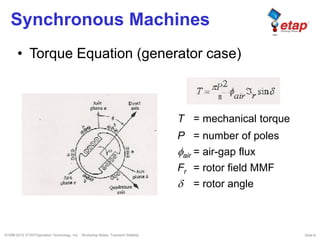
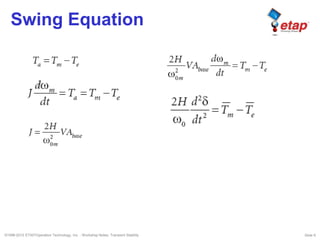
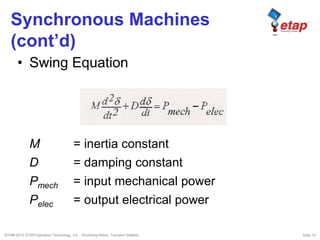
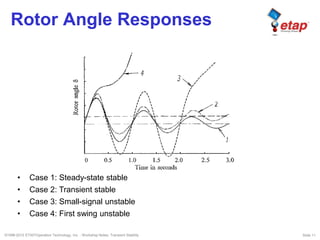
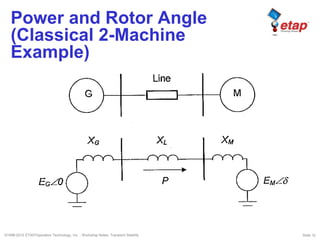
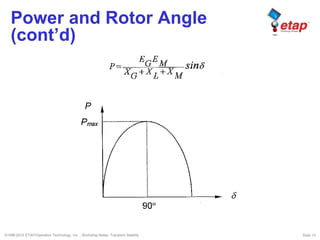
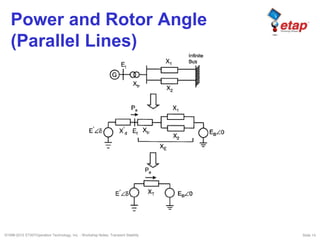
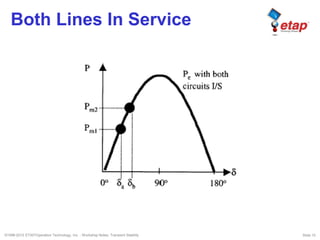
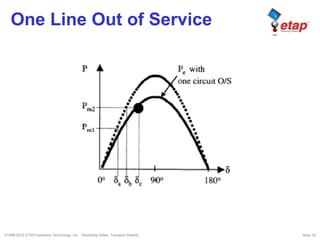
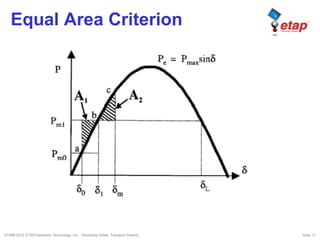
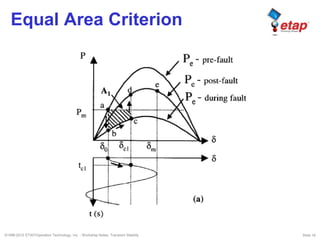
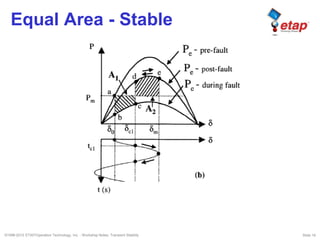
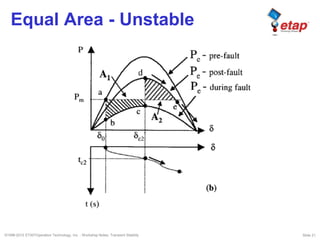
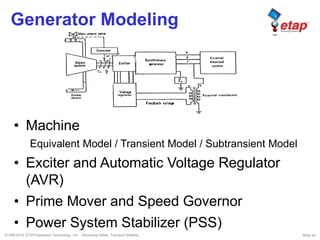
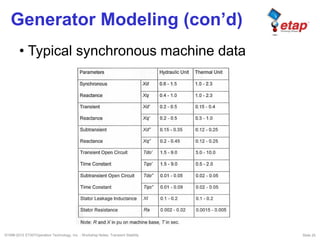
The document discusses transient stability in power systems. Transient stability refers to the ability of synchronous machines to remain in synchronism after a disturbance like a fault. It is impacted by factors like generator loading, inertia, reactance, and fault clearing time. Loss of transient stability can cause outages. Solutions include improving system design to increase synchronizing power, reducing reactance, using power system stabilizers, and implementing fast protection schemes like load shedding.