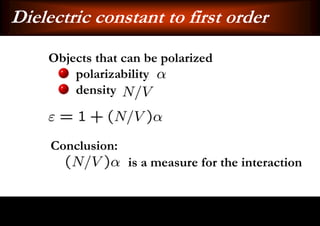
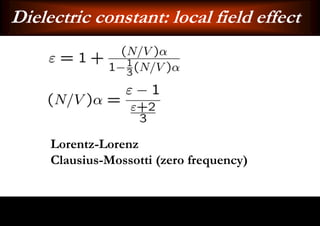
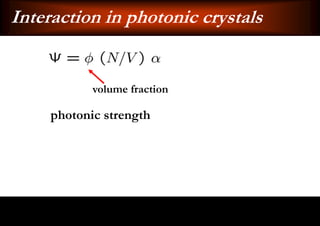
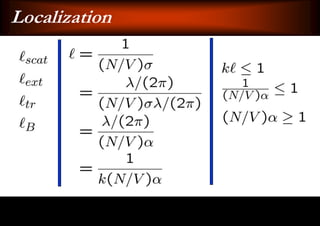
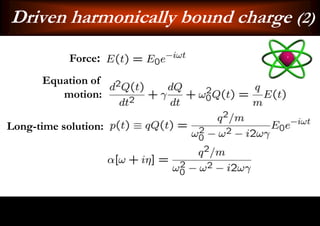
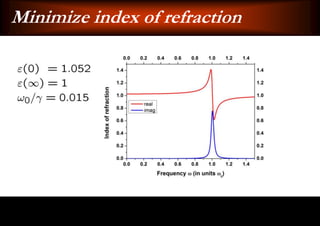
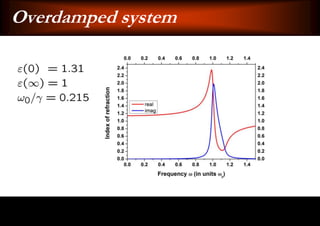
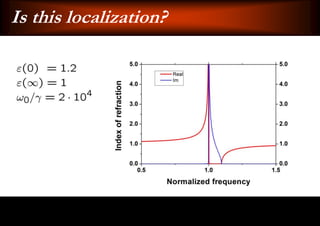
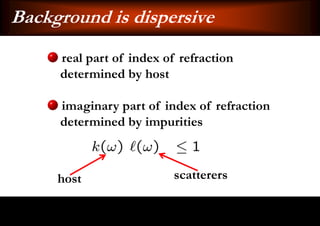
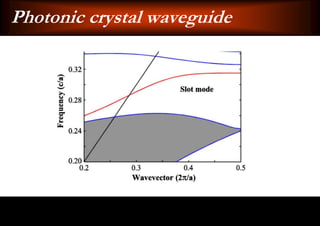
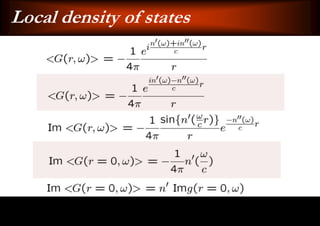
This document discusses light-matter interaction and localization. It begins by introducing dielectric response and establishing that there is a wavevector and dispersion relation. It then discusses density of states and the local density of states. It concludes by stating that the localization criterion for a single scatterer is calculating the average scattering cross-section divided by the volume of the scatterer.