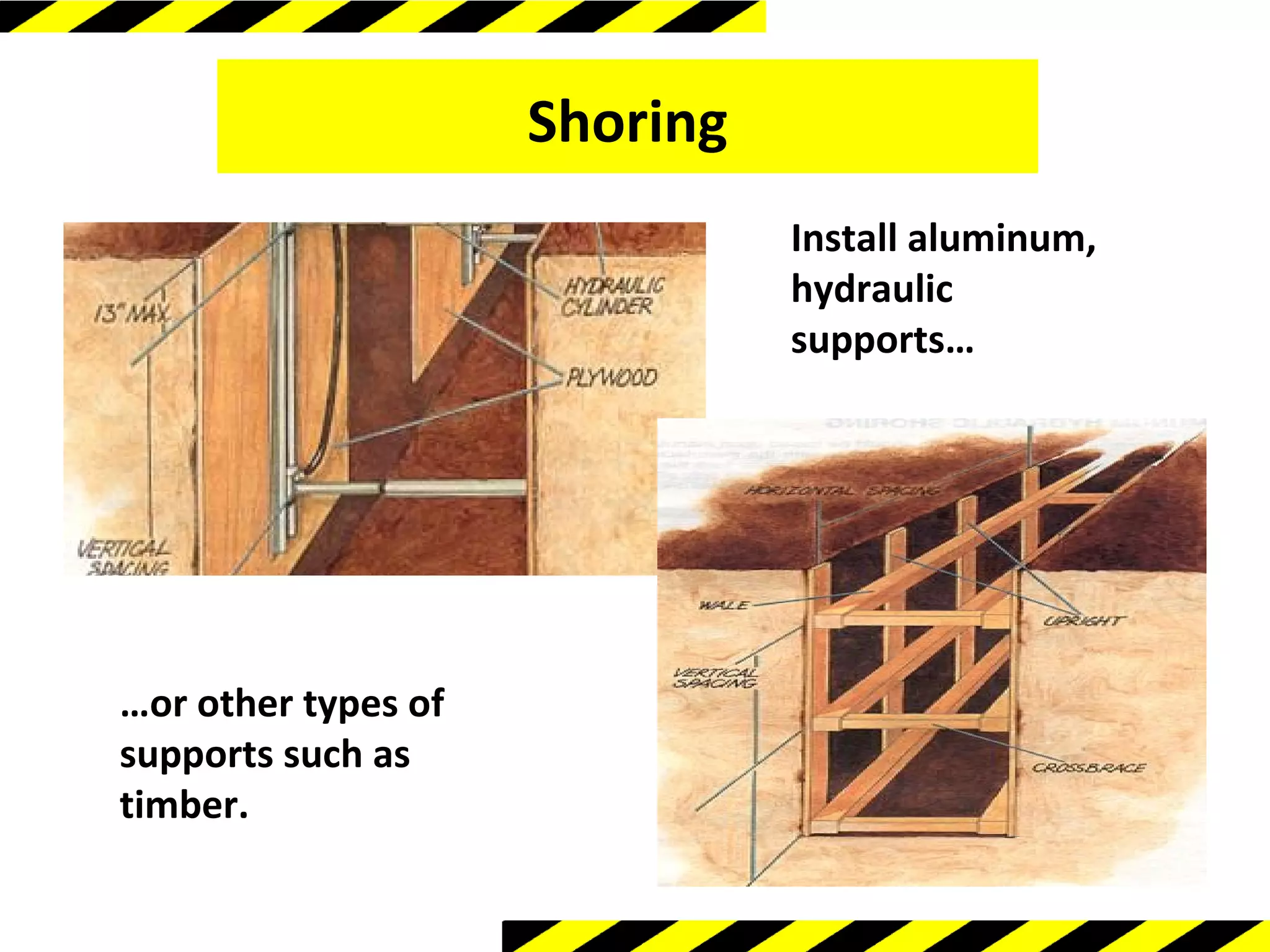
The document discusses excavation safety. It notes that excavating is one of the most hazardous construction operations, with cave-ins posing the greatest risk and often resulting in fatalities. OSHA regulations require protective systems like sloping, shielding, or shoring for trenches over 5 feet deep. A competent person must inspect sites and determine the appropriate protection. Proper ingress/egress, atmospheric testing, and following basic rules can help prevent accidents and save lives. Pre-planning is critical to excavation safety.

![Cave-ins… pose the greatest risk and are much more likely than
other excavation-related accidents to result in
worker fatalities.
• Two workers are killed every month.
• U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) data show that
271 workers died in trenching or excavation cave-
ins from 2000 through 2006.
• Per NIOSH-488 deaths, 1992 and 2000. Averaging 54
fatalities each year.
• More than half of those killed are coworkers, fire
dept. personnel & bystanders attempting to rescue.
[29 CFR 1926.32(f)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13793f2e-f6bb-4b83-bc9e-355323d0197d-150907234418-lva1-app6892/75/Excavation-Safety-Training-Module-1-2-2048.jpg)


















![Preparation saves lives: 12 critical questions
• 1. Have all underground utilities and their estimated locations been accounted for
(sewer, telephone, fuel, electric, water lines)? [29 CFR 1926.651(b)]
• 2. Is there proper access and egress? [29 CFR 1926.651(c)]
• 3. Will there be vehicular traffic exposure near the excavation? [29 CFR
1926.651(d)]
• 4. Is there proper protection from exposure to falling loads? [29 CFR 1926.651(e)]
• 5. Is there a warning system for mobile equipment? [29 CFR 1926.651(f)]
• 6. Is there a potential for exposure to hazardous atmospheres?[29 CFR
1926.651(g)]
• 8. Will the excavation be near existing structures? If so, what is the stability of the
adjacent structures? [29 CFR 1926.651(i)]
• 9. What types of soil will be found?
• 10. Is there adequate protection from loose rock or soil? [29 CFR 1926.651(j)]
• 11. If a protective system is needed, what type of system is adequate? [29 CFR
1926.652(a)]
• 12. If employee exposure to any hazard is anticipated, is there a plan in place to
perform daily inspections of excavations, adjacent areas and protective systems?
[29 CFR 1926.651(k)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13793f2e-f6bb-4b83-bc9e-355323d0197d-150907234418-lva1-app6892/75/Excavation-Safety-Training-Module-1-22-2048.jpg)

