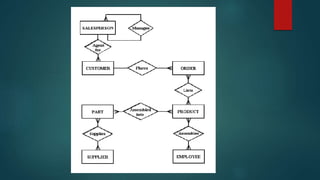
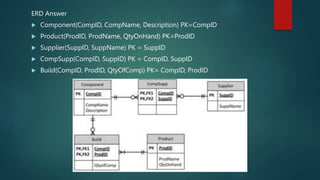
The document describes an entity relationship diagram (ERD) for tracking product and component information for a manufacturing company. It lists the key entities as products, components, suppliers, and their attributes and relationships. Products are made up of multiple components, each component can have one or more suppliers, and the ERD shows the one-to-many relationships between these entities.