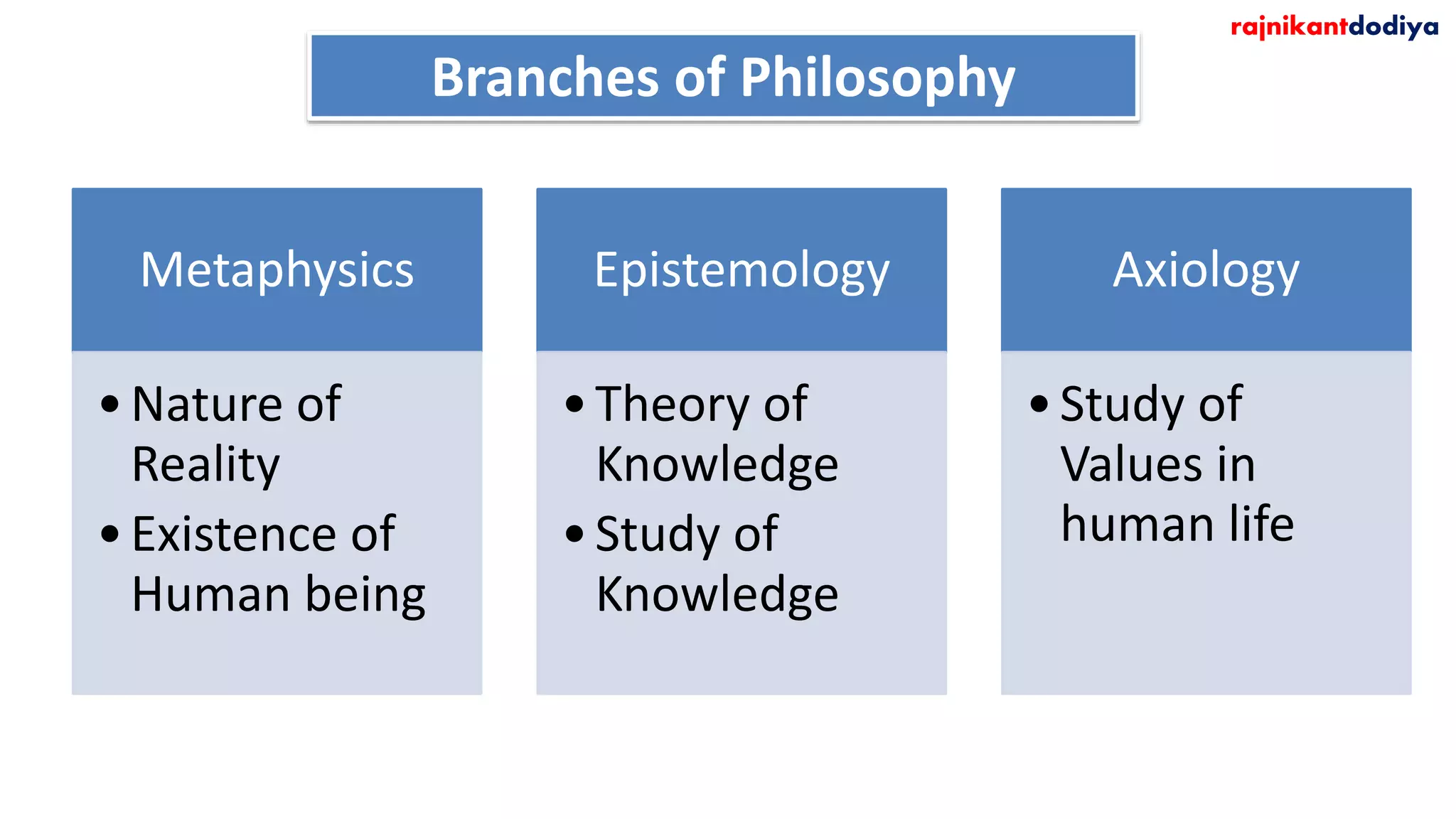
The document discusses the concept of epistemology, defining it as the study of knowledge, its nature, sources, and validity. It emphasizes that philosophy, rooted in love for wisdom, encompasses logical thinking and inquiry into existence and truth. Additionally, it highlights the role of epistemology in education and knowledge acquisition, advocating for accuracy in understanding reality.