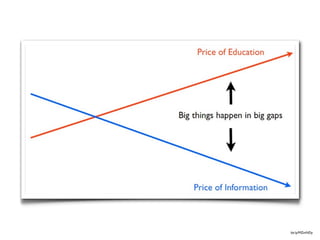
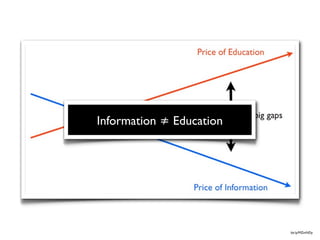
1) The document discusses how the abundance of information, tools, and networks available online is changing the nature of learning and education.
2) It argues that in this new environment, where content and teachers are no longer scarce, the primary value of school must shift from knowledge acquisition to developing skills like creativity, problem solving, and lifelong learning.
3) For education to be effective, it asserts that we need to "unlearn" traditional approaches focused on delivery, competition, and assessment, and instead embrace more collaborative and self-directed models of learning.