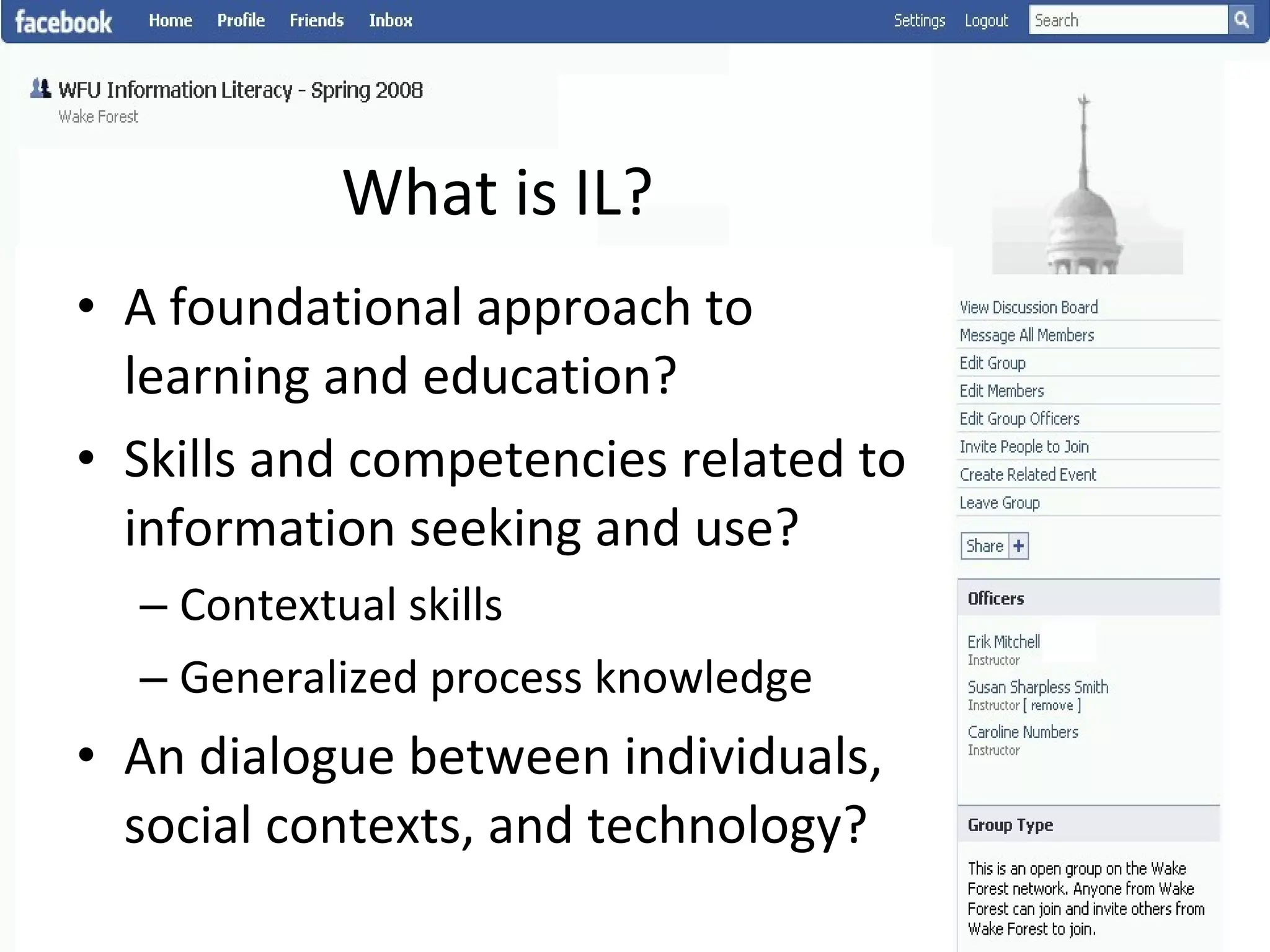
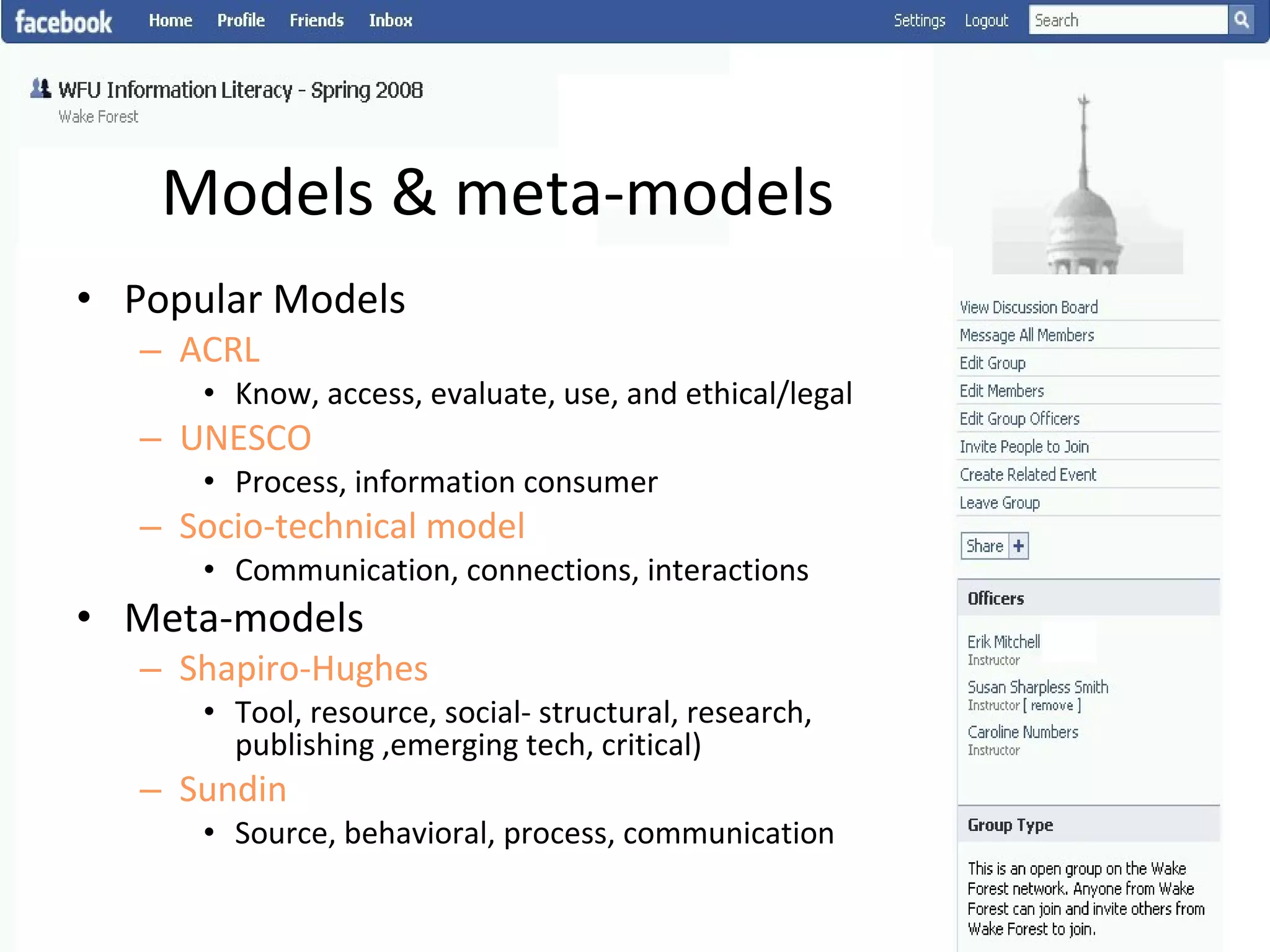
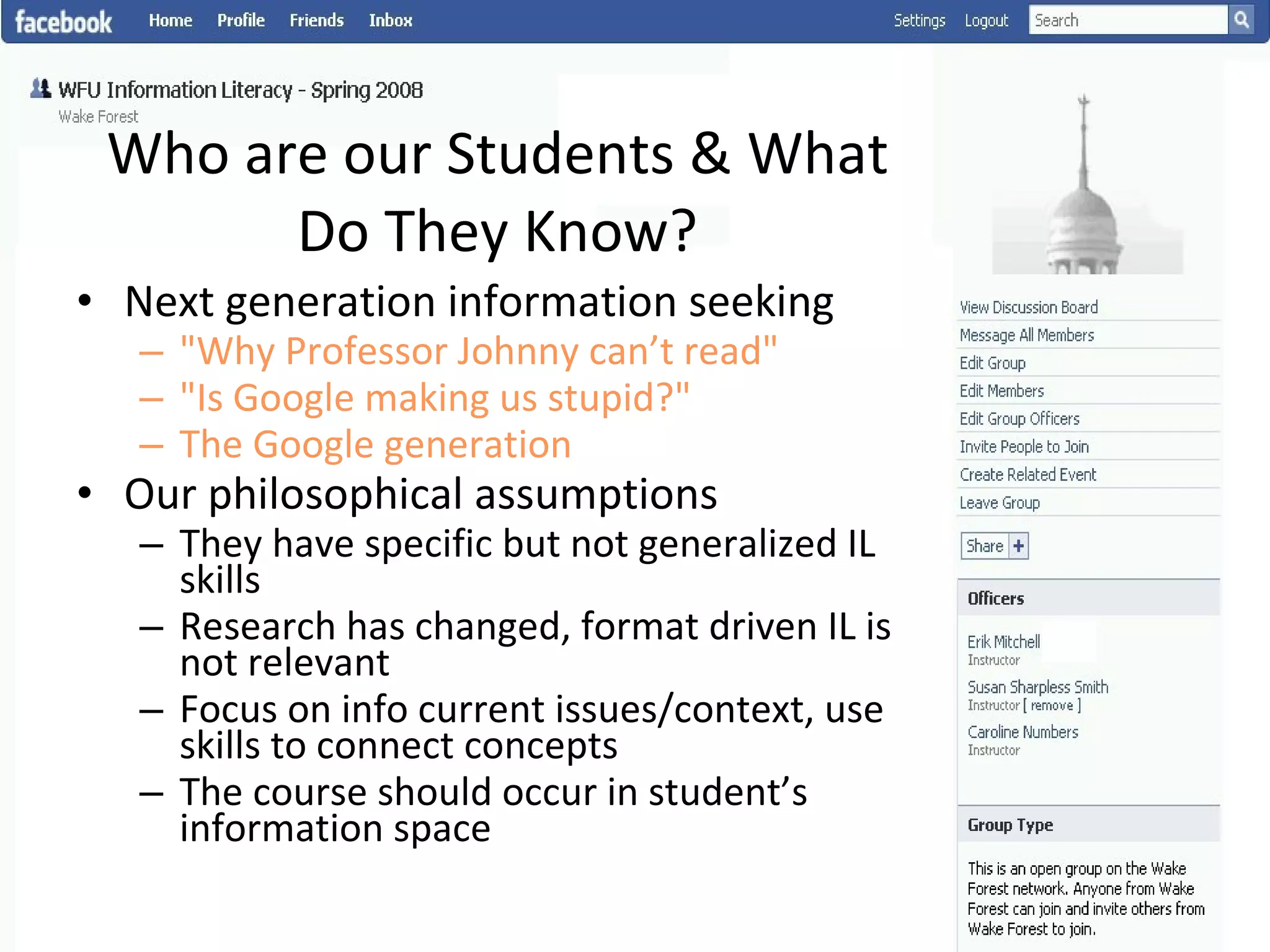
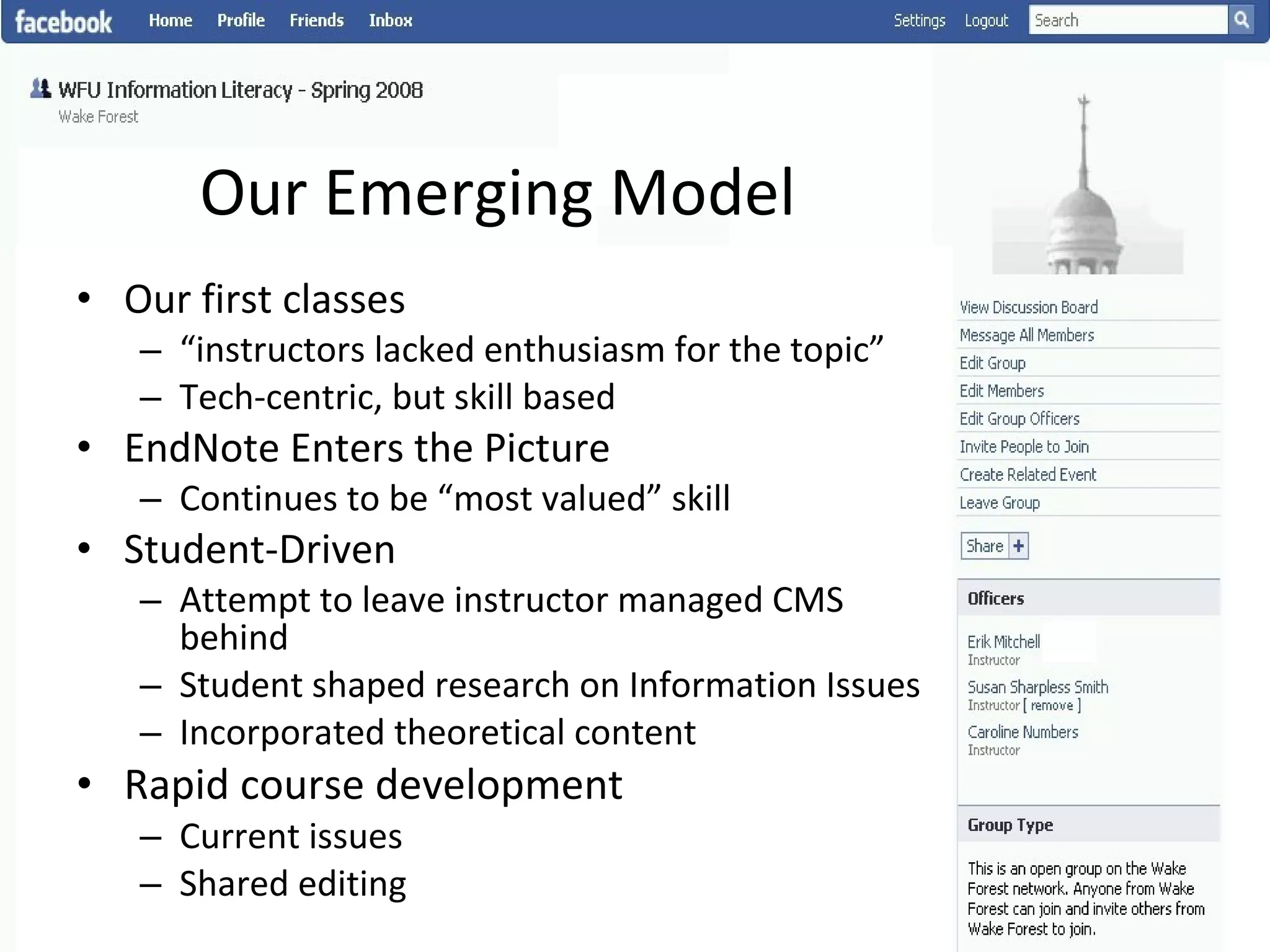
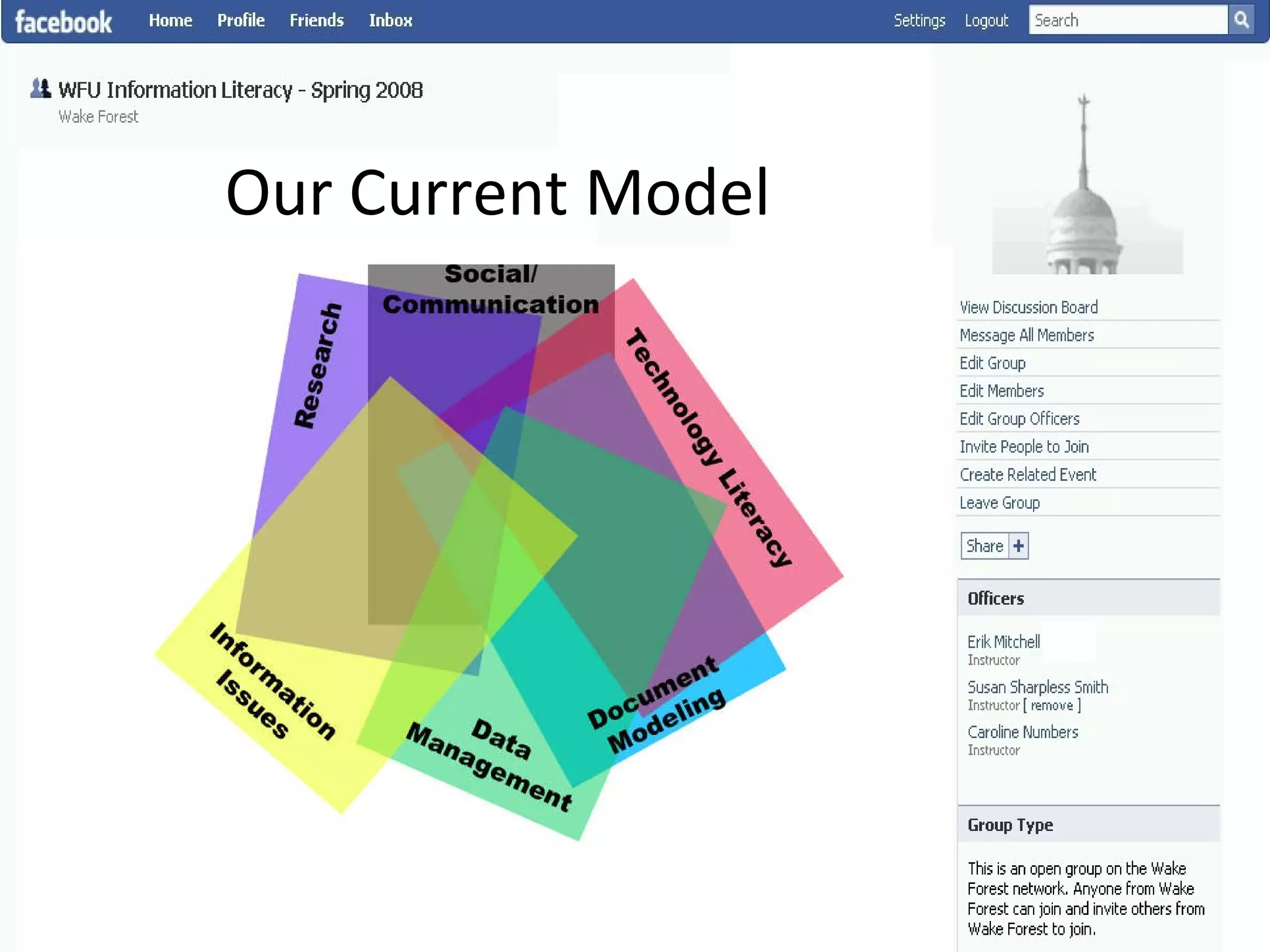
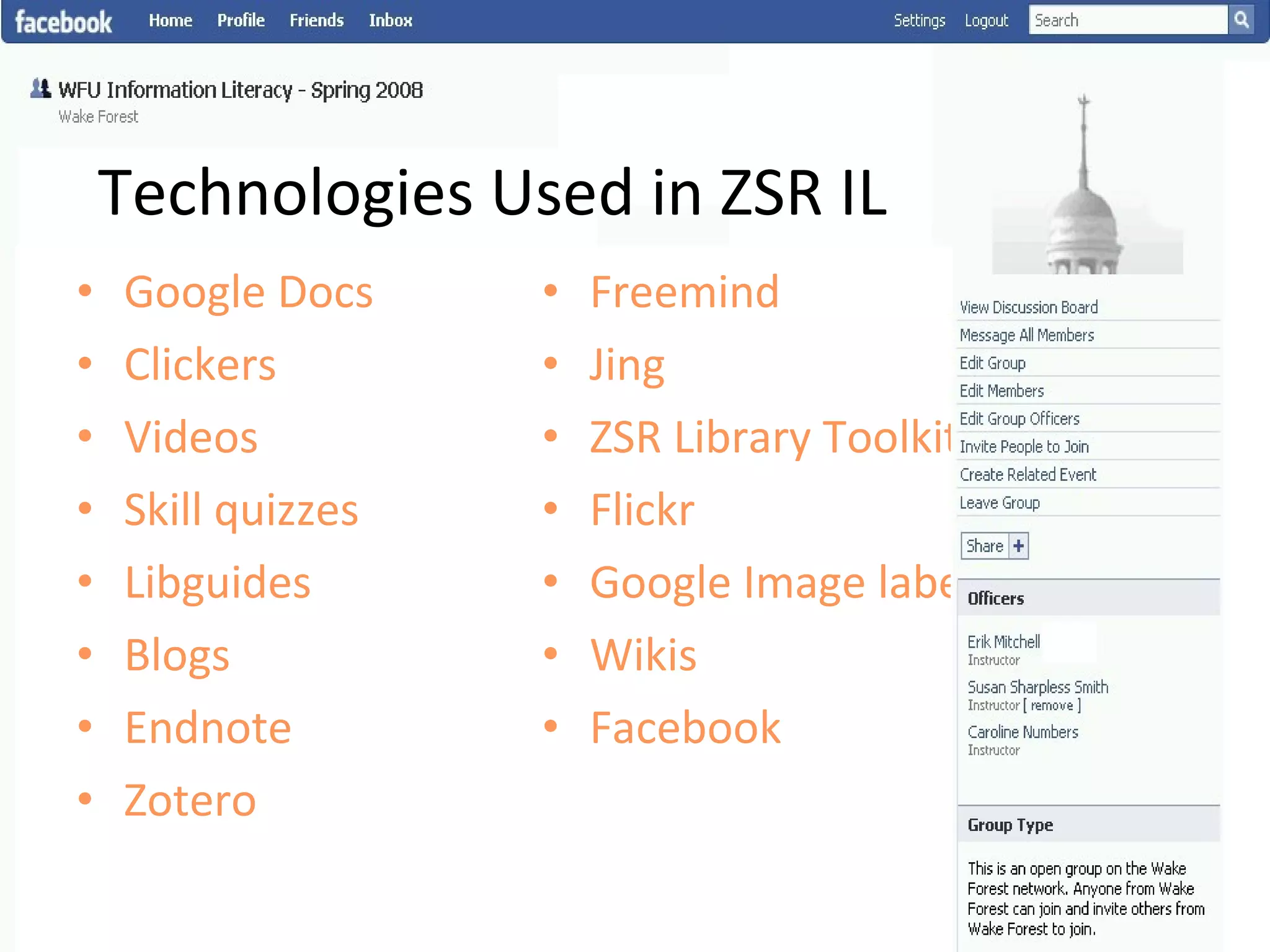
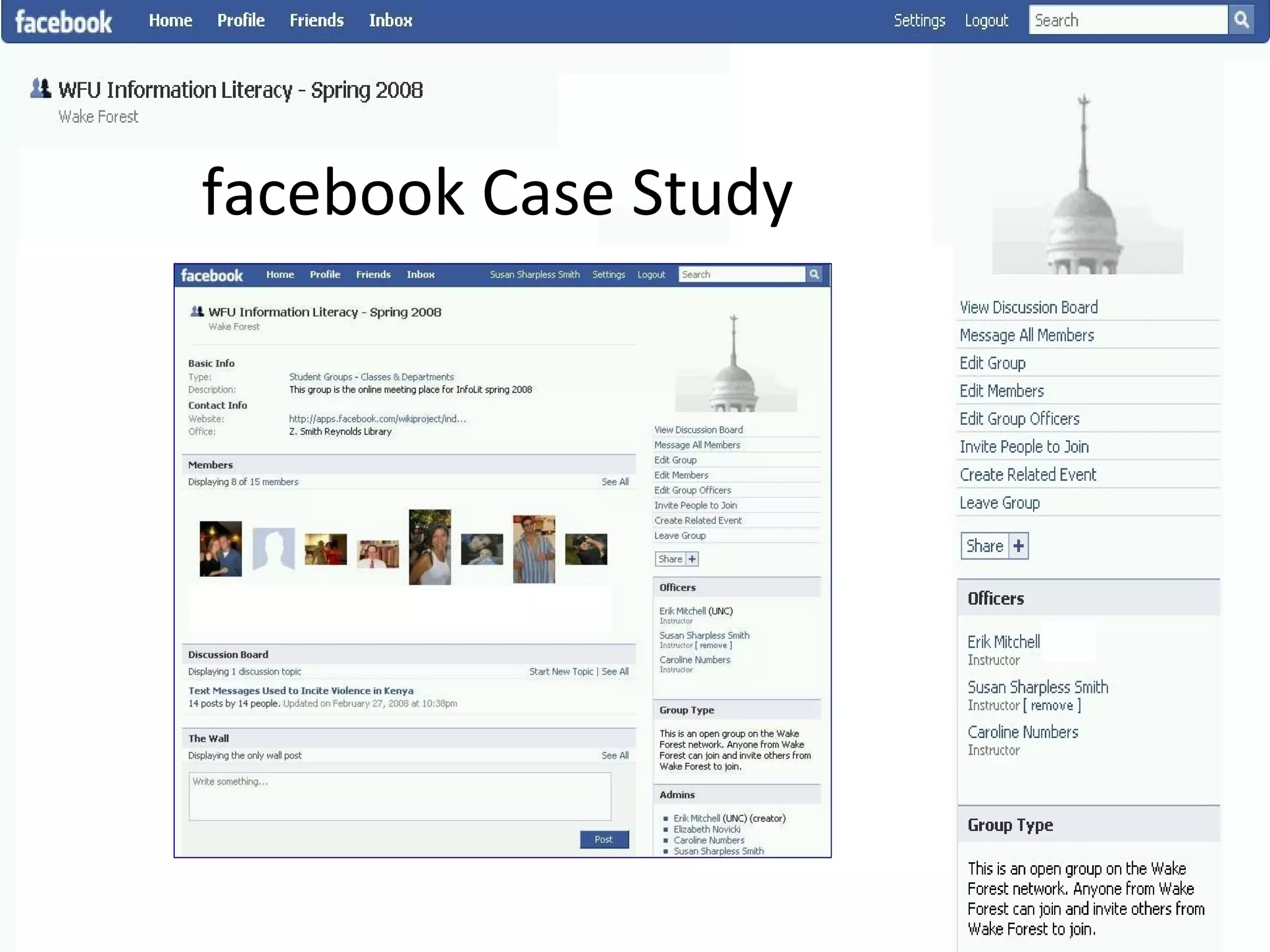
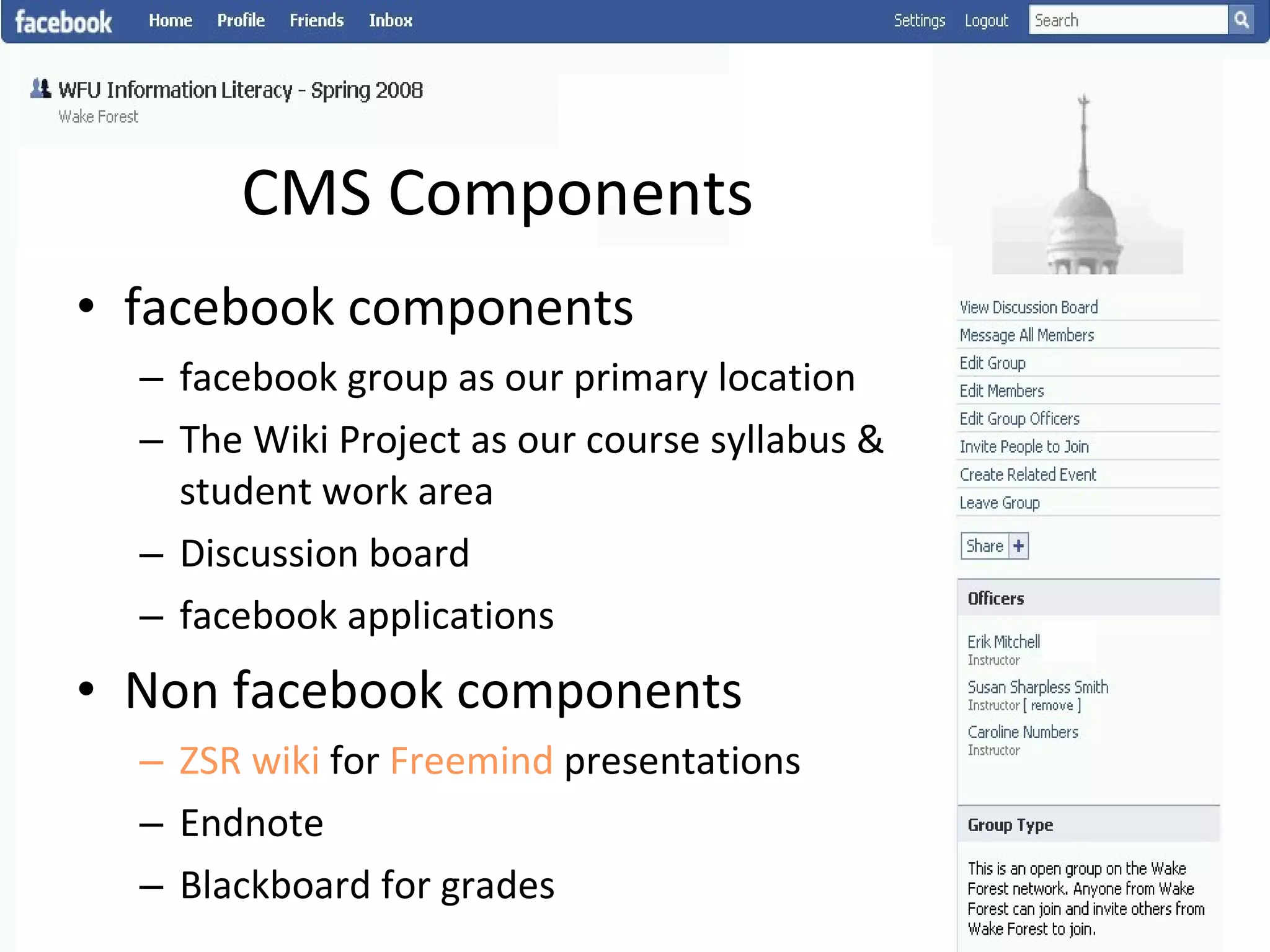
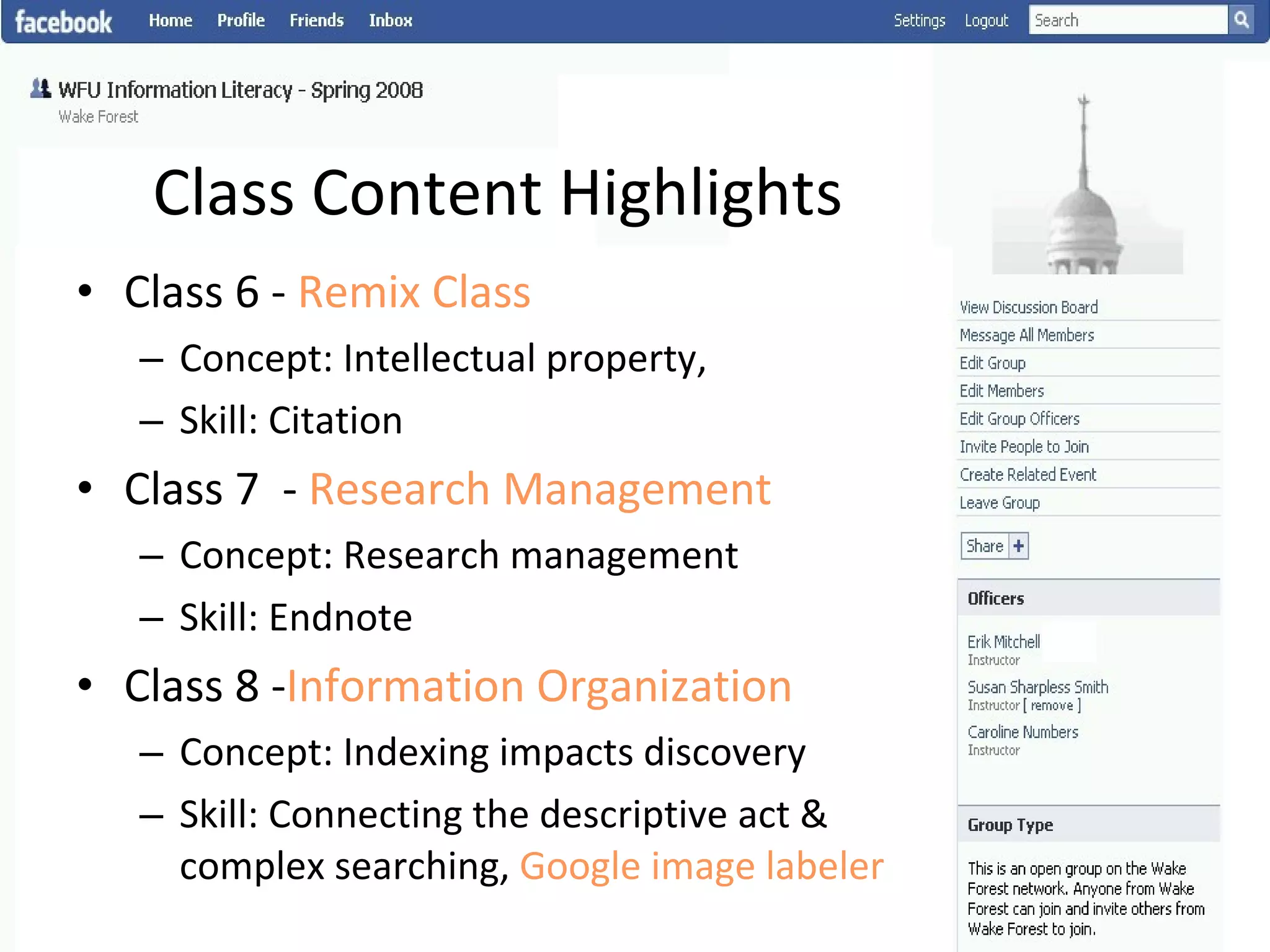
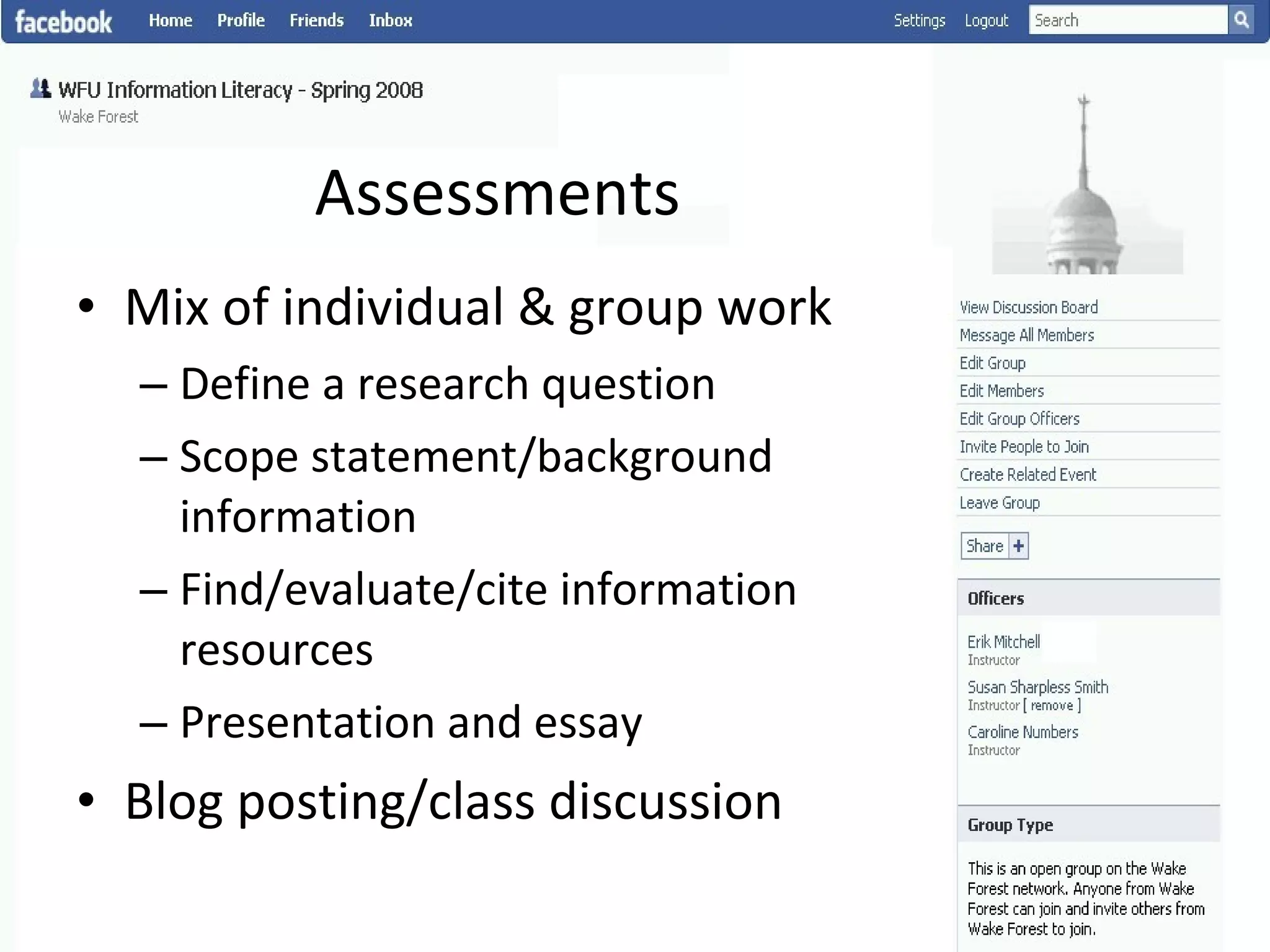
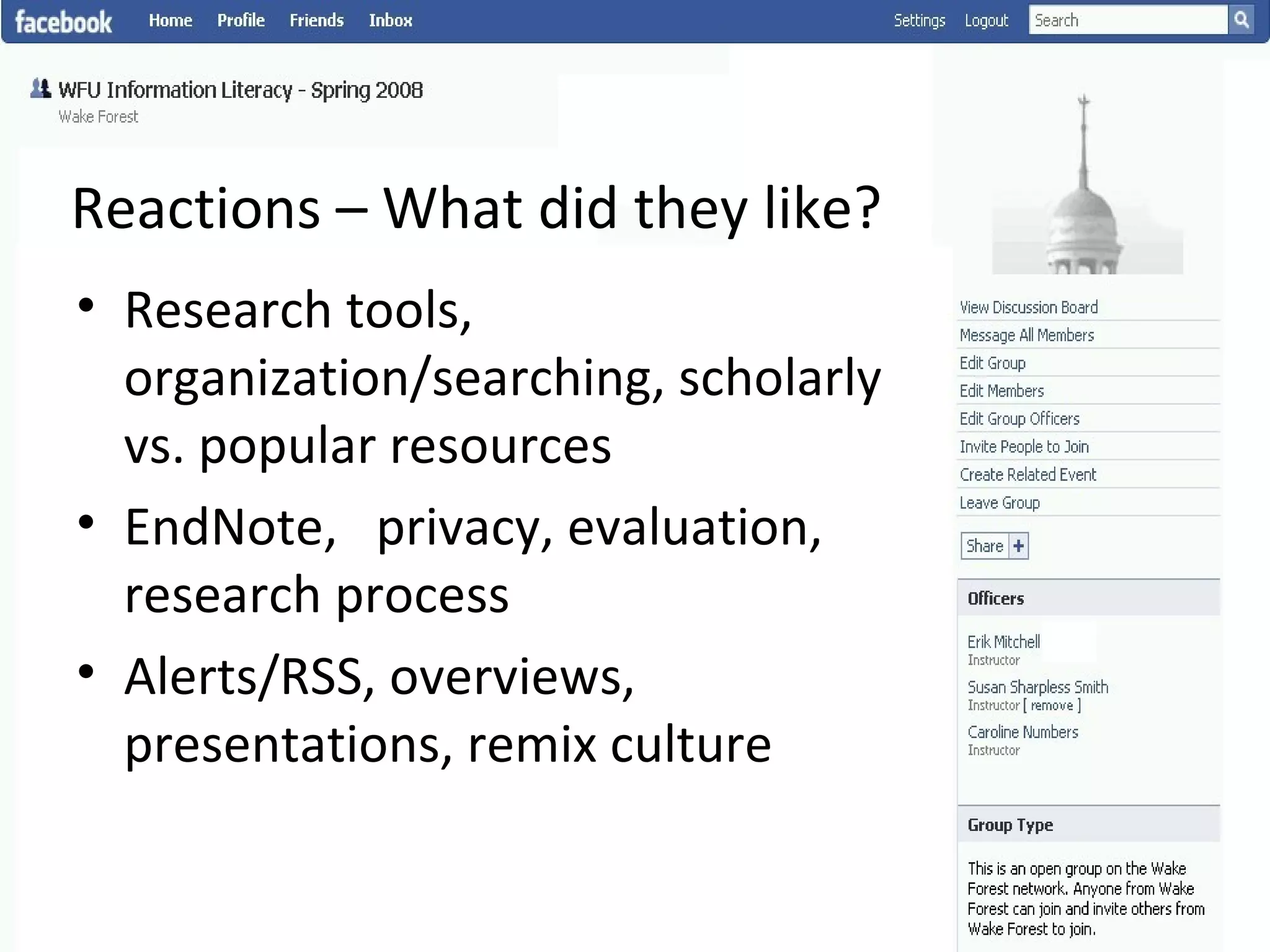
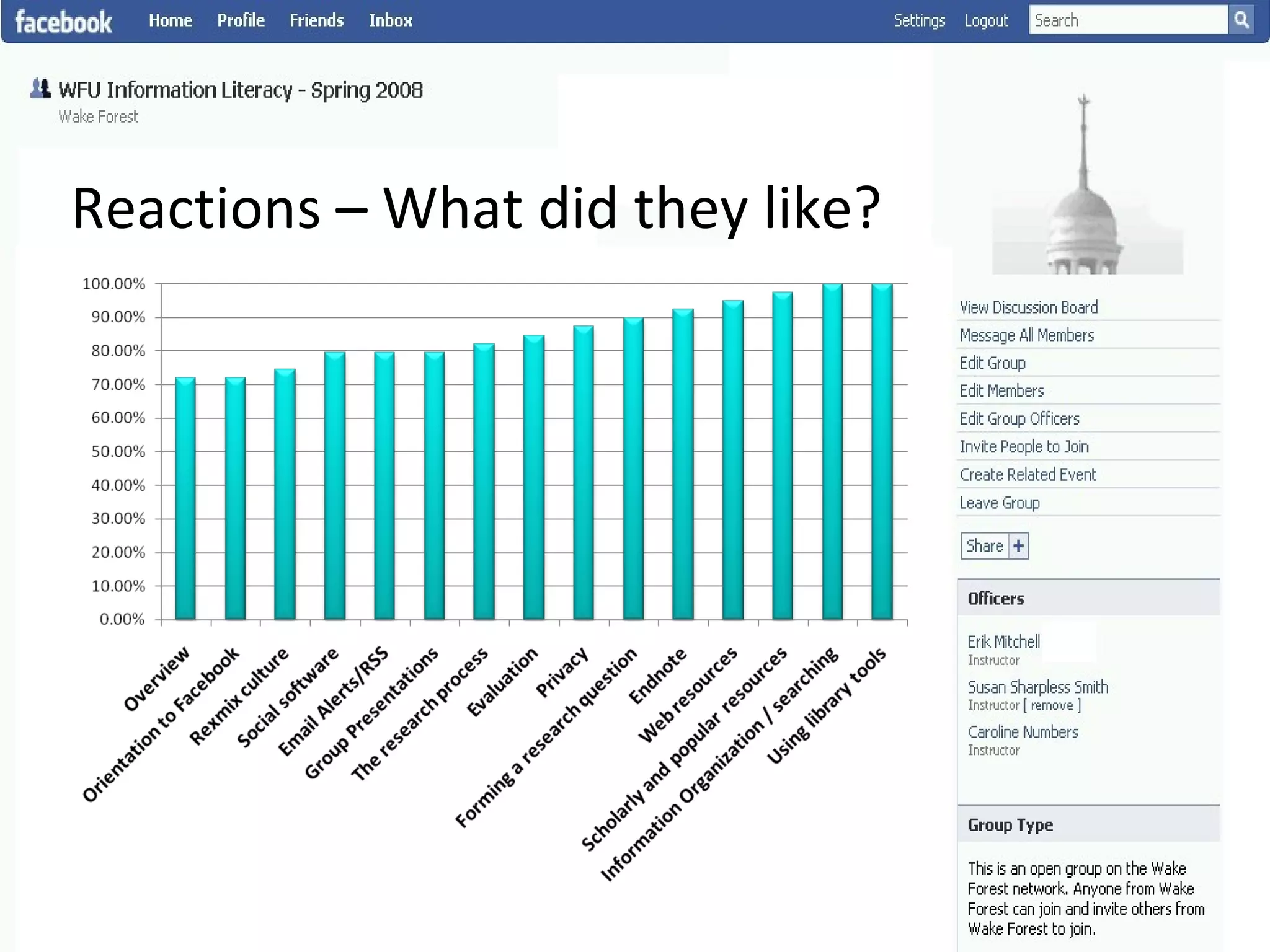
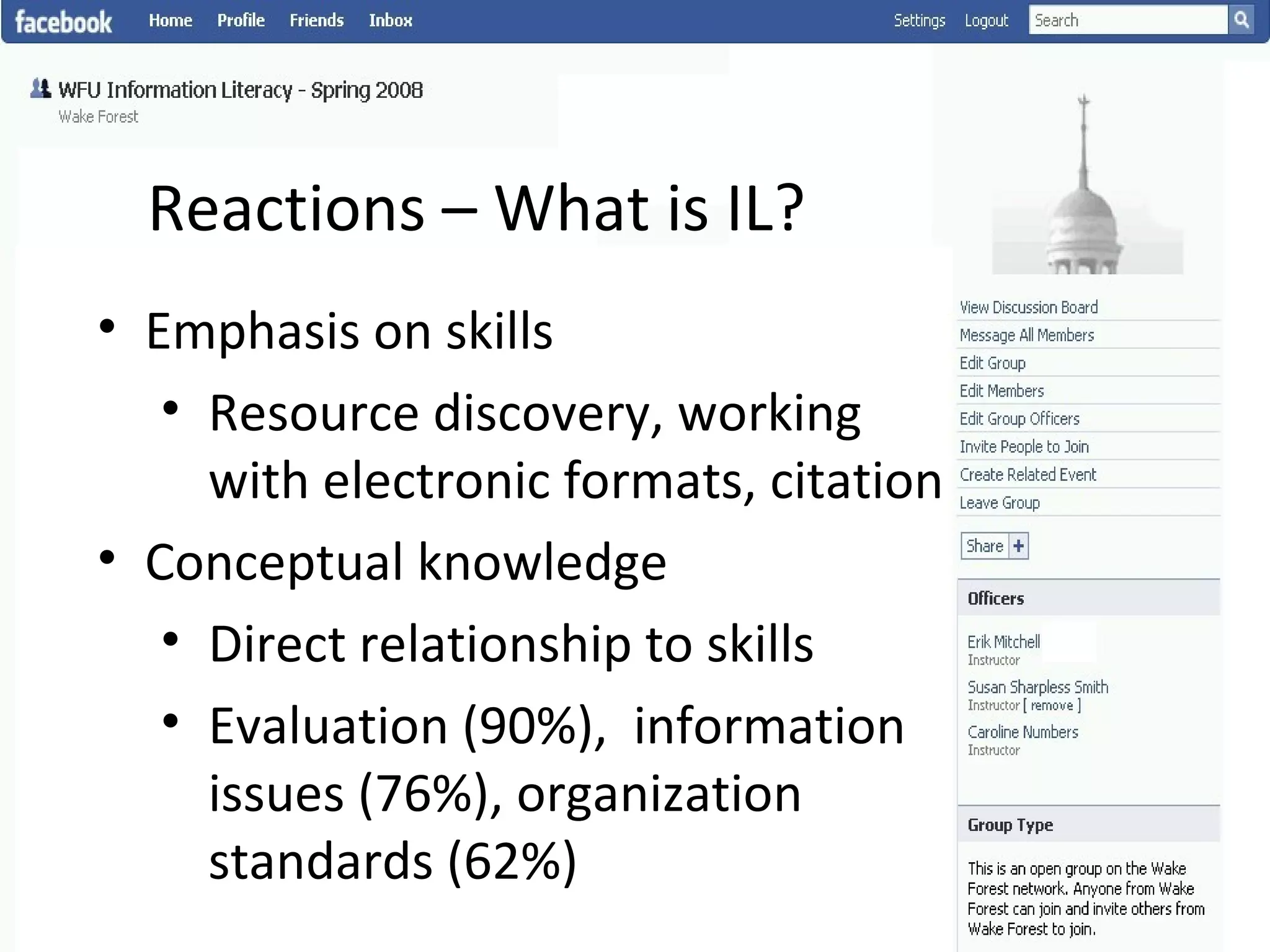
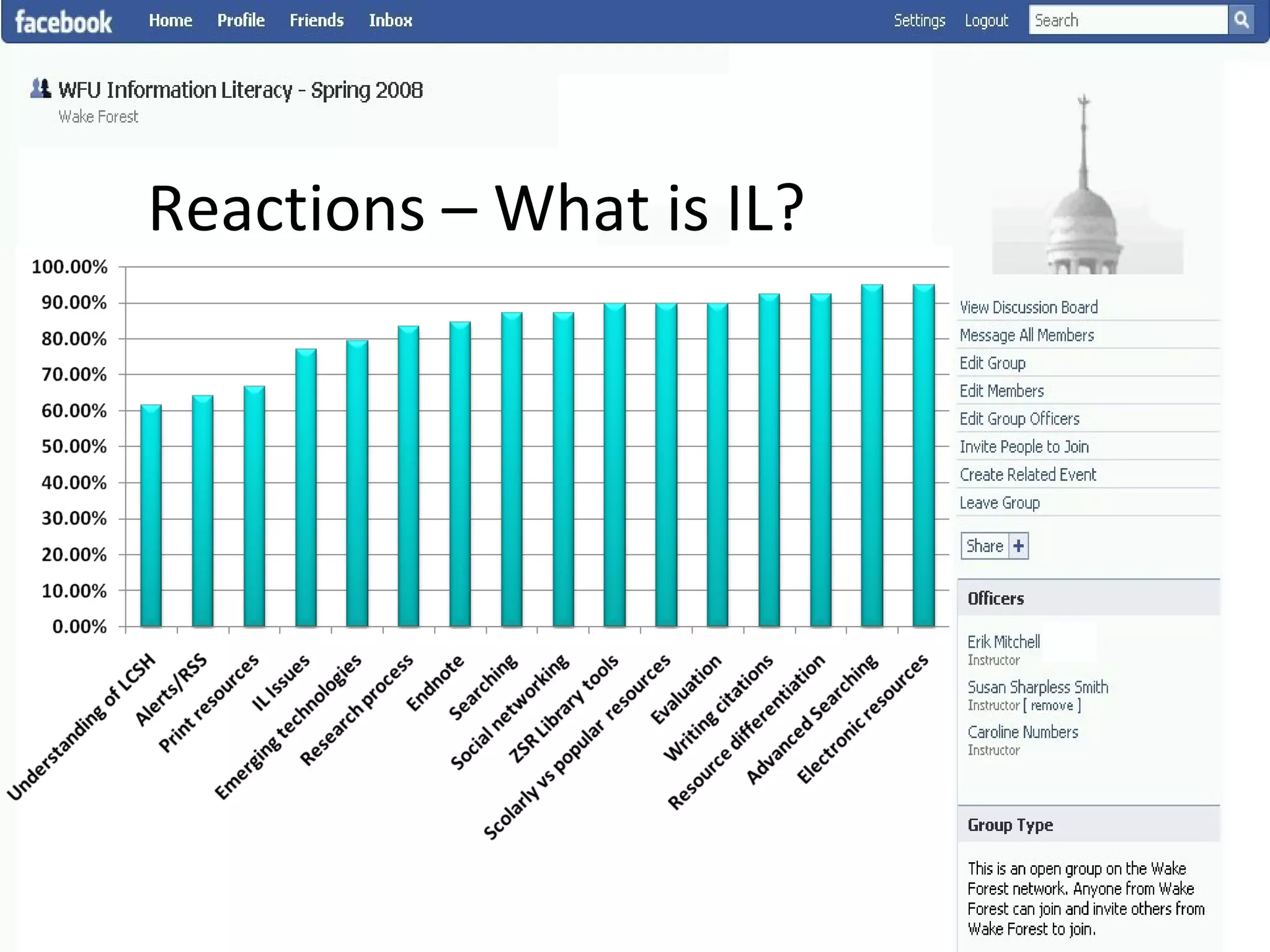
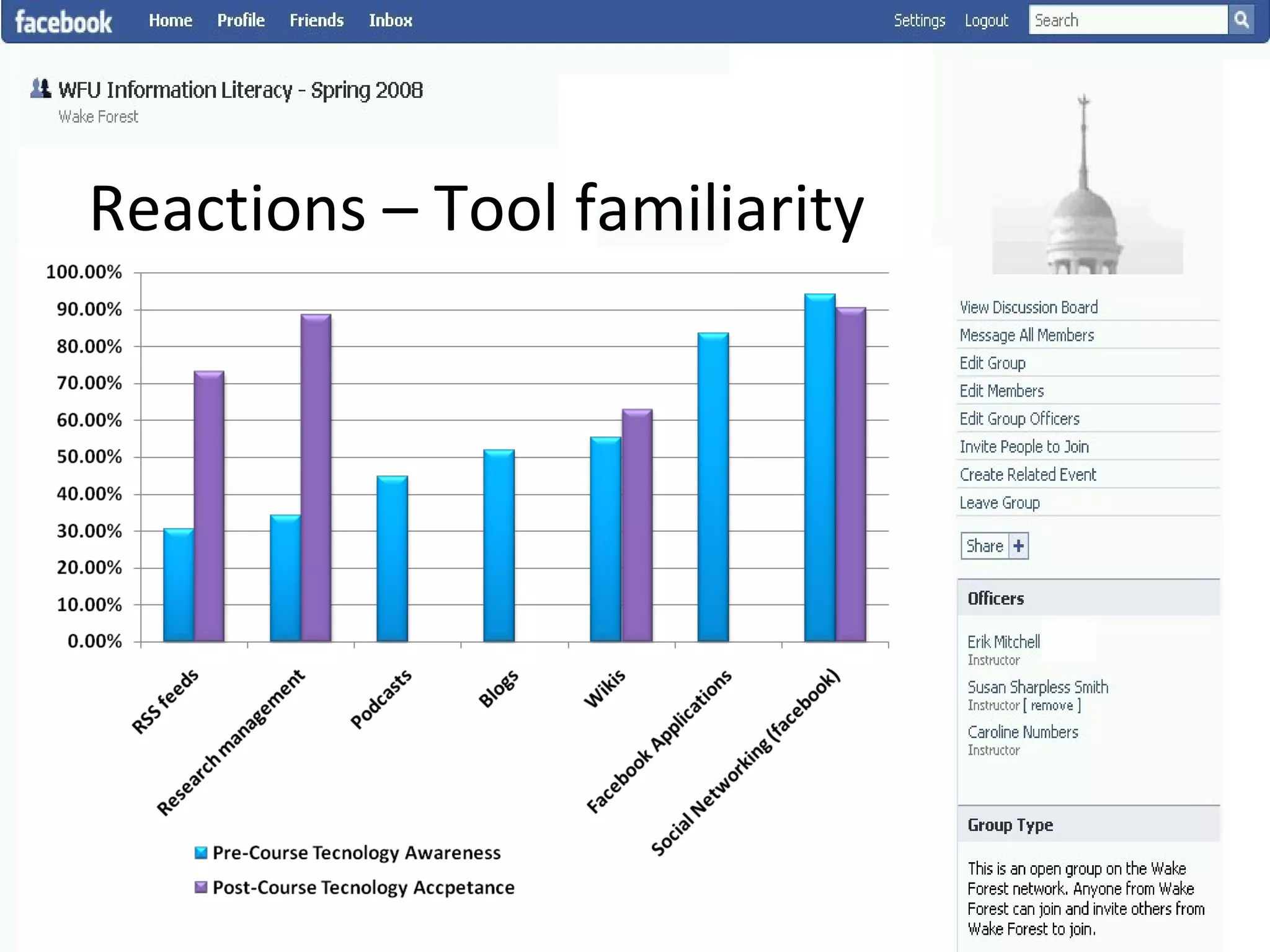
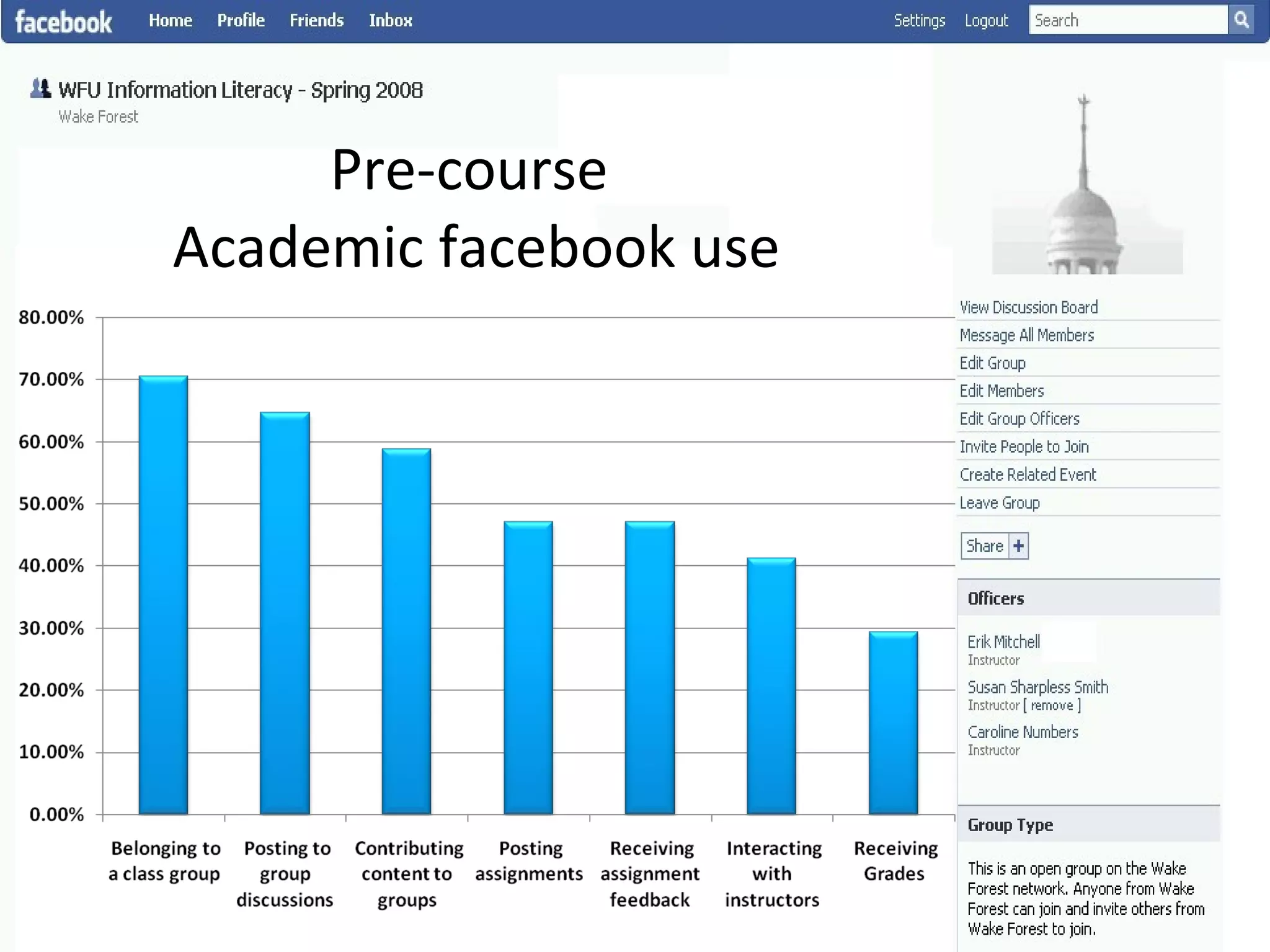
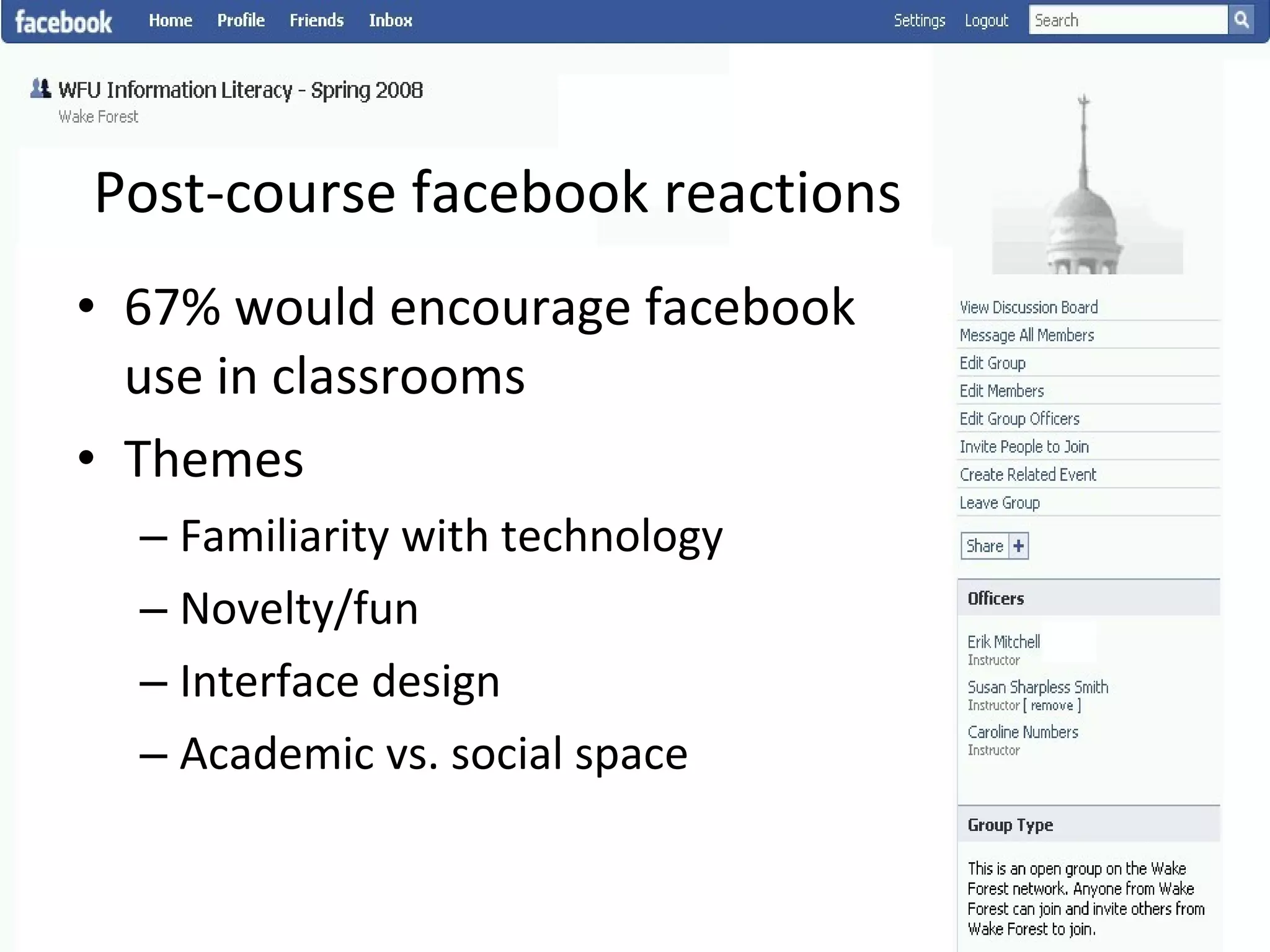
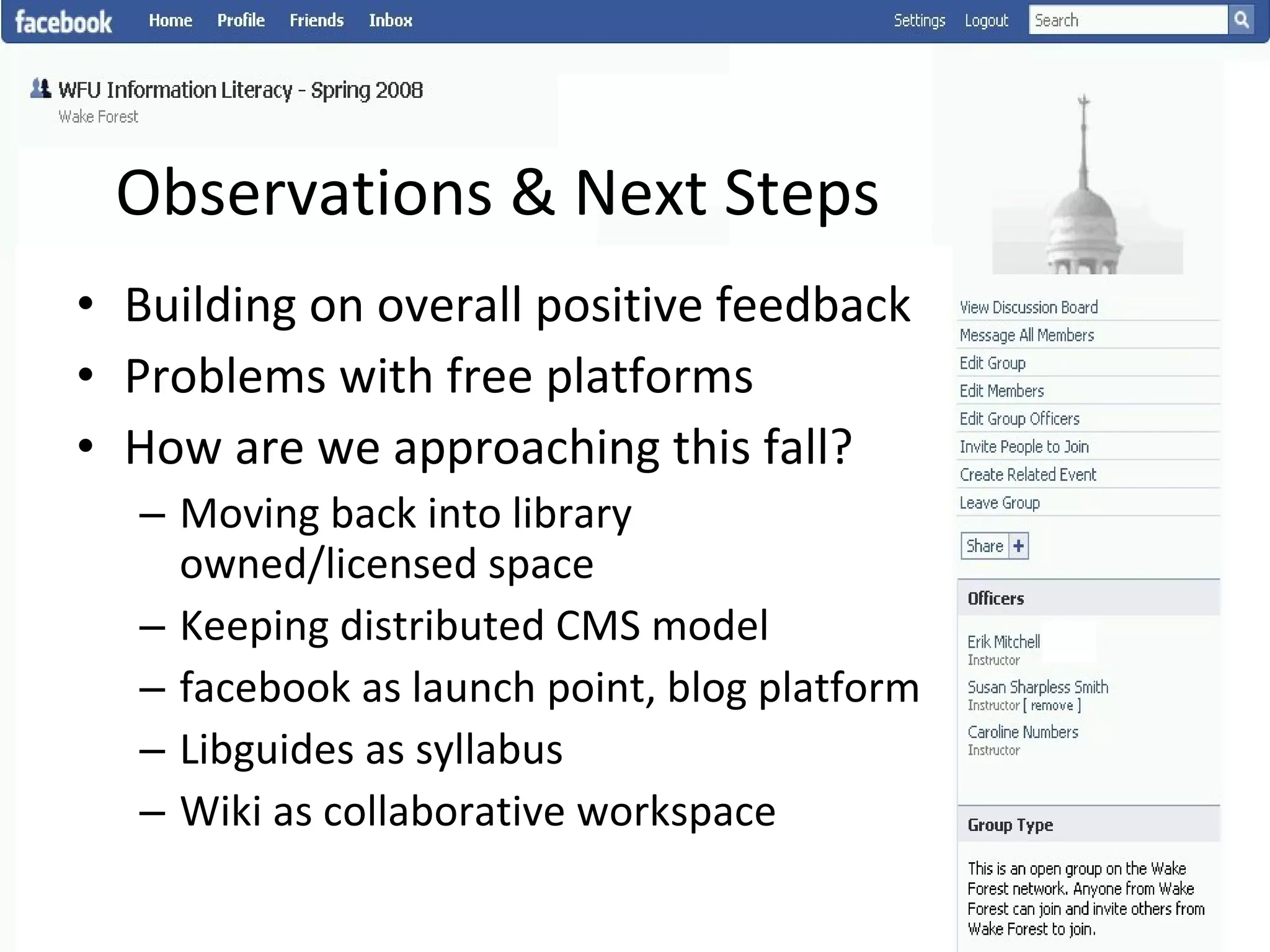
This document summarizes an information literacy course taught at Wake Forest University that used social software and platforms like Facebook, Google Docs, and wikis. It provides an overview of the university, a brief history of information literacy instruction there, and discusses theoretical models of information literacy. It then describes how the course incorporated social platforms into its model, content, and assessments. Student feedback indicated they particularly valued learning research tools and skills. The summary concludes by noting plans to build on lessons learned while addressing limitations of free platforms.
![Contact Information Erik Mitchell [email_address] Susan Smith [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/etmlita-presentation-draft5-100810153059-phpapp01/75/Federated-library-services-23-2048.jpg)