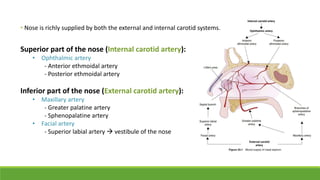
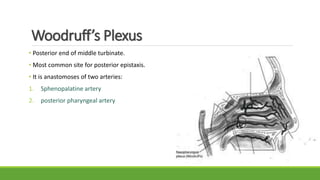
Epistaxis, or nosebleed, is bleeding from inside the nose. It is common and can occur in people of all ages. The nose has a rich blood supply from both the internal and external carotid arteries, making it susceptible to bleeding. The most common site of bleeding is Kiesselbach's plexus in the anterior nasal septum. Epistaxis can be classified as anterior or posterior depending on the location and direction of bleeding. Causes include local trauma, infections, vascular abnormalities, and medications. Management involves first aid measures, cauterization, nasal packing, surgery, or ligation of vessels supplying the nose.