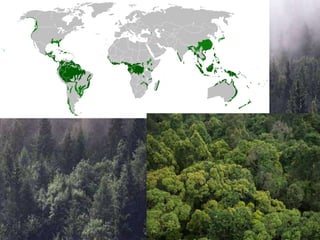
The document summarizes the different types of forests found around the world. It discusses 6 main types: 1) equatorial moist evergreen or rainforest, 2) tropical deciduous forest, 3) Mediterranean forests, 4) temperate broad-leaved deciduous and mixed forest, 5) warm temperate broad-leaved deciduous forest, and 6) coniferous forest. Each forest type is characterized by its location, climate, vegetation, and wildlife. The document also summarizes the types of forests found in India, including coniferous, broadleaved (evergreen, wet evergreen, semi-evergreen, deciduous), thorn, and mangrove forests.