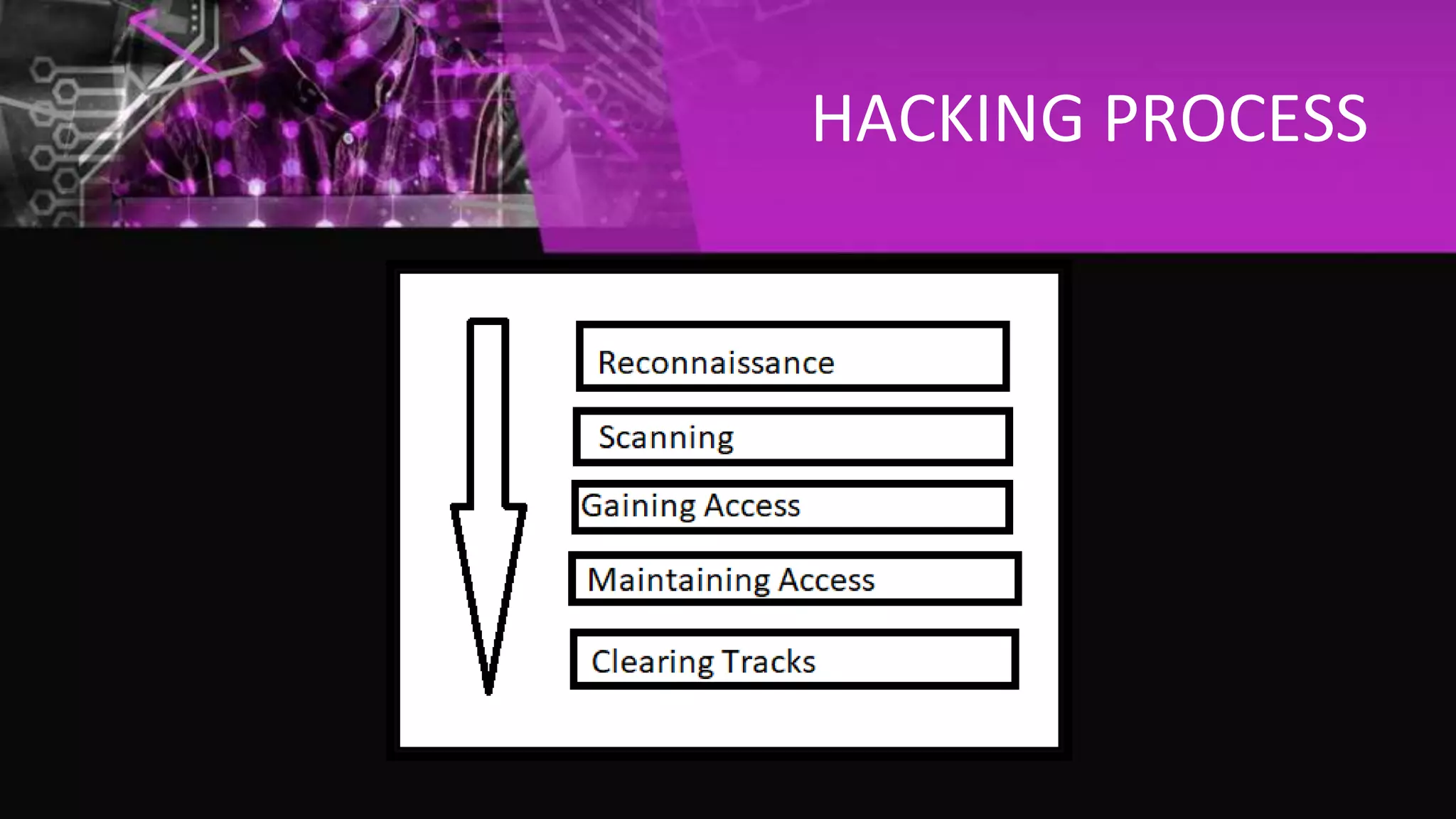
The document discusses ethical hacking. It defines an ethical hacker as someone who uses hacking tools to identify vulnerabilities in systems in order to improve security. There are three types of hackers: black-hat hackers who exploit vulnerabilities maliciously, white-hat hackers who perform security testing legally, and grey-hat hackers who can be legal or illegal depending on purpose. The hacking process involves reconnaissance, scanning, gaining access, maintaining access, and clearing tracks. Ethical hacking requires strong computer skills and patience. It is a career with growing opportunities and average salaries of around Rs. 3.5 lakhs.