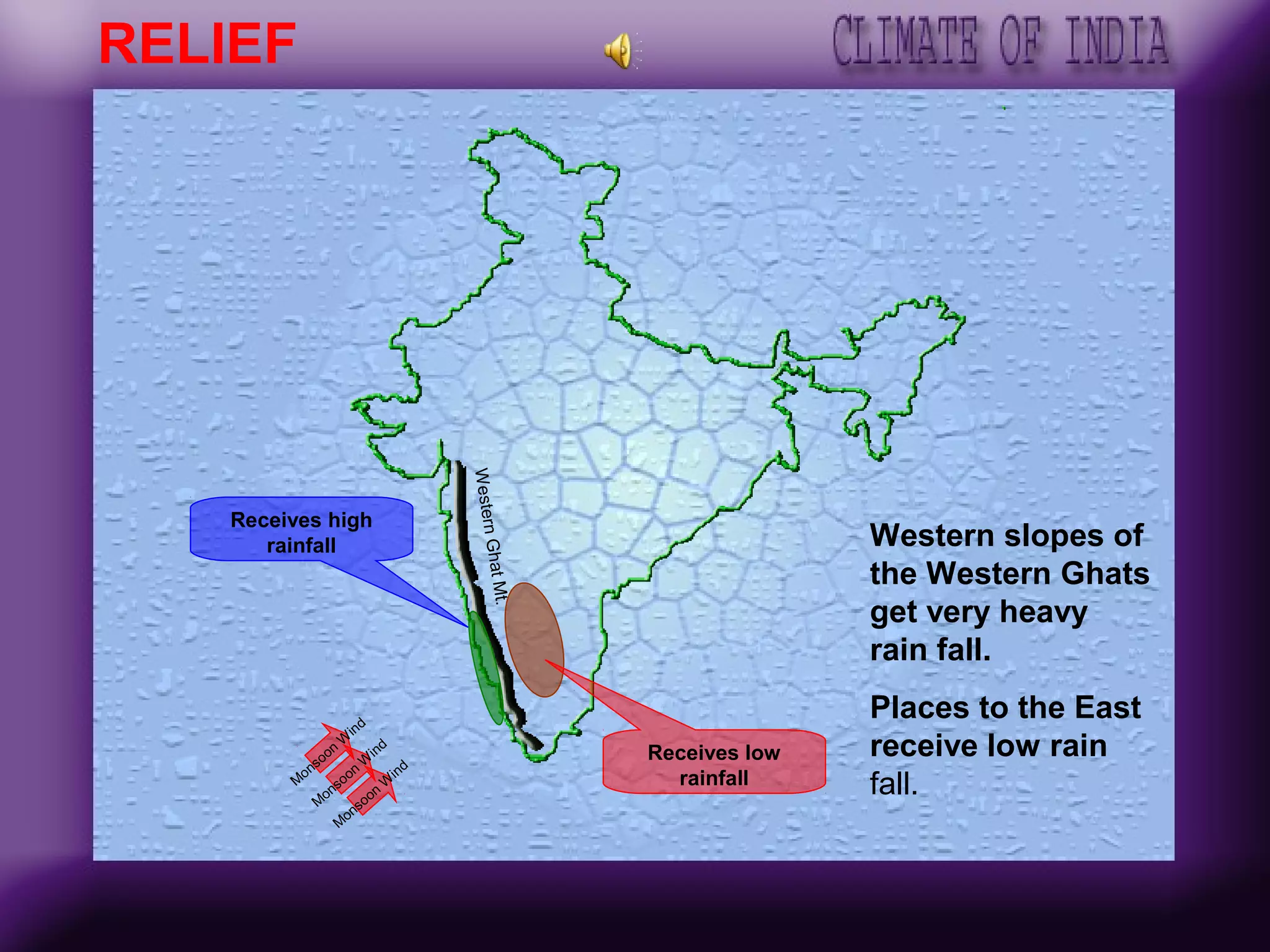
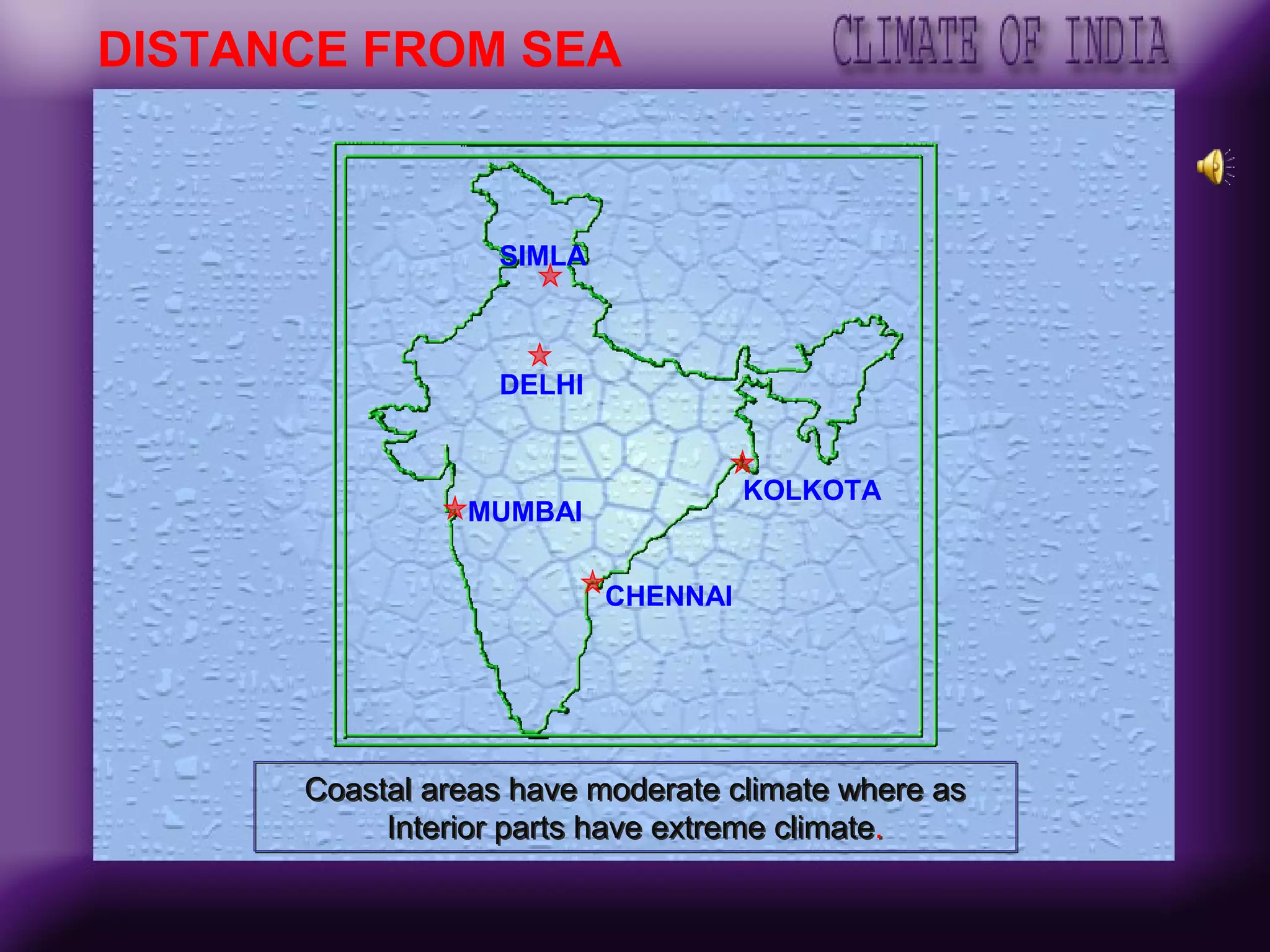
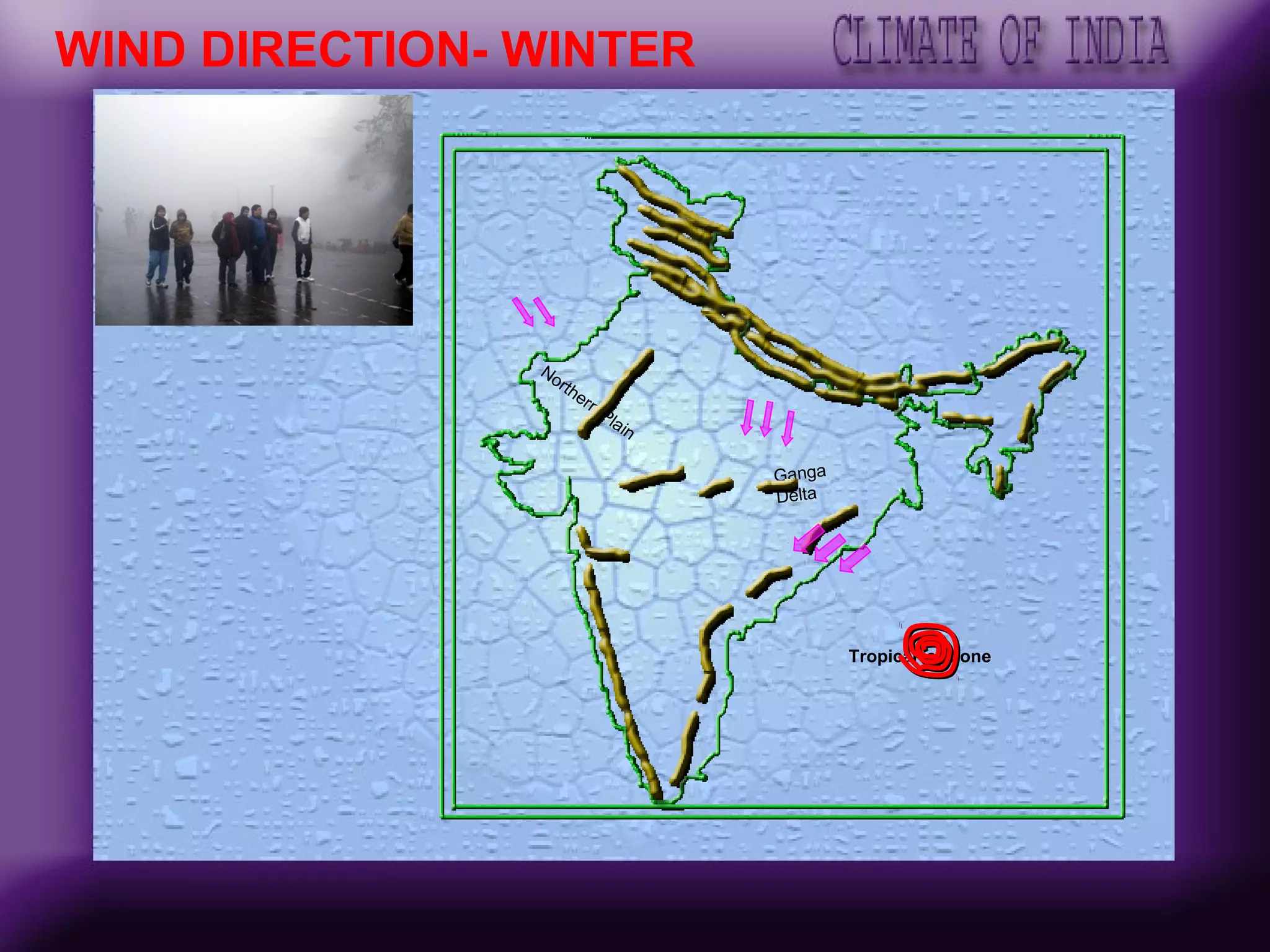
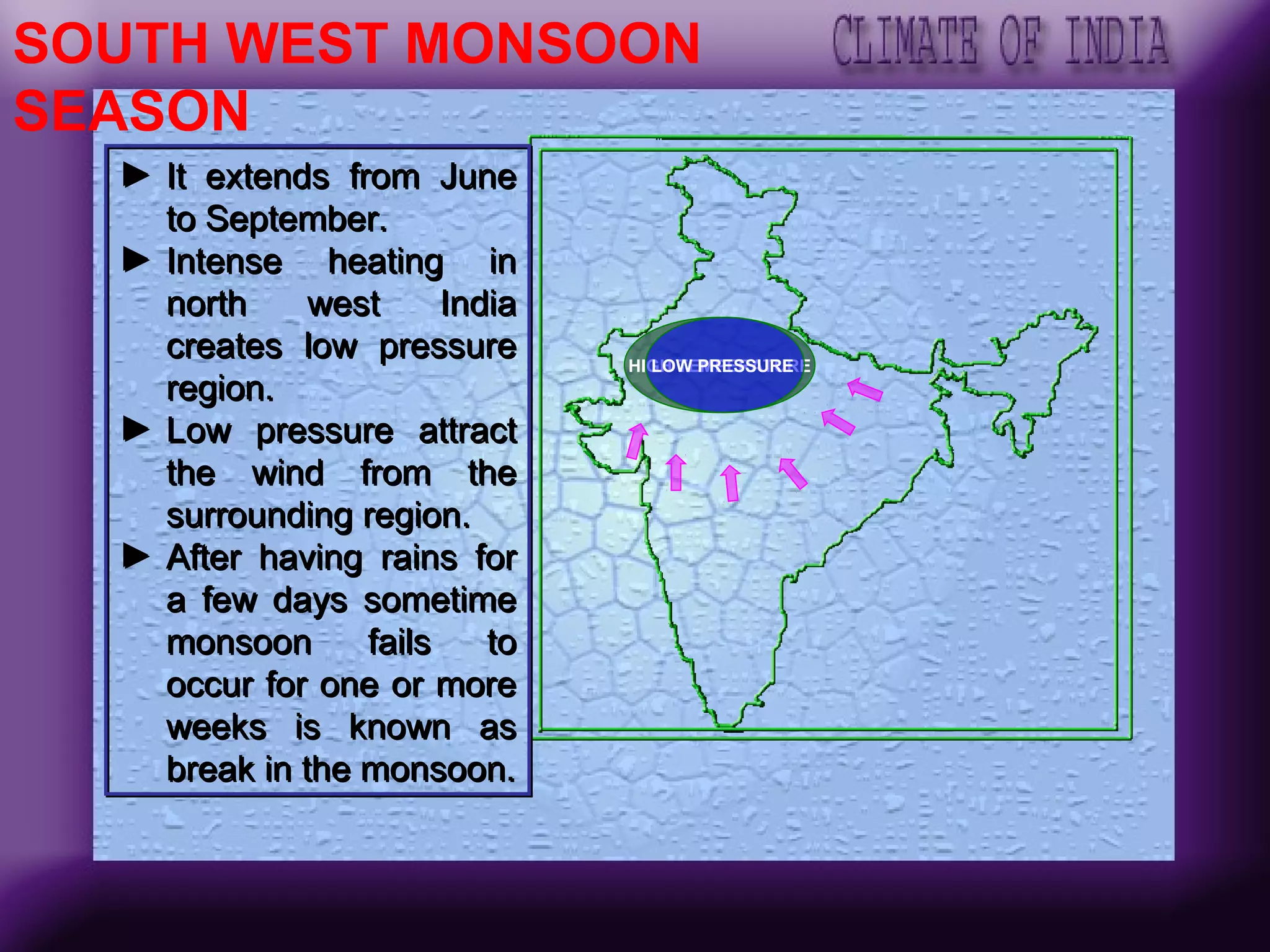
The document discusses the key factors affecting India's climate such as the Himalayas, surrounding seas, relief features, and distance from the sea. It describes the seasonal variations in climate across winter, summer, the southwest monsoon, and retreating monsoon seasons. Spatial variations in rainfall across India are also summarized, from very heavy to scanty rainfall regions. Effects of climate change such as rising sea levels submerging coastal areas are also briefly outlined.