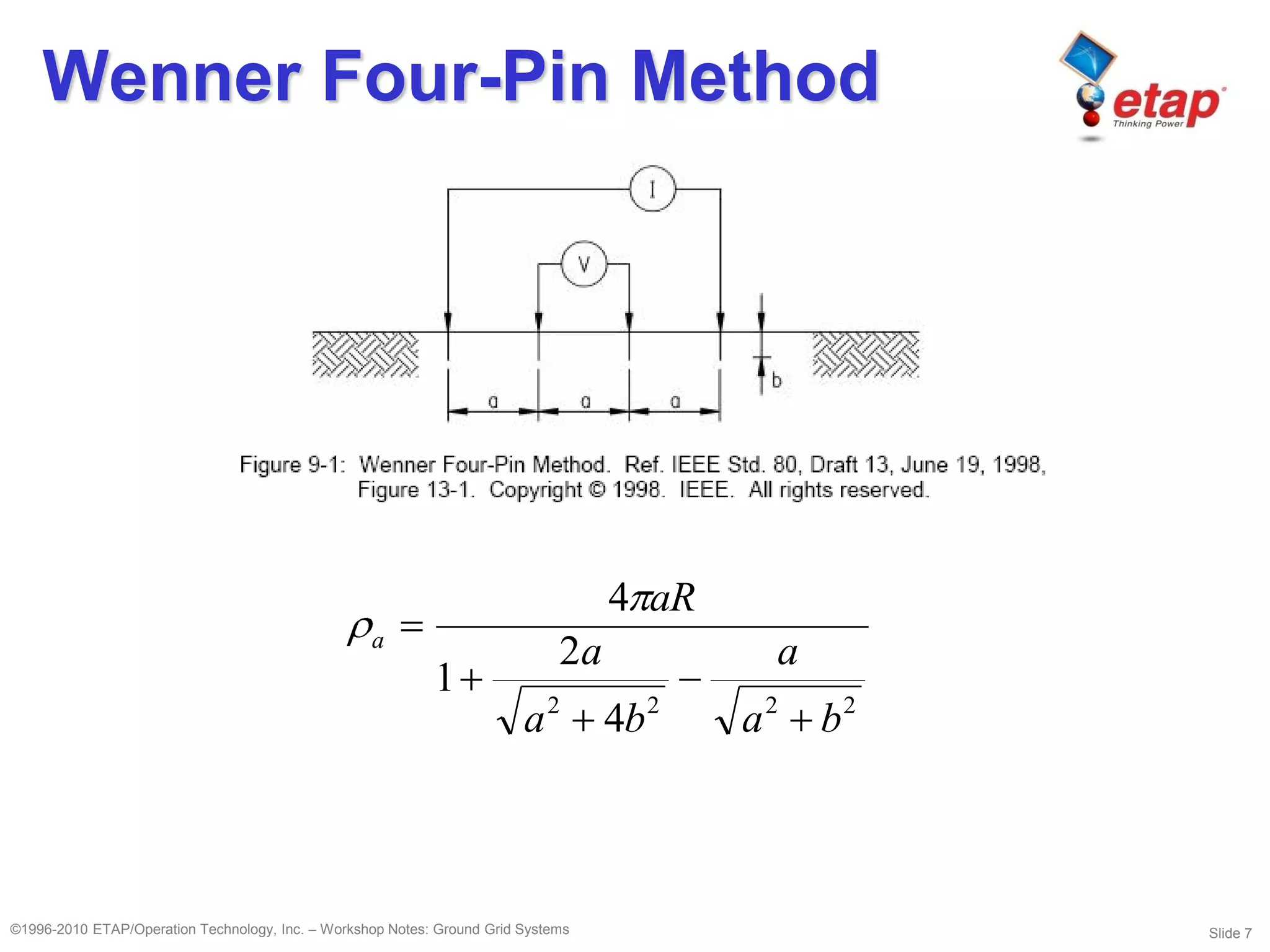
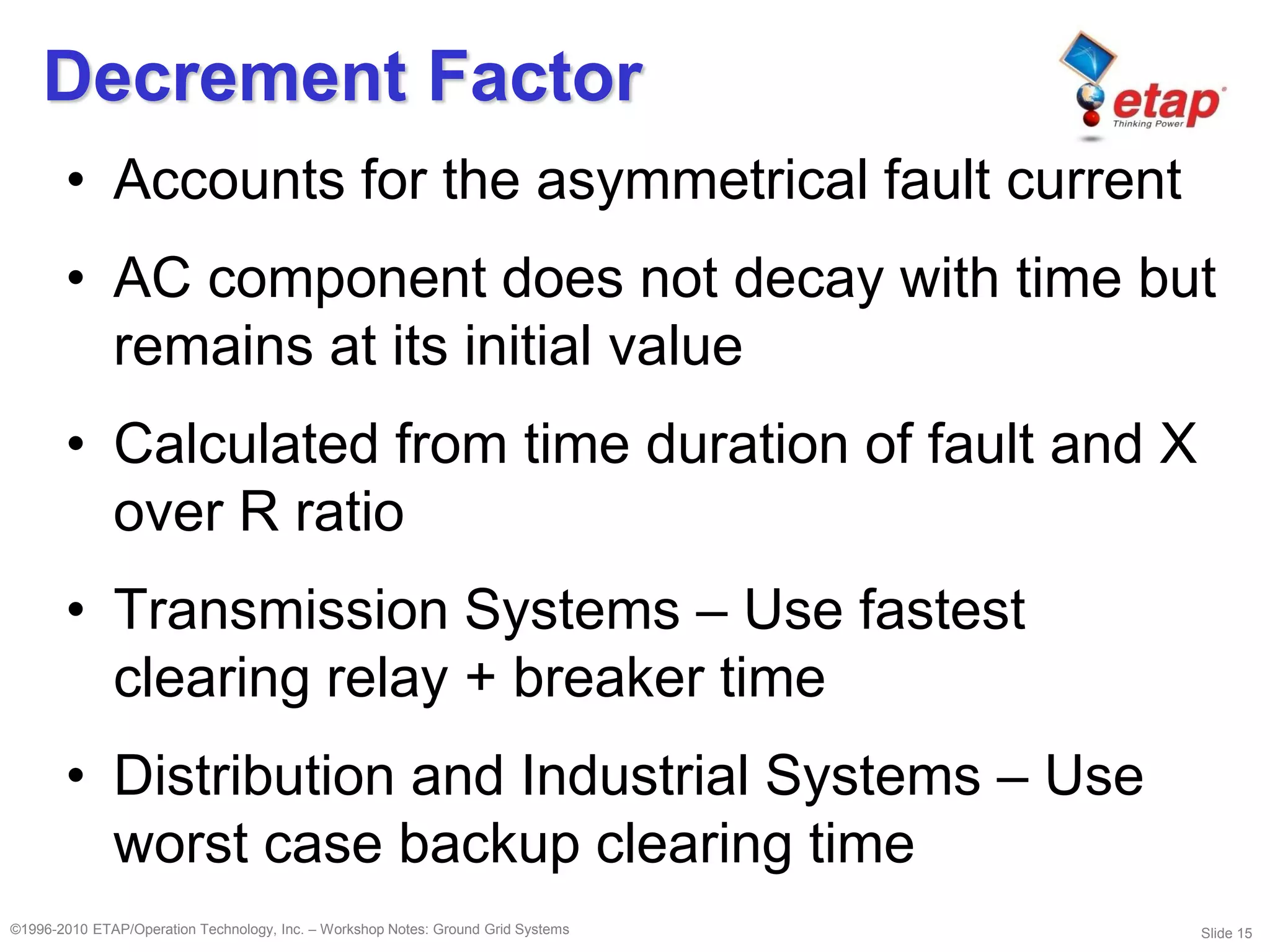
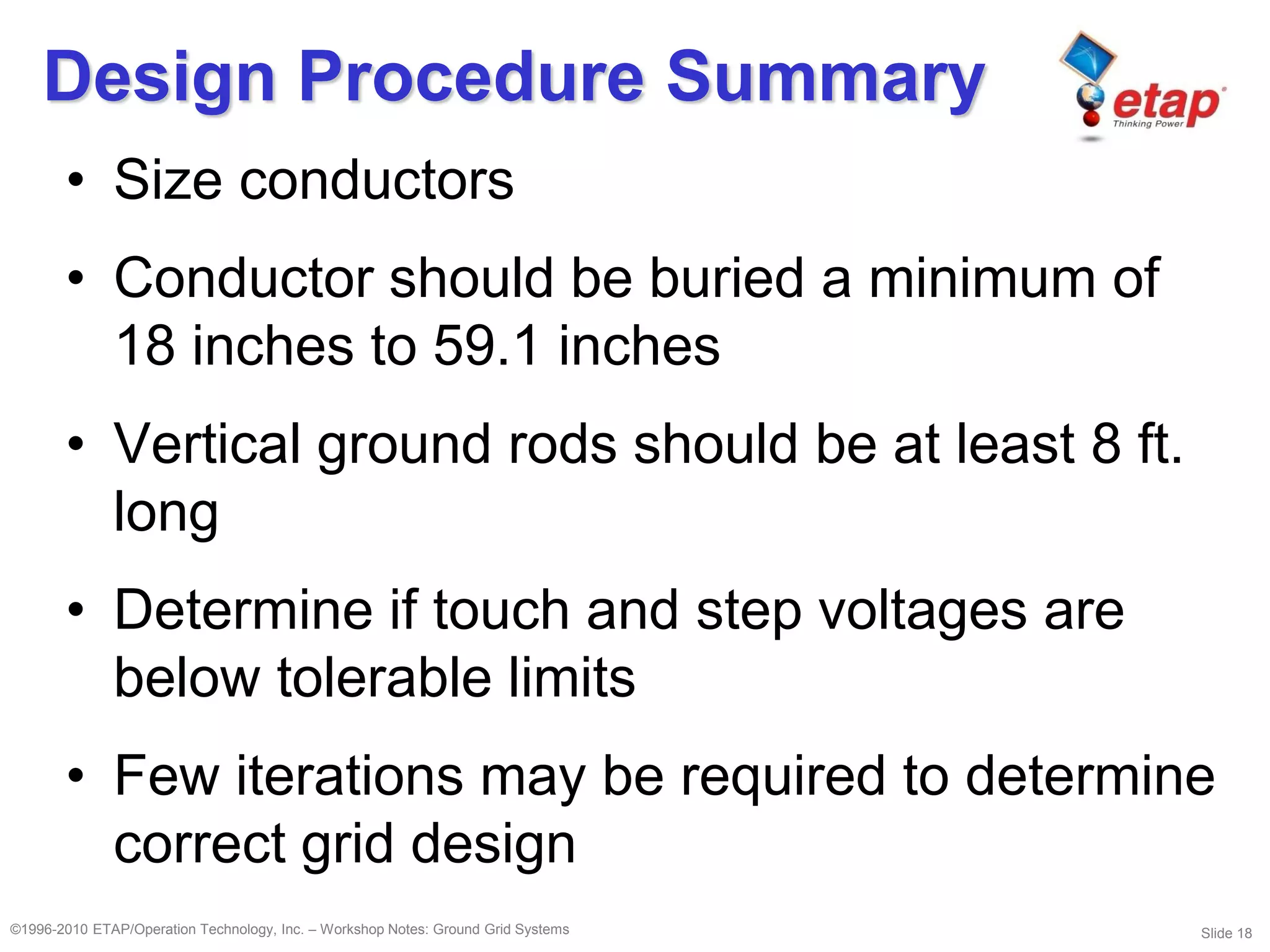
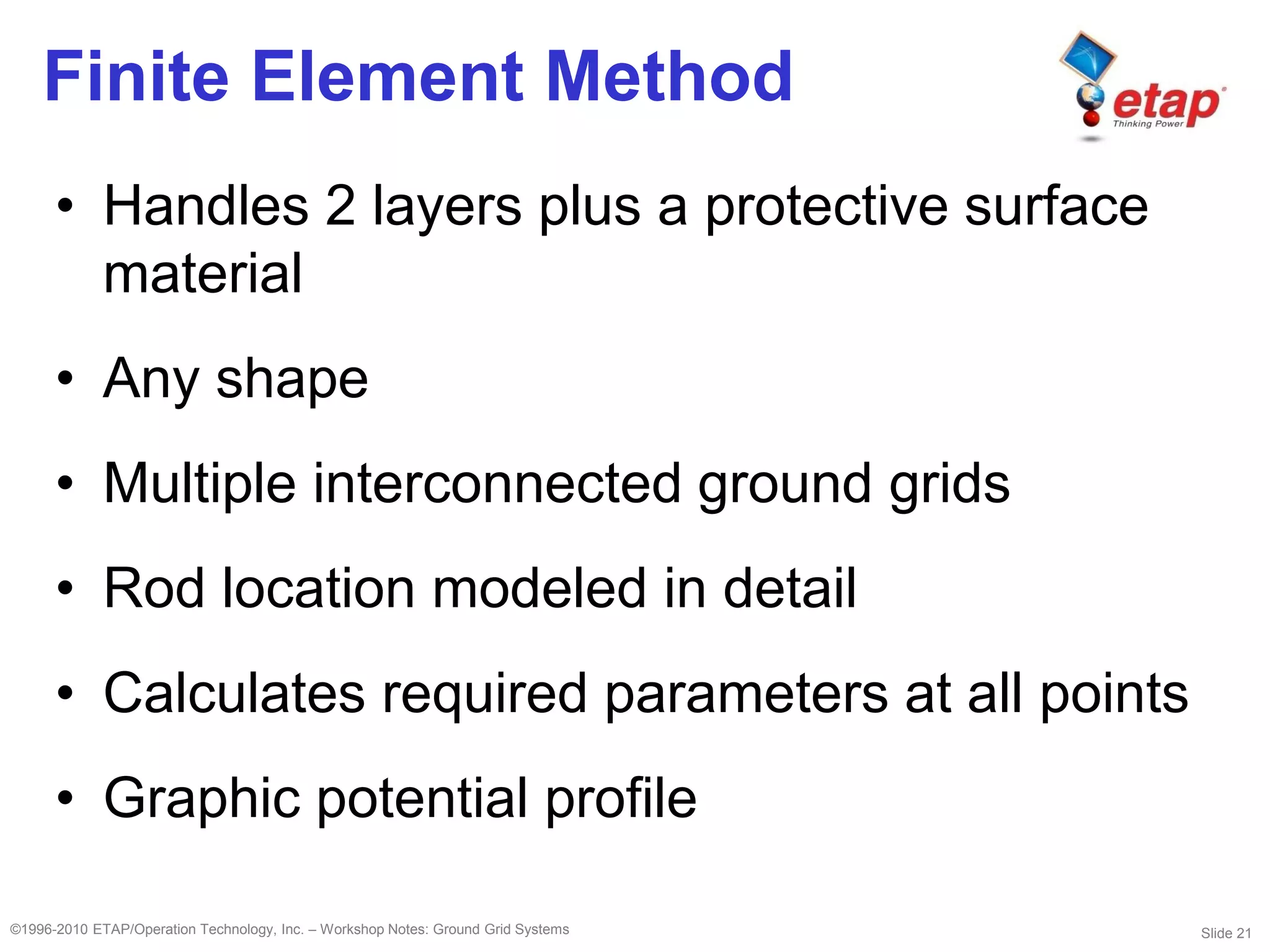
This document discusses ground grid systems used in substations. Ground grids are used to carry and dissipate currents from events like lightning strikes and faults. They help ensure human and animal safety and allow protective relays to operate properly. Designing an effective ground grid involves analyzing soil resistivity, sizing the grid area, determining fault currents, and using methods like the IEEE or finite element approaches to verify touch and step voltages are within limits. Key steps include soil testing, sizing conductors, placing rods, and iterating the design to meet safety criteria.