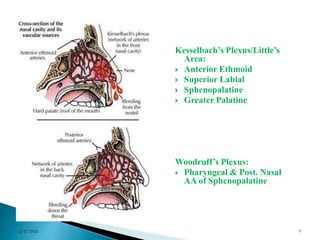
This document discusses epistaxis (nosebleed), including its definition, epidemiology, etiology, risk factors, clinical features, complications, differential diagnoses, treatments, and prevention. It provides details on: the prevalence being 5-10% annually with peaks among those under 10 and over 50; common causes like trauma, infections, hypertension, and coagulopathies; signs like nasal or throat bleeding; potential complications like anemia or aspiration; and treatments including nasal packing, cauterization, or arterial embolization for severe cases.