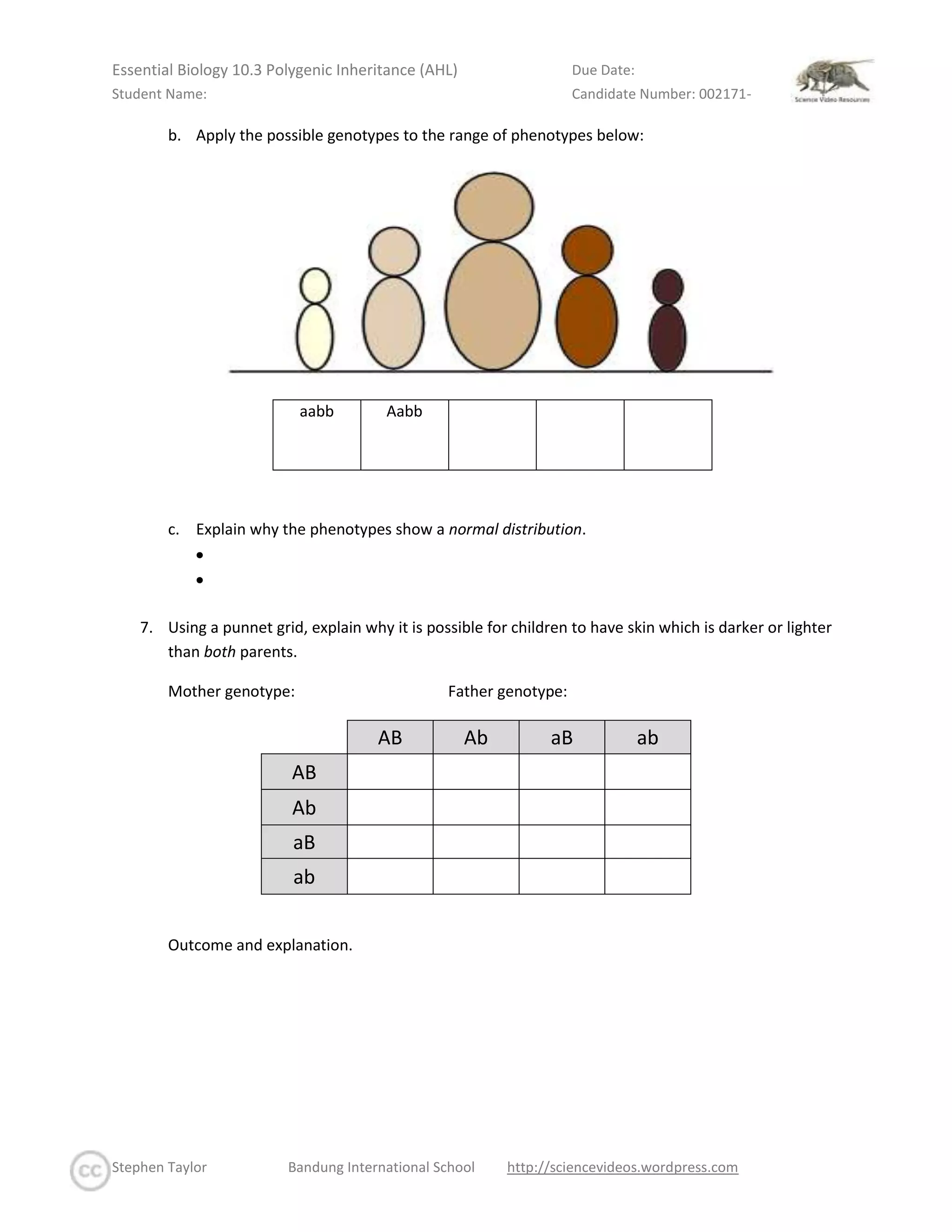
The document provides instructions for students to complete for a biology class. It highlights terms in different colors that correspond to the class objectives that need to be completed before, during, and after class. It also provides several genetics problems involving polygenic inheritance, multiple alleles, and calculating possible genotypes and phenotypes. Sources are to be cited using the CSE citation method. A self-assessment rubric is to be completed before submitting work to the online platform.