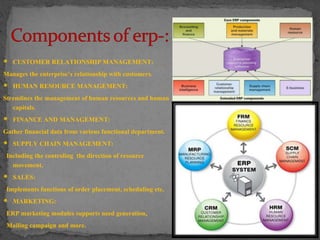
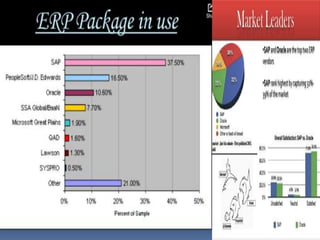
This document discusses enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. It describes ERP as a business management software that integrates various applications to manage key business functions. The document outlines the evolution of ERP from inventory control systems in the 1960s to modern ERP solutions that integrate all enterprise activities. It also discusses the components, implementation, vendors, benefits and challenges of implementing ERP systems.