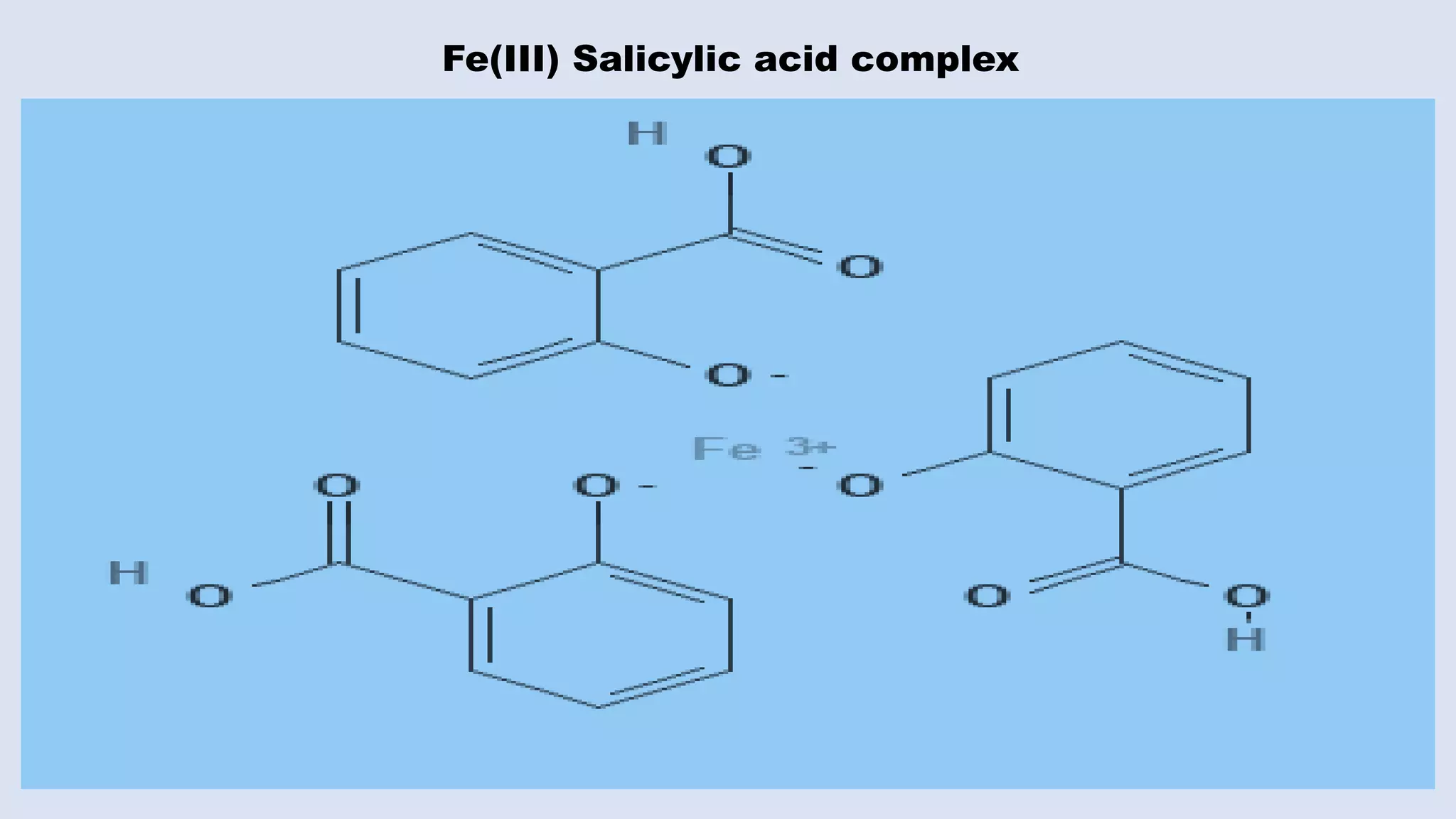
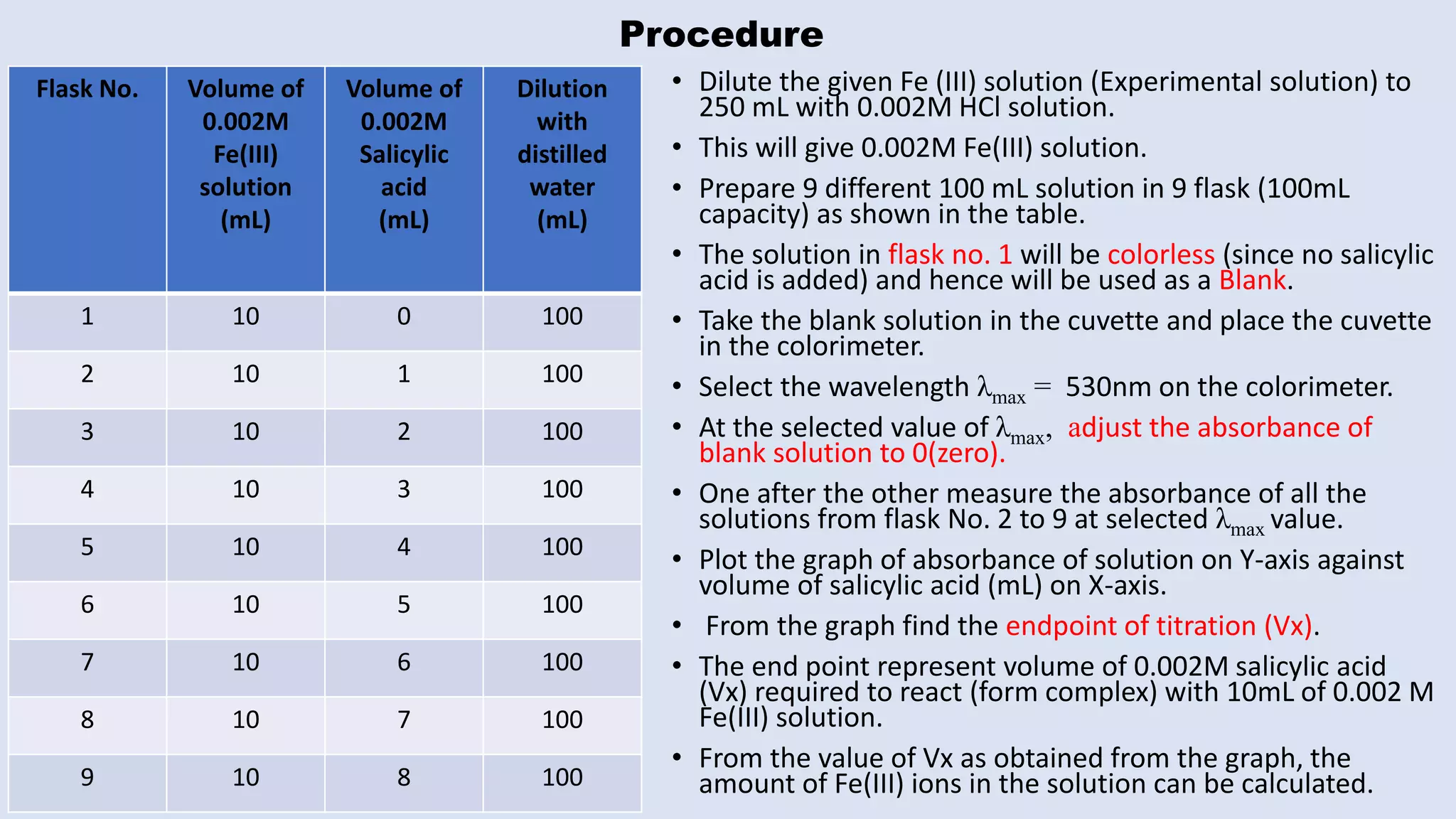
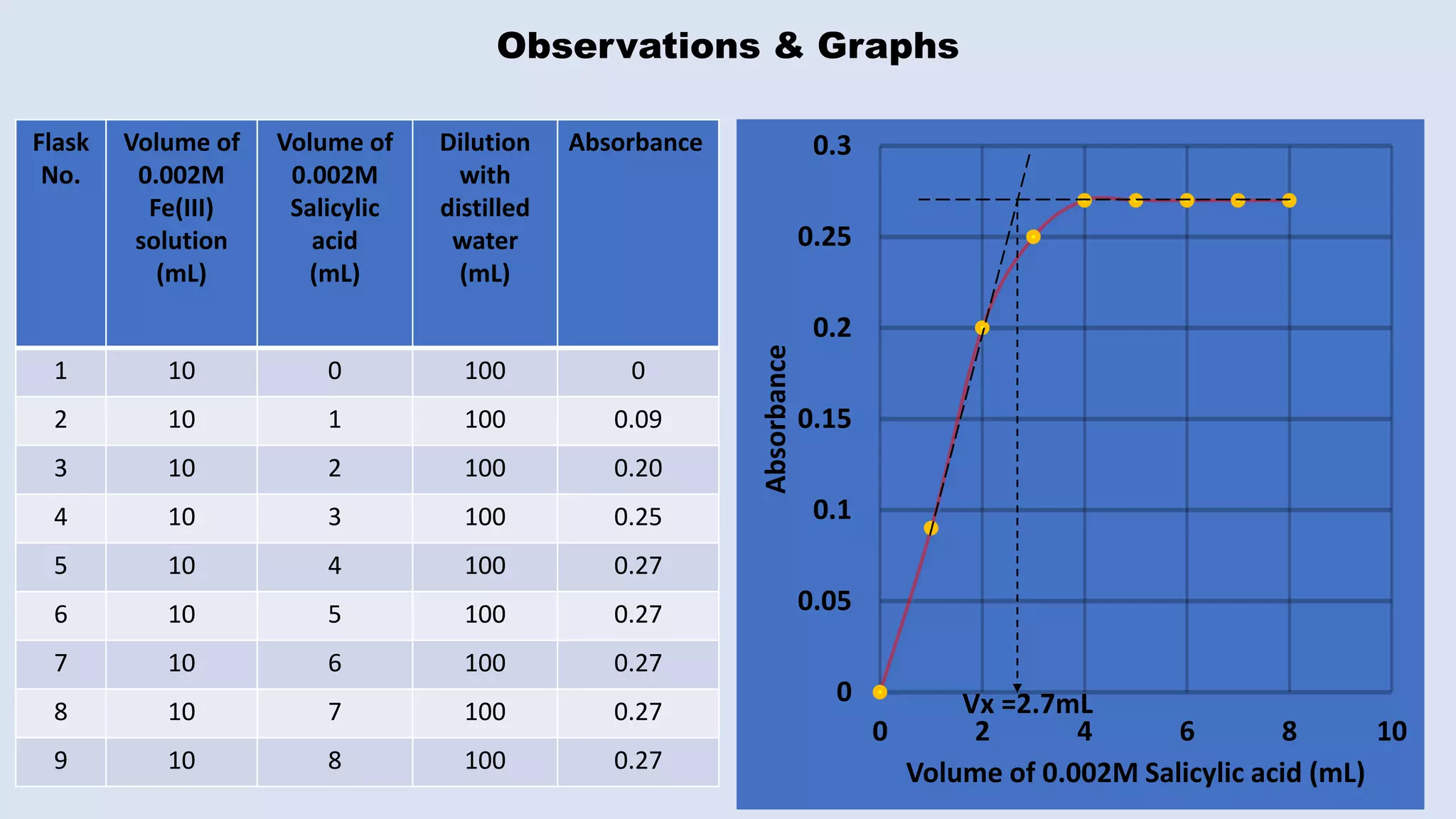
The document outlines the method for estimating Fe(III) in a complex formed with salicylic acid using colorimetry. It explains the principles of the colorimeter, including absorbance measurement and the creation of a calibration graph to determine unknown concentrations. The experiment involves static titration, where varying volumes of salicylic acid are added to a fixed volume of Fe(III) solution, and the optimal salicylic acid volume for color change is used to calculate the amount of Fe(III).