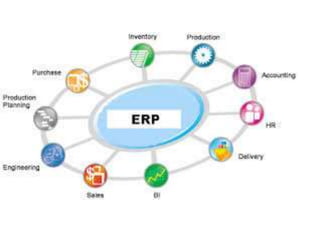
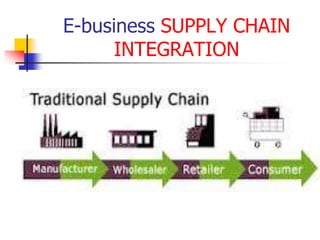
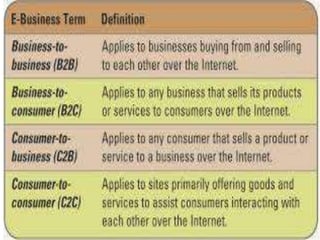
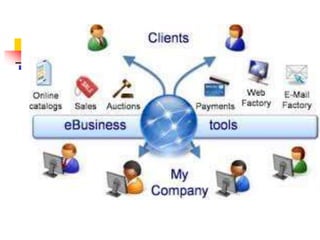
This document discusses how ERP systems and e-business are integrated. It states that e-business has changed the definition of enterprise systems by pushing ERP from internal processes to the network edge and extending ERP capabilities to enable B2B and B2C transactions. The document outlines how e-business focuses on efficiently integrating external, cross-enterprise processes and opens doors to new strategic opportunities by making ERP systems more outward facing and transparent. It provides examples of how e-business integrates supply chain processes and the technologies involved.