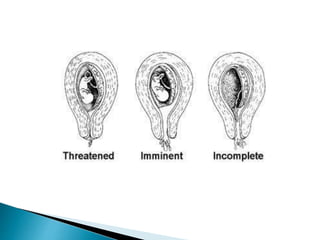
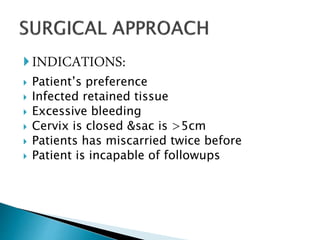
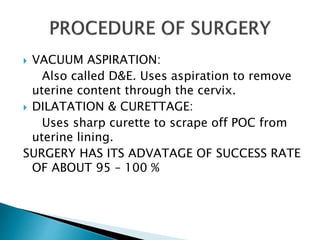
This document discusses types of miscarriage and management options. There are five types of miscarriage based on clinical presentation: threatened, inevitable, incomplete, complete, and missed. Management options depending on the situation include expectant management (watchful waiting), medical treatment using prostaglandins or mifepristone, or surgical treatment like dilation and curettage. Risks of surgical treatment include cervical trauma, subsequent cervical incompetence, uterine perforation and intrauterine adhesions.