Epidural Spinal Cord Stimulation for Modulating Small Sensory Nerve Fibers to the Pancreas: A Pilot Study
•
1 like•751 views
1. The study investigated whether spinal cord stimulation (SCS) could modulate small sensory nerve fibers (SSNFs) innervating the pancreas and preserve pancreatic beta cell function in obese rats and rats treated with resiniferatoxin (RTX) to deplete TRPV1 neurons. 2. SCS at 5Hz, but not 100Hz, increased blood flow to the abdominal skin and pancreas by activating SSNFs expressing TRPV1, while RTX treatment and obesity disrupted this effect. 3. Morphological analysis found disrupted pancreatic islet structure in obese and RTX-treated rats, but SCS preserved islet structure and increased insulin production.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
nNOS activation is involved in insulin-mediated CV effects in the NTS

nNOS activation is involved in insulin-mediated cardiovascular effects in the nucleus tractus solitarii of rats. Insulin injection into the NTS induces nNOS phosphorylation via the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. nNOS is a downstream factor of the insulin-PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. The activation of nNOS-derived NO by the insulin-PI3K-Akt signaling pathway participates in central cardiovascular regulation.
Albu_et_al-2014-Journal_of_Sleep_Research

This study examined the effects of deleting the FK506-binding protein 51 (FKBP51) gene on sleep architecture and stress responses in mice. Polysomnography recordings showed that FKBP51 knockout (KO) mice had increased wakefulness and suppressed non-rapid eye movement sleep and rapid eye movement sleep at baseline compared to wild-type mice. After 6 hours of sleep deprivation or 1 hour of restraint stress, FKBP51 KO mice exhibited less recovery sleep than wild-type mice, although slow-wave activity during non-rapid eye movement sleep was higher in KO mice, especially after sleep deprivation. Microdialysis experiments revealed lower levels of free corticosterone in the hippocampus of FKBP51 KO mice,
Presentazione Sancesario G.

1) The document discusses various physiological mechanisms involved in levodopa-induced dyskinesias, including changes in signaling pathways in the striatum and alterations in gene expression.
2) Studies in monkeys found that high doses of levodopa can induce dyskinesias, and that dyskinesias arise more quickly in severely dopamine-depleted monkeys.
3) Research has shown changes in activity of areas of the motor cortex and basal ganglia with levodopa treatment, as well as differential loss of striatal projection systems in Parkinson's disease.
Aton et al., PNAS 2006 - GABA and Gi/o differentially control circadian rhyth...

1) The study examined how GABA and Gi/o signaling differentially control circadian rhythms and synchrony in SCN clock neurons.
2) Blocking GABA receptors with antagonists increased the amplitude and precision of circadian rhythms in individual neurons but did not impair synchrony between neurons.
3) Inhibiting Gi/o proteins with pertussis toxin disrupted synchrony between neurons and abolished rhythms in many neurons.
PCR en tiempo real 

The document summarizes a study that analyzed gene expression in the hypothalamus of depressed patients compared to controls using laser microdissection and real-time PCR. The study found increased expression of genes involved in activating the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in depressed patients, including corticotropin-releasing factor and receptors for estrogen, vasopressin, and mineralocorticoids. Expression of the androgen receptor, which inhibits the axis, was decreased. This suggests an imbalance in receptor production may contribute to axis hyperactivity in depression. The findings provide molecular evidence for the corticotropin-releasing factor hypothesis of depression.
HB poster - AES2

This study investigated how immune signaling and cell stress gene expression changes in the hippocampus and cerebellum of a rat model for glutamate excitotoxicity neurodegeneration. RNA was extracted from these brain regions in mutant and normal rats at different ages. Gene expression analysis found that genes involved in cytokine signaling were downregulated while cell stress genes were upregulated in mutant rats, suggesting altered immune regulation contributes to neurodegeneration. Specifically, genes related to glutamate metabolism and clusterin expression changed over time and differed between brain regions in ways that could enhance excitotoxic cell damage and death. The results provide insight into how the immune system may initiate neurodegeneration during glutamate excitotoxicity.
Sugammadex-Myasthenia Gravis

This case report describes the successful use of sugammadex to reverse rocuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade in a patient with myasthenia gravis undergoing thymectomy. Sugammadex 8 mg/kg was administered and rapidly reversed the blockade without complications, increasing the patient's train-of-four ratio and bispectral index. The surgery was performed with epidural anesthesia and no additional neuromuscular blocking agents were required. Postoperatively the patient recovered well without respiratory issues. This suggests sugammadex may reduce risks for patients with myasthenia gravis undergoing surgery requiring muscle relaxation reversal.
Goonawardena_SfN 2013 Abstract

This study investigated the effects of NMDA receptor antagonists PCP and ketamine on sustained attention and neuronal oscillations in cynomologus macaques performing a continuous performance test. The macaques were trained to touch target stimuli and ignore distractor stimuli. They were then implanted with EEG electrodes and given doses of PCP or ketamine. The drugs decreased performance accuracy on the task. PCP enhanced low and high gamma oscillations and suppressed alpha and beta oscillations in frontal and visual cortices around stimulus presentations compared to vehicle. PCP also enhanced high gamma oscillations for correct responses compared to errors or rejections in frontal cortex. Both drugs suppressed beta oscillations for correct responses in visual cortex. The results suggest NMDA receptor antagonists impair
Recommended
nNOS activation is involved in insulin-mediated CV effects in the NTS

nNOS activation is involved in insulin-mediated cardiovascular effects in the nucleus tractus solitarii of rats. Insulin injection into the NTS induces nNOS phosphorylation via the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. nNOS is a downstream factor of the insulin-PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. The activation of nNOS-derived NO by the insulin-PI3K-Akt signaling pathway participates in central cardiovascular regulation.
Albu_et_al-2014-Journal_of_Sleep_Research

This study examined the effects of deleting the FK506-binding protein 51 (FKBP51) gene on sleep architecture and stress responses in mice. Polysomnography recordings showed that FKBP51 knockout (KO) mice had increased wakefulness and suppressed non-rapid eye movement sleep and rapid eye movement sleep at baseline compared to wild-type mice. After 6 hours of sleep deprivation or 1 hour of restraint stress, FKBP51 KO mice exhibited less recovery sleep than wild-type mice, although slow-wave activity during non-rapid eye movement sleep was higher in KO mice, especially after sleep deprivation. Microdialysis experiments revealed lower levels of free corticosterone in the hippocampus of FKBP51 KO mice,
Presentazione Sancesario G.

1) The document discusses various physiological mechanisms involved in levodopa-induced dyskinesias, including changes in signaling pathways in the striatum and alterations in gene expression.
2) Studies in monkeys found that high doses of levodopa can induce dyskinesias, and that dyskinesias arise more quickly in severely dopamine-depleted monkeys.
3) Research has shown changes in activity of areas of the motor cortex and basal ganglia with levodopa treatment, as well as differential loss of striatal projection systems in Parkinson's disease.
Aton et al., PNAS 2006 - GABA and Gi/o differentially control circadian rhyth...

1) The study examined how GABA and Gi/o signaling differentially control circadian rhythms and synchrony in SCN clock neurons.
2) Blocking GABA receptors with antagonists increased the amplitude and precision of circadian rhythms in individual neurons but did not impair synchrony between neurons.
3) Inhibiting Gi/o proteins with pertussis toxin disrupted synchrony between neurons and abolished rhythms in many neurons.
PCR en tiempo real 

The document summarizes a study that analyzed gene expression in the hypothalamus of depressed patients compared to controls using laser microdissection and real-time PCR. The study found increased expression of genes involved in activating the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in depressed patients, including corticotropin-releasing factor and receptors for estrogen, vasopressin, and mineralocorticoids. Expression of the androgen receptor, which inhibits the axis, was decreased. This suggests an imbalance in receptor production may contribute to axis hyperactivity in depression. The findings provide molecular evidence for the corticotropin-releasing factor hypothesis of depression.
HB poster - AES2

This study investigated how immune signaling and cell stress gene expression changes in the hippocampus and cerebellum of a rat model for glutamate excitotoxicity neurodegeneration. RNA was extracted from these brain regions in mutant and normal rats at different ages. Gene expression analysis found that genes involved in cytokine signaling were downregulated while cell stress genes were upregulated in mutant rats, suggesting altered immune regulation contributes to neurodegeneration. Specifically, genes related to glutamate metabolism and clusterin expression changed over time and differed between brain regions in ways that could enhance excitotoxic cell damage and death. The results provide insight into how the immune system may initiate neurodegeneration during glutamate excitotoxicity.
Sugammadex-Myasthenia Gravis

This case report describes the successful use of sugammadex to reverse rocuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade in a patient with myasthenia gravis undergoing thymectomy. Sugammadex 8 mg/kg was administered and rapidly reversed the blockade without complications, increasing the patient's train-of-four ratio and bispectral index. The surgery was performed with epidural anesthesia and no additional neuromuscular blocking agents were required. Postoperatively the patient recovered well without respiratory issues. This suggests sugammadex may reduce risks for patients with myasthenia gravis undergoing surgery requiring muscle relaxation reversal.
Goonawardena_SfN 2013 Abstract

This study investigated the effects of NMDA receptor antagonists PCP and ketamine on sustained attention and neuronal oscillations in cynomologus macaques performing a continuous performance test. The macaques were trained to touch target stimuli and ignore distractor stimuli. They were then implanted with EEG electrodes and given doses of PCP or ketamine. The drugs decreased performance accuracy on the task. PCP enhanced low and high gamma oscillations and suppressed alpha and beta oscillations in frontal and visual cortices around stimulus presentations compared to vehicle. PCP also enhanced high gamma oscillations for correct responses compared to errors or rejections in frontal cortex. Both drugs suppressed beta oscillations for correct responses in visual cortex. The results suggest NMDA receptor antagonists impair
Schizophrenia Powerpoint

Schizophrenia symptoms can range from mild to severe and include positive, negative, and cognitive symptoms. Positive symptoms refer to psychotic behaviors like hallucinations and delusions. Negative symptoms impact emotions and functioning, like lack of facial expressions or motivation. Cognitive symptoms make it difficult to care for oneself or work due to impaired decision making and attention. While genes may play a role, environment before birth can also influence risk. Standard treatment includes antipsychotic drugs, but natural supplements can help reduce side effects like liver toxicity or involuntary movements.
Schizophrenia

The document provides an overview of recent updates in schizophrenia research from 2008-2014. It summarizes changes in diagnostic classifications like the DSM-V, research on phenomenology such as delusions and hallucinations, epidemiological aspects including global burden and treatment gaps, neurobiological factors like genetics and imaging research, and interventions including early phase treatments and prevention strategies. The presentation outline indicates it will cover these topics in further depth across multiple slides.
Direct Nerve Stimulation Slides from Webinar June 2015

Splashed on the media headlines are case studies of people benefiting from epidural stimulation after paralysis or using vagus nerve stimulation as a rehabilitation tool after a paralyzing stroke. How do you make sense of it all? This webinar will introduce the latest technology applications and the published research supporting or negating them. Take away what you need to know to make an informed decision.
Informative speech schizophrenia powerpoint speech

Schizophrenia is a chronic brain disorder that affects about 1% of people at some point in their lives. It often first develops between ages 16-30. While genes are a factor, environmental influences like prenatal conditions or substance use also contribute. Symptoms include hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking/speech, and reduced emotional expression. Treatments include antipsychotic medications, therapy like cognitive behavioral therapy, and potentially institutional care. The exact causes are unknown but likely involve both genetic and environmental factors interacting during brain development.
Schizophrenia Powerpoint

Schizophrenia is a psychotic disorder that affects about 1% of people worldwide, deteriorating personal, social, and occupational functioning through strange perceptions, disturbed thought processes, unusual emotions, and motor abnormalities. It causes symptoms like auditory hallucinations, disorganized thinking, paranoia, delusions, and disorganized speech. Schizophrenia is diagnosed based on symptoms and can be of five main types, and both biological and psychological factors may contribute to its causes and treatment may involve medications and therapy.
Schizophrenia & other psychotic disorder

Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders involve positive, negative, and disorganized symptoms that distort thinking, perception, and behavior. Schizophrenia is a chronic condition defined by fundamental distortions in thought, perception, emotion, and behavior. It affects about 1% of the population and typically emerges in early adulthood. Treatment involves antipsychotic medications to reduce positive symptoms as well as psychosocial support. The causes are complex and involve genetic, neurological, developmental, and environmental factors.
Schizophrenia

This document provides an overview of the phenomenology of schizophrenia, including a historical perspective on how it has been conceptualized over time. It describes the clinical manifestations and thought disorders commonly seen in schizophrenia, such as formal thought disorders involving disorganized thinking, disorders of thought flow/tempo, disorders of thought possession, and disorders involving delusional thinking. It also briefly discusses misidentification syndromes that can occur.
Schizophrenia (1)

The document provides information about schizophrenia, including its definition, symptoms, diagnosis, course, treatment, and etiology. Some key points:
- Schizophrenia is defined by positive and negative symptoms that last at least 6 months and cause deterioration in functioning.
- It affects about 1% of the population and typically emerges in late adolescence/early adulthood.
- Symptoms include hallucinations, delusions, disorganized speech and behavior, emotional blunting, and lack of motivation.
- Treatment involves antipsychotic medication and psychosocial support like therapy. The exact causes are unknown but are thought to involve genetic and environmental factors impacting brain development.
Schizophrenia ppt

Schizophrenia is a group of psychoses affecting young adults that causes changes in behavior, perception, thoughts and emotions. It has a prevalence of 0.5-1% globally. Genetics plays a role, with a higher risk for those with a family history. Environmental factors like family dynamics, stress, drugs and infections during pregnancy may also contribute. Symptoms include hallucinations, delusions, disorganized speech and behavior. Treatment involves antipsychotic medication, psychosocial support, rehabilitation and family education. Outcomes vary, with about 30% making a good recovery and 30% remaining handicapped long-term.
Schizophrenia (1)

The document discusses schizophrenia, defining it as a mental disorder characterized by distortions in thinking, perception, and emotional expression. It outlines the key symptoms of schizophrenia, including positive symptoms like hallucinations and delusions, and negative symptoms like reduced speech and emotional expression. The document also covers the history of schizophrenia, diagnostic criteria, course of illness, subtypes, and diagnostic classifications.
Schizophrenia

This is a project for a high school AP Psychology course. This is a fictionalized account of having a psychological ailment. For questions about this blog project or its content please email the teacher Chris Jocham: jocham@fultonschools.org
Focused Ultrasound Neuromodulation

Driving Slow-Oscillations (1 Hz) in rats with optical readout via two-photon microscopy.
Alternative download link: https://dl.dropboxusercontent.com/u/6757026/slideShare/neuromodFUS_v2016.pdf
TBI feature

Rats were trained to recognize a sequence of five odors. Neuronal activity was recorded in the hippocampus as rats performed this task. The study found that approximately 26% of hippocampal neurons encoded temporal relationships between odors by changing firing rates depending on whether an odor was in or out of the learned sequence. Some neurons responded more to in-sequence odors, others to out-of-sequence odors. The neuronal ensemble activity reflected whether items were in the correct temporal order. This suggests hippocampal neurons encode temporal relationships between events, important for episodic memory.
hemichannel makes it a major contributor toionic dysregula

hemichannel makes it a major contributor to
ionic dysregulation in ischemia. Second, Px1
hemichannel opening may result in efflux of
glucose and adenosine triphosphate (ATP),
further compromising the neuron_s recovery
from an ischemic insult. Consistent with this
was our observation that fluorescent dyes
became membrane-permeable only during
OGD. Hemichannels are putative conduits for
ATP release from astrocytes (21) and in the
cochlea (22). Third, the large amplitude of
the Px1 hemichannel current at holding po-
tentials near the neuron_s resting membrane
potential (È –60 mV) indicates that these
currents likely contribute substantially to
Banoxic depolarization,[ a poorly understood
but well-recognized and key component of
ischemic neuronal death (2, 23, 24). There-
fore, hemichannel opening may be an impor-
tant new pharmacological target to prevent
neuronal death in stroke.
References and Notes
1. A. J. Hansen, Physiol. Rev. 65, 101 (1985).
2. P. Lipton, Physiol. Rev. 79, 1431 (1999).
3. M. Kamermans et al., Science 292, 1178 (2001).
4. J. E. Contreras et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99, 495
(2002).
5. R. P. Kondo, S. Y. Wang, S. A. John, J. N. Weiss,
J. I. Goldhaber, J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 32, 1859 (2000).
6. H. Li et al., J. Cell Biol. 134, 1019 (1996).
7. L. Bao, S. Locovei, G. Dahl, FEBS Lett. 572, 65
(2004).
8. R. Bruzzone, M. T. Barbe, N. J. Jakob, H. Monyer,
J. Neurochem. 92, 1033 (2005).
9. R. Bruzzone, S. G. Hormuzdi, M. T. Barbe, A. Herb,
H. Monyer, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100, 13644
(2003).
10. See supporting material on Science Online.
11. J. Gao et al., Neuron 48, 635 (2005).
12. M. Aarts et al., Cell 115, 863 (2003).
13. C. Tomasetto, M. J. Neveu, J. Daley, P. K. Horan, R. Sager,
J. Cell Biol. 122, 157 (1993).
14. G. Feng et al., Neuron 28, 41 (2000).
15. A. Nimmerjahn, F. Kirchhoff, J. N. Kerr, F. Helmchen,
Nat. Methods 1, 31 (2004).
16. G. Sohl, S. Maxeiner, K. Willecke, Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 6,
191 (2005).
17. J. C. Saez, M. A. Retamal, D. Basilio, F. F. Bukauskas,
M. V. Bennett, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1711, 215 (2005).
18. R. J. Thompson, M. H. Nordeen, K. E. Howell,
J. H. Caldwell, Biophys. J. 83, 278 (2002).
19. M. L. Fung, G. G. Haddad, Brain Res. 762, 97 (1997).
20. H. Benveniste, J. Drejer, A. Schousboe, N. H. Diemer,
J. Neurochem. 43, 1369 (1984).
21. C. E. Stout, J. L. Costantin, C. C. Naus, A. C. Charles,
J. Biol. Chem. 277, 10482 (2002).
22. H. B. Zhao, N. Yu, C. R. Fleming, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.
U.S.A. 102, 18724 (2005).
23. T. R. Anderson, C. R. Jarvis, A. J. Biedermann, C. Molnar,
R. D. Andrew, J. Neurophysiol. 93, 963 (2005).
24. G. G. Somjen, Physiol. Rev. 81, 1065 (2001).
25. Supported by the Canadian Institutes for Health Research
and the Canadian Stroke Network. B.A.M. has a Tier 1
Canada Research Chair in Neuroscience and a Michael
Smith Foundation for Health Research distinguished
scholar award. We thank Y.-T. Wang, C. C. Naus, and
T. Snutch for critical re ...
hinckley poster5 (2)

This study analyzed genetic variants in the KCNE1 gene and its flanking sequences in 48 human heart tissue samples. The researchers identified at least 6 alternative splice variants of the KCNE1 gene expressed differentially across individuals. They also found evidence of at least 3 alternative promoters for KCNE1. Genotyping of two SNPs showed a weak association between one SNP and levels of splice variants. The study aims to further analyze genetic associations in a larger sample size to achieve sufficient statistical power.
AriMandlerPoster1

1) The document examines ATF3 expression in cardiomyocytes in response to phenylephrine (PE) treatment.
2) Immunofluorescent staining of cardiomyocytes showed increased ATF3 nuclear staining after 0.5 hours of PE treatment, which decreased after 2 hours.
3) Quantitative PCR analysis found c-Jun mRNA was induced after 2 hours of PE, but ATF3, Egr1, and Fos mRNA levels remained unchanged.
A disinhibitory microcircuit initiates critical period plasticity in the visu...

Earlysensoryexperienceinstructsthematurationofneuralcircuitry in the cortex1,2. This has been studied extensively in the primary visualcortex,inwhichlossofvisiontooneeyepermanentlydegrades corticalresponsivenesstothateye3,4,aphenomenonknownasocular dominance plasticity (ODP). Cortical inhibition mediates this process4–6,butthepreciseroleofspecificclassesofinhibitoryneurons in ODP is controversial. Here we report that evoked firing rates of binocular excitatory neurons in the primary visual cortex immediatelydropbyhalfwhenvisionisrestrictedtooneeye,butgradually return to normal over the followingtwenty-four hours, despite the fact that vision remains restricted to one eye. This restoration of binocular-like excitatory firing rates after monocular deprivation resultsfromarapid,althoughtransient,reductioninthefiringrates of fast-spiking, parvalbumin-positive (PV) interneurons, which in turncanbeattributedtoadecreaseinlocalexcitatorycircuitinput onto PV interneurons.This reduction in PV-cell-evoked responses after monocular lid suture is restricted to the critical period for ODPandappearstobenecessaryforsubsequentshiftsinexcitatory ODP. Pharmacologically enhancing inhibition at the time of sight deprivation blocks ODP and, conversely, pharmacogenetic reduction of PV cell firing rates can extend the critical period for ODP. Thesefindingsdefinethemicrocircuitchangesinitiatingcompetitive
plasticityduringcriticalperiodsofcorticaldevelopment.Moreover, they show that the restoration of evoked firing rates of layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons by PV-specific disinhibition is a key step in the progression of ODP.
A disinhibitory microcircuit initiates critical period plasticity in the visu...

Early sensory experience instructs the maturation of neural circuitry in the cortex1, 2. This has been studied extensively in the primary visual cortex, in which loss of vision to one eye permanently degrades cortical responsiveness to that eye3, 4, a phenomenon known as ocular dominance plasticity (ODP). Cortical inhibition mediates this process4, 5, 6, but the precise role of specific classes of inhibitory neurons in ODP is controversial. Here we report that evoked firing rates of binocular excitatory neurons in the primary visual cortex immediately drop by half when vision is restricted to one eye, but gradually return to normal over the following twenty-four hours, despite the fact that vision remains restricted to one eye. This restoration of binocular-like excitatory firing rates after monocular deprivation results from a rapid, although transient, reduction in the firing rates of fast-spiking, parvalbumin-positive (PV) interneurons, which in turn can be attributed to a decrease in local excitatory circuit input onto PV interneurons. This reduction in PV-cell-evoked responses after monocular lid suture is restricted to the critical period for ODP and appears to be necessary for subsequent shifts in excitatory ODP. Pharmacologically enhancing inhibition at the time of sight deprivation blocks ODP and, conversely, pharmacogenetic reduction of PV cell firing rates can extend the critical period for ODP. These findings define the microcircuit changes initiating competitive plasticity during critical periods of cortical development. Moreover, they show that the restoration of evoked firing rates of layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons by PV-specific disinhibition is a key step in the progression of ODP.
Application of PEA reduces WDR RF size - Final edit

This document describes a study that investigated whether the fatty acid amide N-palmitoylethanolamine (PEA) can reduce inflammation-induced expansion of wide dynamic range neurone (WDR) receptive fields (RFs) in rats. PEA is an endogenous ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α), which has anti-inflammatory effects. The study found that intraplantar injection of PEA prior to carrageenan-induced inflammation significantly reduced the expansion of WDR RFs and attenuated hyperalgesia. Blocking PPAR-α with GW6471 prevented the effects of PEA, suggesting PEA acts through PPAR-α activation to reduce
Characterization of the human HCN1 channel and its inhibition by capsazepine

1. The human hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated 1 (hHCN1) subunit was expressed in mammalian cell lines and its electrophysiological properties were characterized using patch-clamp recordings.
2. Activation of hHCN1 generated a slowly activating, non-inactivating inward current similar to native hyperpolarization-activated currents (Ih). Ih was blocked by known blockers Cs+, ZD 7288, and zatebradine.
3. The VR1 receptor antagonist capsazepine inhibited hHCN1-mediated currents in a concentration-dependent, reversible manner by shifting the activation curve and slowing current activation kinetics.
Nobels days 2013

1) The document examines how 17β-estradiol may reduce vascular inflammation by down-regulating the NLRP3 inflammasome and related proinflammatory cytokines like IL-6 and IL-8 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and aortic smooth muscle cells (AOSMCs).
2) Exogenous 17β-estradiol was shown to significantly decrease expression of NLRP3, caspase-1, and IL-1β in HUVECs and also reduced IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8 levels in AOSMCs.
3) Down-regulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and proinflammatory cytokines by estrogen may be one mechanism for
Nader

This study examined the effects of bacterial endotoxin (LPS) on myocardial function during ischemia-reperfusion injury. Rabbits were injected with increasing doses of LPS or saline prior to inducing myocardial ischemia through coronary artery occlusion. Higher LPS doses suppressed cardiac contractility and worsened injury compared to lower doses or saline. Blocking TNF-alpha prevented the additional harmful effects of LPS on cardiac function after ischemia. The findings suggest that bacterial endotoxins can exacerbate ischemia-reperfusion injury in a dose-dependent manner mediated through TNF-alpha.
More Related Content
Viewers also liked
Schizophrenia Powerpoint

Schizophrenia symptoms can range from mild to severe and include positive, negative, and cognitive symptoms. Positive symptoms refer to psychotic behaviors like hallucinations and delusions. Negative symptoms impact emotions and functioning, like lack of facial expressions or motivation. Cognitive symptoms make it difficult to care for oneself or work due to impaired decision making and attention. While genes may play a role, environment before birth can also influence risk. Standard treatment includes antipsychotic drugs, but natural supplements can help reduce side effects like liver toxicity or involuntary movements.
Schizophrenia

The document provides an overview of recent updates in schizophrenia research from 2008-2014. It summarizes changes in diagnostic classifications like the DSM-V, research on phenomenology such as delusions and hallucinations, epidemiological aspects including global burden and treatment gaps, neurobiological factors like genetics and imaging research, and interventions including early phase treatments and prevention strategies. The presentation outline indicates it will cover these topics in further depth across multiple slides.
Direct Nerve Stimulation Slides from Webinar June 2015

Splashed on the media headlines are case studies of people benefiting from epidural stimulation after paralysis or using vagus nerve stimulation as a rehabilitation tool after a paralyzing stroke. How do you make sense of it all? This webinar will introduce the latest technology applications and the published research supporting or negating them. Take away what you need to know to make an informed decision.
Informative speech schizophrenia powerpoint speech

Schizophrenia is a chronic brain disorder that affects about 1% of people at some point in their lives. It often first develops between ages 16-30. While genes are a factor, environmental influences like prenatal conditions or substance use also contribute. Symptoms include hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking/speech, and reduced emotional expression. Treatments include antipsychotic medications, therapy like cognitive behavioral therapy, and potentially institutional care. The exact causes are unknown but likely involve both genetic and environmental factors interacting during brain development.
Schizophrenia Powerpoint

Schizophrenia is a psychotic disorder that affects about 1% of people worldwide, deteriorating personal, social, and occupational functioning through strange perceptions, disturbed thought processes, unusual emotions, and motor abnormalities. It causes symptoms like auditory hallucinations, disorganized thinking, paranoia, delusions, and disorganized speech. Schizophrenia is diagnosed based on symptoms and can be of five main types, and both biological and psychological factors may contribute to its causes and treatment may involve medications and therapy.
Schizophrenia & other psychotic disorder

Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders involve positive, negative, and disorganized symptoms that distort thinking, perception, and behavior. Schizophrenia is a chronic condition defined by fundamental distortions in thought, perception, emotion, and behavior. It affects about 1% of the population and typically emerges in early adulthood. Treatment involves antipsychotic medications to reduce positive symptoms as well as psychosocial support. The causes are complex and involve genetic, neurological, developmental, and environmental factors.
Schizophrenia

This document provides an overview of the phenomenology of schizophrenia, including a historical perspective on how it has been conceptualized over time. It describes the clinical manifestations and thought disorders commonly seen in schizophrenia, such as formal thought disorders involving disorganized thinking, disorders of thought flow/tempo, disorders of thought possession, and disorders involving delusional thinking. It also briefly discusses misidentification syndromes that can occur.
Schizophrenia (1)

The document provides information about schizophrenia, including its definition, symptoms, diagnosis, course, treatment, and etiology. Some key points:
- Schizophrenia is defined by positive and negative symptoms that last at least 6 months and cause deterioration in functioning.
- It affects about 1% of the population and typically emerges in late adolescence/early adulthood.
- Symptoms include hallucinations, delusions, disorganized speech and behavior, emotional blunting, and lack of motivation.
- Treatment involves antipsychotic medication and psychosocial support like therapy. The exact causes are unknown but are thought to involve genetic and environmental factors impacting brain development.
Schizophrenia ppt

Schizophrenia is a group of psychoses affecting young adults that causes changes in behavior, perception, thoughts and emotions. It has a prevalence of 0.5-1% globally. Genetics plays a role, with a higher risk for those with a family history. Environmental factors like family dynamics, stress, drugs and infections during pregnancy may also contribute. Symptoms include hallucinations, delusions, disorganized speech and behavior. Treatment involves antipsychotic medication, psychosocial support, rehabilitation and family education. Outcomes vary, with about 30% making a good recovery and 30% remaining handicapped long-term.
Schizophrenia (1)

The document discusses schizophrenia, defining it as a mental disorder characterized by distortions in thinking, perception, and emotional expression. It outlines the key symptoms of schizophrenia, including positive symptoms like hallucinations and delusions, and negative symptoms like reduced speech and emotional expression. The document also covers the history of schizophrenia, diagnostic criteria, course of illness, subtypes, and diagnostic classifications.
Schizophrenia

This is a project for a high school AP Psychology course. This is a fictionalized account of having a psychological ailment. For questions about this blog project or its content please email the teacher Chris Jocham: jocham@fultonschools.org
Viewers also liked (11)
Direct Nerve Stimulation Slides from Webinar June 2015

Direct Nerve Stimulation Slides from Webinar June 2015
Informative speech schizophrenia powerpoint speech

Informative speech schizophrenia powerpoint speech
Similar to Epidural Spinal Cord Stimulation for Modulating Small Sensory Nerve Fibers to the Pancreas: A Pilot Study
Focused Ultrasound Neuromodulation

Driving Slow-Oscillations (1 Hz) in rats with optical readout via two-photon microscopy.
Alternative download link: https://dl.dropboxusercontent.com/u/6757026/slideShare/neuromodFUS_v2016.pdf
TBI feature

Rats were trained to recognize a sequence of five odors. Neuronal activity was recorded in the hippocampus as rats performed this task. The study found that approximately 26% of hippocampal neurons encoded temporal relationships between odors by changing firing rates depending on whether an odor was in or out of the learned sequence. Some neurons responded more to in-sequence odors, others to out-of-sequence odors. The neuronal ensemble activity reflected whether items were in the correct temporal order. This suggests hippocampal neurons encode temporal relationships between events, important for episodic memory.
hemichannel makes it a major contributor toionic dysregula

hemichannel makes it a major contributor to
ionic dysregulation in ischemia. Second, Px1
hemichannel opening may result in efflux of
glucose and adenosine triphosphate (ATP),
further compromising the neuron_s recovery
from an ischemic insult. Consistent with this
was our observation that fluorescent dyes
became membrane-permeable only during
OGD. Hemichannels are putative conduits for
ATP release from astrocytes (21) and in the
cochlea (22). Third, the large amplitude of
the Px1 hemichannel current at holding po-
tentials near the neuron_s resting membrane
potential (È –60 mV) indicates that these
currents likely contribute substantially to
Banoxic depolarization,[ a poorly understood
but well-recognized and key component of
ischemic neuronal death (2, 23, 24). There-
fore, hemichannel opening may be an impor-
tant new pharmacological target to prevent
neuronal death in stroke.
References and Notes
1. A. J. Hansen, Physiol. Rev. 65, 101 (1985).
2. P. Lipton, Physiol. Rev. 79, 1431 (1999).
3. M. Kamermans et al., Science 292, 1178 (2001).
4. J. E. Contreras et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99, 495
(2002).
5. R. P. Kondo, S. Y. Wang, S. A. John, J. N. Weiss,
J. I. Goldhaber, J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 32, 1859 (2000).
6. H. Li et al., J. Cell Biol. 134, 1019 (1996).
7. L. Bao, S. Locovei, G. Dahl, FEBS Lett. 572, 65
(2004).
8. R. Bruzzone, M. T. Barbe, N. J. Jakob, H. Monyer,
J. Neurochem. 92, 1033 (2005).
9. R. Bruzzone, S. G. Hormuzdi, M. T. Barbe, A. Herb,
H. Monyer, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100, 13644
(2003).
10. See supporting material on Science Online.
11. J. Gao et al., Neuron 48, 635 (2005).
12. M. Aarts et al., Cell 115, 863 (2003).
13. C. Tomasetto, M. J. Neveu, J. Daley, P. K. Horan, R. Sager,
J. Cell Biol. 122, 157 (1993).
14. G. Feng et al., Neuron 28, 41 (2000).
15. A. Nimmerjahn, F. Kirchhoff, J. N. Kerr, F. Helmchen,
Nat. Methods 1, 31 (2004).
16. G. Sohl, S. Maxeiner, K. Willecke, Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 6,
191 (2005).
17. J. C. Saez, M. A. Retamal, D. Basilio, F. F. Bukauskas,
M. V. Bennett, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1711, 215 (2005).
18. R. J. Thompson, M. H. Nordeen, K. E. Howell,
J. H. Caldwell, Biophys. J. 83, 278 (2002).
19. M. L. Fung, G. G. Haddad, Brain Res. 762, 97 (1997).
20. H. Benveniste, J. Drejer, A. Schousboe, N. H. Diemer,
J. Neurochem. 43, 1369 (1984).
21. C. E. Stout, J. L. Costantin, C. C. Naus, A. C. Charles,
J. Biol. Chem. 277, 10482 (2002).
22. H. B. Zhao, N. Yu, C. R. Fleming, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.
U.S.A. 102, 18724 (2005).
23. T. R. Anderson, C. R. Jarvis, A. J. Biedermann, C. Molnar,
R. D. Andrew, J. Neurophysiol. 93, 963 (2005).
24. G. G. Somjen, Physiol. Rev. 81, 1065 (2001).
25. Supported by the Canadian Institutes for Health Research
and the Canadian Stroke Network. B.A.M. has a Tier 1
Canada Research Chair in Neuroscience and a Michael
Smith Foundation for Health Research distinguished
scholar award. We thank Y.-T. Wang, C. C. Naus, and
T. Snutch for critical re ...
hinckley poster5 (2)

This study analyzed genetic variants in the KCNE1 gene and its flanking sequences in 48 human heart tissue samples. The researchers identified at least 6 alternative splice variants of the KCNE1 gene expressed differentially across individuals. They also found evidence of at least 3 alternative promoters for KCNE1. Genotyping of two SNPs showed a weak association between one SNP and levels of splice variants. The study aims to further analyze genetic associations in a larger sample size to achieve sufficient statistical power.
AriMandlerPoster1

1) The document examines ATF3 expression in cardiomyocytes in response to phenylephrine (PE) treatment.
2) Immunofluorescent staining of cardiomyocytes showed increased ATF3 nuclear staining after 0.5 hours of PE treatment, which decreased after 2 hours.
3) Quantitative PCR analysis found c-Jun mRNA was induced after 2 hours of PE, but ATF3, Egr1, and Fos mRNA levels remained unchanged.
A disinhibitory microcircuit initiates critical period plasticity in the visu...

Earlysensoryexperienceinstructsthematurationofneuralcircuitry in the cortex1,2. This has been studied extensively in the primary visualcortex,inwhichlossofvisiontooneeyepermanentlydegrades corticalresponsivenesstothateye3,4,aphenomenonknownasocular dominance plasticity (ODP). Cortical inhibition mediates this process4–6,butthepreciseroleofspecificclassesofinhibitoryneurons in ODP is controversial. Here we report that evoked firing rates of binocular excitatory neurons in the primary visual cortex immediatelydropbyhalfwhenvisionisrestrictedtooneeye,butgradually return to normal over the followingtwenty-four hours, despite the fact that vision remains restricted to one eye. This restoration of binocular-like excitatory firing rates after monocular deprivation resultsfromarapid,althoughtransient,reductioninthefiringrates of fast-spiking, parvalbumin-positive (PV) interneurons, which in turncanbeattributedtoadecreaseinlocalexcitatorycircuitinput onto PV interneurons.This reduction in PV-cell-evoked responses after monocular lid suture is restricted to the critical period for ODPandappearstobenecessaryforsubsequentshiftsinexcitatory ODP. Pharmacologically enhancing inhibition at the time of sight deprivation blocks ODP and, conversely, pharmacogenetic reduction of PV cell firing rates can extend the critical period for ODP. Thesefindingsdefinethemicrocircuitchangesinitiatingcompetitive
plasticityduringcriticalperiodsofcorticaldevelopment.Moreover, they show that the restoration of evoked firing rates of layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons by PV-specific disinhibition is a key step in the progression of ODP.
A disinhibitory microcircuit initiates critical period plasticity in the visu...

Early sensory experience instructs the maturation of neural circuitry in the cortex1, 2. This has been studied extensively in the primary visual cortex, in which loss of vision to one eye permanently degrades cortical responsiveness to that eye3, 4, a phenomenon known as ocular dominance plasticity (ODP). Cortical inhibition mediates this process4, 5, 6, but the precise role of specific classes of inhibitory neurons in ODP is controversial. Here we report that evoked firing rates of binocular excitatory neurons in the primary visual cortex immediately drop by half when vision is restricted to one eye, but gradually return to normal over the following twenty-four hours, despite the fact that vision remains restricted to one eye. This restoration of binocular-like excitatory firing rates after monocular deprivation results from a rapid, although transient, reduction in the firing rates of fast-spiking, parvalbumin-positive (PV) interneurons, which in turn can be attributed to a decrease in local excitatory circuit input onto PV interneurons. This reduction in PV-cell-evoked responses after monocular lid suture is restricted to the critical period for ODP and appears to be necessary for subsequent shifts in excitatory ODP. Pharmacologically enhancing inhibition at the time of sight deprivation blocks ODP and, conversely, pharmacogenetic reduction of PV cell firing rates can extend the critical period for ODP. These findings define the microcircuit changes initiating competitive plasticity during critical periods of cortical development. Moreover, they show that the restoration of evoked firing rates of layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons by PV-specific disinhibition is a key step in the progression of ODP.
Application of PEA reduces WDR RF size - Final edit

This document describes a study that investigated whether the fatty acid amide N-palmitoylethanolamine (PEA) can reduce inflammation-induced expansion of wide dynamic range neurone (WDR) receptive fields (RFs) in rats. PEA is an endogenous ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α), which has anti-inflammatory effects. The study found that intraplantar injection of PEA prior to carrageenan-induced inflammation significantly reduced the expansion of WDR RFs and attenuated hyperalgesia. Blocking PPAR-α with GW6471 prevented the effects of PEA, suggesting PEA acts through PPAR-α activation to reduce
Characterization of the human HCN1 channel and its inhibition by capsazepine

1. The human hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated 1 (hHCN1) subunit was expressed in mammalian cell lines and its electrophysiological properties were characterized using patch-clamp recordings.
2. Activation of hHCN1 generated a slowly activating, non-inactivating inward current similar to native hyperpolarization-activated currents (Ih). Ih was blocked by known blockers Cs+, ZD 7288, and zatebradine.
3. The VR1 receptor antagonist capsazepine inhibited hHCN1-mediated currents in a concentration-dependent, reversible manner by shifting the activation curve and slowing current activation kinetics.
Nobels days 2013

1) The document examines how 17β-estradiol may reduce vascular inflammation by down-regulating the NLRP3 inflammasome and related proinflammatory cytokines like IL-6 and IL-8 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and aortic smooth muscle cells (AOSMCs).
2) Exogenous 17β-estradiol was shown to significantly decrease expression of NLRP3, caspase-1, and IL-1β in HUVECs and also reduced IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8 levels in AOSMCs.
3) Down-regulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and proinflammatory cytokines by estrogen may be one mechanism for
Nader

This study examined the effects of bacterial endotoxin (LPS) on myocardial function during ischemia-reperfusion injury. Rabbits were injected with increasing doses of LPS or saline prior to inducing myocardial ischemia through coronary artery occlusion. Higher LPS doses suppressed cardiac contractility and worsened injury compared to lower doses or saline. Blocking TNF-alpha prevented the additional harmful effects of LPS on cardiac function after ischemia. The findings suggest that bacterial endotoxins can exacerbate ischemia-reperfusion injury in a dose-dependent manner mediated through TNF-alpha.
YALE POSTER presentation (3)

- STEP levels are elevated in Fragile X mice and inhibit long-term potentiation.
- Researchers tested the STEP inhibitor TC-2153 in wild type and Fragile X mice.
- TC-2153 treatment led to increased phosphorylation of STEP substrates like NR2B, Pyk2 and ERK1/2 in both wild type and Fragile X mice by inhibiting STEP.
- This suggests that TC-2153 may be an effective treatment for cognitive deficits in Fragile X Syndrome by blocking the elevated STEP activity.
Trans cranial magnetic stimulation - Diagnostic & Therapeutic application

Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a non-invasive technique that uses electromagnetic induction to stimulate neural tissue without causing pain. TMS can have acute effects like activating neural circuits or disrupting speech, as well as prolonged effects like changing synaptic strength and modulating cortical excitability. TMS has diagnostic applications like measuring motor thresholds and central motor conduction time to evaluate motor pathways, and therapeutic applications for treating depression, Parkinson's disease, neuropathic pain, and more. Common TMS protocols include single pulse, paired pulse, and repetitive TMS with low or high frequency stimulation. TMS is generally safe but can infrequently cause minor side effects like headaches.
SandhuPoster2011

1) Dopamine transmission in the basal ganglia controls motor behavior through two pathways - the direct pathway which stimulates motion, and the indirect pathway which inhibits motion.
2) CK1δ over-expression disrupts this system, possibly through dopamine deficiency caused by downregulation of D1 and D2 receptors.
3) This study found an increase in calretinin-containing neurons in the striatum of CK1δ over-expressing mice, suggesting this imbalance contributes to their ADHD-like behaviors.
and lifelong absence of FXR as occurs inthe FXR-null model, .docx

and lifelong absence of FXR as occurs in
the FXR-null model, can result in
abnormal metabolic effects that are quite
different from those caused by acute,
transient antagonism of this receptor.
Because the FXR-null mouse was
produced using Cre–loxP technology,
conditional disruption of this allele after
normal development has occurred can
now be used to help resolve this issue. An
alternative explanation is that the site(s)
of pharmacological action of
guggulsterone do not include all of the
tissues in which FXR is functional, such as
the liver and gut (i.e. although FXR
synthesis is uniformly absent from all
tissues of the FXR-null mouse model,
guggulsterone might antagonize FXR only
within a subset of these sites). In the
absence of in vivo data regarding the
modulation of FXR target gene expression
by guggulsterone, this is difficult to judge.
Thus, it remains a possibility that the
effects of orally-administered
guggulsterone occur primarily at the level
of the gut (i.e. versus gut and liver), for
instance, by affecting cholesterol
absorption and bile-acid reuptake
processes regulated by FXR, rather than
the hepatic biosynthesis and transport of
bile acids. Again, the conditional nature of
the strategy used to create the FXR-null
mouse model allows for tissue-specific
deletion of the FXR gene and might help
resolve this issue.
As reinforced by the recent work of
Urizar et al. [3], as well as by the present
therapeutic use of bile-acid binding
resins for hypercholesterolemia, there
exists an intimate linkage between bile
acid and cholesterol metabolism. Recent
demonstrations that FXR is also involved
in the regulation of genes (e.g. encoding
apolipoprotein A-I, apolipoprotein C-II
and phospholipids transfer protein) [4–6]
more closely linked with lipid rather
than bile-acid homeostasis, presents
additional avenues by which FXR
ligands could be beneficial for the
treatment of disorders of lipid
metabolism. As suggested by the work of
Urizar et al. [3] and others (e.g. [7]),
careful and comprehensive study of the
effects of natural products, such as
guggulsterone, on the function of nuclear
hormone receptors, is likely to yield
additional agents with desirable
therapeutic effects.
References
1 Sinal, C.J. et al. (2000) Targeted disruption of the
nuclear receptor FXR/BAR impairs bile acid and
lipid homeostasis. Cell 102, 731–744
2 Singh, R.B. et al. (1994) Hypolipidemic and
antioxidant effects of Commiphora mukul as an
adjunct to dietary therapy in patients with
hypercholesterolemia. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 8,
659–664
3 Urizar, N.L. et al. (2002) A natural product that
lowers cholesterol as an antagonist ligand for
FXR. Science 296, 1703–1706
4 Claudel, T. et al. (2002) Bile acid-activated nuclear
receptor FXR suppresses apolipoprotein A-I
transcription via a negative FXR response
element. J. Clin. Invest. 109, 961–971
5 Kast, H.R. et al. (2001) Farnesoid X-activated
receptor induces apolipoprotein C-II
transcription: a molecular mech.
A Mathematical Bivariate Generalized Poisson Model for Cortisol Awakening Res...

This document discusses a mathematical bivariate generalized Poisson model for analyzing cortisol awakening response (CAR) in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS). It presents the probability generating function (PGF) and moment generating function (MGF) for the bivariate generalized Poisson distribution. CAR is higher in relapsing-remitting MS patients compared to secondary-progressive MS patients and healthy controls. Treated RRMS patients show a higher CAR than untreated RRMS patients. RRMS patients with increased disability scores over time also have a higher CAR. Graphs of the PGF and MGF based on data from RRMS, SPMS and healthy patients support these findings. The model provides a way to analyze circadian cortisol patterns and
A typical Realization of the process with linear recovery of Aldosterone

Hypercortisolism as a sign of hypothamamus-pituitary-adrenocortical (HPA) axis overactivity and sleep EEG
changes are frequently observed in depression. Closely related to the
HPA axis is the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) as 1. adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) is a
common stimulus for cortisol and aldosterone, 2. cortisol release is suppressed by mineralocorticoid receptor
(MR) agonists 3. angiotensin II (ATII) releases CRH and vasopressin from the hypothalamus. The first passage
time and the bounds of the survival functions for the application are also obtained
My Pain 2015

This research paper examines the effects of activating small-conductance calcium-activated potassium (SK) channels in the spinal cord on reducing mechanical hypersensitivity in a rat model of inflammatory pain. The study finds that intrathecal administration of the SK channel activator NS309 dose-dependently attenuates mechanical hypersensitivity induced by complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) inflammation. Additionally, coadministration of NS309 with the NMDA receptor antagonist DL-AP5 reduces the dose of DL-AP5 needed to produce antinociceptive effects in the CFA pain model. This suggests that activating SK channels in the spinal cord can modulate the effects of NMDA receptor antagonists and potentially reduce their unwanted side effects.
NKCC1 Poster for SIRS 2010

Poster I presented at the Schizophrenia International Research Society conference in Florence in April, 2010.
Intracranial Aneurysm Growth in vivo - Robert Krams

Article: https://robertkrams.co.uk/disturbed-flow-induces-a-sustained-stochastic-nf-κb-activation-which-may-support-intracranial-aneurysm-growth-in-vivo/
Similar to Epidural Spinal Cord Stimulation for Modulating Small Sensory Nerve Fibers to the Pancreas: A Pilot Study (20)
hemichannel makes it a major contributor toionic dysregula

hemichannel makes it a major contributor toionic dysregula
A disinhibitory microcircuit initiates critical period plasticity in the visu...

A disinhibitory microcircuit initiates critical period plasticity in the visu...
A disinhibitory microcircuit initiates critical period plasticity in the visu...

A disinhibitory microcircuit initiates critical period plasticity in the visu...
Application of PEA reduces WDR RF size - Final edit

Application of PEA reduces WDR RF size - Final edit
Characterization of the human HCN1 channel and its inhibition by capsazepine

Characterization of the human HCN1 channel and its inhibition by capsazepine
Trans cranial magnetic stimulation - Diagnostic & Therapeutic application

Trans cranial magnetic stimulation - Diagnostic & Therapeutic application
and lifelong absence of FXR as occurs inthe FXR-null model, .docx

and lifelong absence of FXR as occurs inthe FXR-null model, .docx
A Mathematical Bivariate Generalized Poisson Model for Cortisol Awakening Res...

A Mathematical Bivariate Generalized Poisson Model for Cortisol Awakening Res...
A typical Realization of the process with linear recovery of Aldosterone

A typical Realization of the process with linear recovery of Aldosterone
Intracranial Aneurysm Growth in vivo - Robert Krams

Intracranial Aneurysm Growth in vivo - Robert Krams
Recently uploaded
Know the difference between Endodontics and Orthodontics.

Your smile is beautiful.
Let’s be honest. Maintaining that beautiful smile is not an easy task. It is more than brushing and flossing. Sometimes, you might encounter dental issues that need special dental care. These issues can range anywhere from misalignment of the jaw to pain in the root of teeth.
biomechanics of running. Dr.dhwani.pptx

The biomechanics of running involves the study of the mechanical principles underlying running movements. It includes the analysis of the running gait cycle, which consists of the stance phase (foot contact to push-off) and the swing phase (foot lift-off to next contact). Key aspects include kinematics (joint angles and movements, stride length and frequency) and kinetics (forces involved in running, including ground reaction and muscle forces). Understanding these factors helps in improving running performance, optimizing technique, and preventing injuries.
Hemodialysis: Chapter 5, Dialyzers Overview - Dr.Gawad

- Video recording of this lecture in English language: https://youtu.be/Pt1nA32sdHQ
- Video recording of this lecture in Arabic language: https://youtu.be/uFdc9F0rlP0
- Link to download the book free: https://nephrotube.blogspot.com/p/nephrotube-nephrology-books.html
- Link to NephroTube website: www.NephroTube.com
- Link to NephroTube social media accounts: https://nephrotube.blogspot.com/p/join-nephrotube-on-social-media.html
Medical Quiz ( Online Quiz for API Meet 2024 ).pdf

This quiz was conducted as a promotional event for the 2024 Annual Meet of Kerala Chapter of API.
More than 20 participants took part everyday !
Breast cancer: Post menopausal endocrine therapy

Breast cancer in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive (HR+) status is a common and complex condition that necessitates a multifaceted approach to management. HR+ breast cancer means that the cancer cells grow in response to hormones such as estrogen and progesterone. This subtype is prevalent among postmenopausal women and typically exhibits a more indolent course compared to other forms of breast cancer, which allows for a variety of treatment options.
Diagnosis and Staging
The diagnosis of HR+ breast cancer begins with clinical evaluation, imaging, and biopsy. Imaging modalities such as mammography, ultrasound, and MRI help in assessing the extent of the disease. Histopathological examination and immunohistochemical staining of the biopsy sample confirm the diagnosis and hormone receptor status by identifying the presence of estrogen receptors (ER) and progesterone receptors (PR) on the tumor cells.
Staging involves determining the size of the tumor (T), the involvement of regional lymph nodes (N), and the presence of distant metastasis (M). The American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) staging system is commonly used. Accurate staging is critical as it guides treatment decisions.
Treatment Options
Endocrine Therapy
Endocrine therapy is the cornerstone of treatment for HR+ breast cancer in postmenopausal women. The primary goal is to reduce the levels of estrogen or block its effects on cancer cells. Commonly used agents include:
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs): Tamoxifen is a SERM that binds to estrogen receptors, blocking estrogen from stimulating breast cancer cells. It is effective but may have side effects such as increased risk of endometrial cancer and thromboembolic events.
Aromatase Inhibitors (AIs): These drugs, including anastrozole, letrozole, and exemestane, lower estrogen levels by inhibiting the aromatase enzyme, which converts androgens to estrogen in peripheral tissues. AIs are generally preferred in postmenopausal women due to their efficacy and safety profile compared to tamoxifen.
Selective Estrogen Receptor Downregulators (SERDs): Fulvestrant is a SERD that degrades estrogen receptors and is used in cases where resistance to other endocrine therapies develops.
Combination Therapies
Combining endocrine therapy with other treatments enhances efficacy. Examples include:
Endocrine Therapy with CDK4/6 Inhibitors: Palbociclib, ribociclib, and abemaciclib are CDK4/6 inhibitors that, when combined with endocrine therapy, significantly improve progression-free survival in advanced HR+ breast cancer.
Endocrine Therapy with mTOR Inhibitors: Everolimus, an mTOR inhibitor, can be added to endocrine therapy for patients who have developed resistance to aromatase inhibitors.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is generally reserved for patients with high-risk features, such as large tumor size, high-grade histology, or extensive lymph node involvement. Regimens often include anthracyclines and taxanes.
STUDIES IN SUPPORT OF SPECIAL POPULATIONS: GERIATRICS E7

Unit 4: MRA 103T Regulatory affairs
This guideline is directed principally toward new Molecular Entities that are
likely to have significant use in the elderly, either because the disease intended
to be treated is characteristically a disease of aging ( e.g., Alzheimer's disease) or
because the population to be treated is known to include substantial numbers of
geriatric patients (e.g., hypertension).
Skin Diseases That Happen During Summer.

Summer is a time for fun in the sun, but the heat and humidity can also wreak havoc on your skin. From itchy rashes to unwanted pigmentation, several skin conditions become more prevalent during these warmer months.
Cervical Disc Arthroplasty ORSI 2024.pptx

Indication and installation of a mobile cervical disc prosthesis. Benefits of the PRODISC C VIVO mobile disc prosthesis (Centinel Spine)
KENT'S REPERTORY by dr niranjan mohanty.pptx

its a presentation on Dr kents Repertory by Dr niranjan Mohanty
“Psychiatry and the Humanities”: An Innovative Course at the University of Mo...

“Psychiatry and the Humanities”: An Innovative Course at the University of Mo...Université de Montréal
“Psychiatry and the Humanities”: An Innovative Course at the University of Montreal Expanding the medical model to embrace the humanities. Link: https://www.psychiatrictimes.com/view/-psychiatry-and-the-humanities-an-innovative-course-at-the-university-of-montreal5 Effective Homeopathic Medicines for Irregular Periods

Discover the benefits of homeopathic medicine for irregular periods with our guide on 5 common remedies. Learn how these natural treatments can help regulate menstrual cycles and improve overall menstrual health.
Visit Us: https://drdeepikashomeopathy.com/service/irregular-periods-treatment/
Top Travel Vaccinations in Manchester

Travel vaccination in Manchester offers comprehensive immunization services for individuals planning international trips. Expert healthcare providers administer vaccines tailored to your destination, ensuring you stay protected against various diseases. Conveniently located clinics and flexible appointment options make it easy to get the necessary shots before your journey. Stay healthy and travel with confidence by getting vaccinated in Manchester. Visit us: www.nxhealthcare.co.uk
PGx Analysis in VarSeq: A User’s Perspective

Since our release of the PGx capabilities in VarSeq, we’ve had a few months to gather some insights from various use cases. Some users approach PGx workflows by means of array genotyping or what seems to be a growing trend of adding the star allele calling to the existing NGS pipeline for whole genome data. Luckily, both approaches are supported with the VarSeq software platform. The genotyping method being used will also dictate what the scope of the tertiary analysis will be. For example, are your PGx reports a standalone pipeline or would your lab’s goal be to handle a dual-purpose workflow and report on PGx + Diagnostic findings.
The purpose of this webcast is to:
Discuss and demonstrate the approaches with array and NGS genotyping methods for star allele calling to prep for downstream analysis.
Following genotyping, explore alternative tertiary workflow concepts in VarSeq to handle PGx reporting.
Moreover, we will include insights users will need to consider when validating their PGx workflow for all possible star alleles and options you have for automating your PGx analysis for large number of samples. Please join us for a session dedicated to the application of star allele genotyping and subsequent PGx workflows in our VarSeq software.
Foundation of Yoga, YCB Level-3, Unit-1 

Unit -1 of Yoga certification board, level 3, all topics covered. An exam conducted by ministry of Ayush for yoga enthusiastic students.
Pollen and Fungal allergy: aeroallergy.pdf

Pollen and Fungal allergy: aeroallergy.pdfChulalongkorn Allergy and Clinical Immunology Research Group
Pollen and Fungal allergy
Presented by Chaloemchai Chumsaengchotsakul, MD.
June 14, 2024Recently uploaded (20)
Know the difference between Endodontics and Orthodontics.

Know the difference between Endodontics and Orthodontics.
Hemodialysis: Chapter 5, Dialyzers Overview - Dr.Gawad

Hemodialysis: Chapter 5, Dialyzers Overview - Dr.Gawad
Medical Quiz ( Online Quiz for API Meet 2024 ).pdf

Medical Quiz ( Online Quiz for API Meet 2024 ).pdf
STUDIES IN SUPPORT OF SPECIAL POPULATIONS: GERIATRICS E7

STUDIES IN SUPPORT OF SPECIAL POPULATIONS: GERIATRICS E7
“Psychiatry and the Humanities”: An Innovative Course at the University of Mo...

“Psychiatry and the Humanities”: An Innovative Course at the University of Mo...
5 Effective Homeopathic Medicines for Irregular Periods

5 Effective Homeopathic Medicines for Irregular Periods
pharmacy exam preparation for undergradute students.pptx

pharmacy exam preparation for undergradute students.pptx
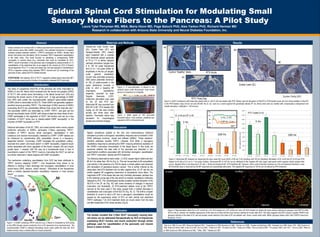
Epidural Spinal Cord Stimulation for Modulating Small Sensory Nerve Fibers to the Pancreas: A Pilot Study
- 1. Epidural Spinal Cord Stimulation for Modulating Small Sensory Nerve Fibers to the Pancreas: A Pilot Study Laura Tyler Perryman MS, MBA, Maria Hizon MD, Page Baluch PhD, Alex Yarkov PhD, Richard Herman MD Research in collaboration with Arizona State University and Neural Diabetes Foundation, Inc. Abstract Materials and Methods Discussion References Obese animals and humans with or without glucose/insulin dysfunction often exhibit small sensory nerve fiber (SSNF) neuropathy. One potential mechanism is impaired transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) expression on SSNFs. Studies have shown that spinal cord stimulation (SCS) increases TRPV1-dependent vasodilatation in the lower limbs. This study focused on identifying a corresponding SSNF neuropathy in visceral tissue (e.g., pancreas) that could be modulated by SCS. TRPV1 neuron innervation of the pancreas was investigated by measurements of: (1) vasodilatation of the abdominal skin (a surrogate for the viscera) by SCS of thoracic neural segments T9 to T11 in lean and obese rats, and rats exposed to resiniferatoxin (RTX) a capsaicin analog which depletes TRPV1 neurons and (2) morphology of the pancreas of lean, obese and RTX treated animals. HYPOTHESIS: 5Hz biphasic SCS of T9-T11 segments creates higher blood flow (BF) to the pancreas preserving the function of neuropathic stressed ISLET beta cells. Zucker Fatty (ZF) Zucker Lean (ZL) Results Twenty-one male Zucker Lean (ZL), Zucker Fatty (ZF), and Sprague-Dawley (SD) rodents were implanted with a unipolar SCS electrode placed epidurally at T9 to T11 to deliver biphasic cathodal stimulation (ranges from 5 to 100 Hz pulse frequencies and 0.2 to 1 ms pulse widths for amplitudes in the low A ranges) under general anesthesia. Current was controlled producing EMG action potentials (minimum of 100 V peak-to-peak) in the upper abdominal muscles in order to elicit a baseline BF (neurogenic vasodilatory) response, recorded by laser Doppler flowmetry (LDF). Antidromic stimulation was used on the ZF and RTX rats. Abdominal BF was recorded from 80% MT to MT. RTX-treated (250 mg/kg, sc) SD rats were studied acutely and three days after injection. Pancreatic tissue was harvested for morphological studies and confocal imaging. Figure 2. A neurostimulator is placed in the epidural space under fluoroscope. Inset shows device in comparison to a fingertip. Figure 4. ISLET architecture with beta-cells stained dark in: (4A-C) SD rats treated with RTX. Please note the disruption of ISLETS in RTX-treated acute rats and virtual abolition of ISLETS in the RTX-treated 3-day chronic rat and (4D-4E) the ZL rat, used as a control against the genetically altered ZF rat, whose beta cells are marked with compensatory enlargement and cellular disruption. Calibration = 100 microns. The Islets of Langerhans (ISLETS) of the pancreas are richly innervated by SSNFs (C and A - fibers) which emanate from the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) of T9-T11 with central axons terminating in the lateral dorsal horn (DH) and traversing the dorsal column of the spinal cord 1 . A high percentage of SSNF from DRG cells contain the neurotransmitter calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) which is transmitted to ISLETS. These SSNFs are generally capsaicin-sensitive neurons encoding TRPV1. The phenotype of DRG neurons of SSNFs innervating ISLETS are considerably different than those that innervate skin 2 . The pancreatic SSNFs are dominated by CGRP, TRPV1, and glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) with values at least two times those of skin. CGRP participates in the regulation of ISLET cell function and can be a key modulator of ISLET stress due to obesity-related SSNF neuropathy 3 or the induction of SSNF neuropathy by RTX 4 . Electrical stimulation of the DC, DRG, and mixed sensori-motor nerves causes antidromic activation of SSNFs, particularly C-fibers expressing TRPV1. Excitation of TRPV1 neurons elicits neurogenic vasodilatation in both cutaneous and visceral microvessels, mediated by CGRP 5 . CGRP release can be influenced by noradrenaline (NA) sympathetic nerves in a frequency-dependent fashion 6 . Conversely, CGRP modulates NA sympathetic outflow 7 , neuronal nitric oxide 8 , and insulin action 9 . In SSNF neuropathy, impaired insulin action associated with down regulation of the insulin receptor (IR) and insulin growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) may be a fundamental factor in loss of neurotrophic support of the TRPV1 neurons innervating the ISLET as well as be a factor observed in obese subjects with SSNF neuropathy 3 . The mechanism underlying vasodilatation from SCS has been attributed to TRPV1 neurons releasing CGRP 10,11 . Low frequencies have shown to be effective in eliciting C-fiber discharge and neurogenic vasodilatation in most neural tissue (DRG, sensory, mixed nerves) 13 . Stimulation at low frequencies elicits a marked capsaicin-sensitive vasodilatory response in most sensory tissue 6 . Introduction 1 Won et al 1998; Su et al 1987; Wang and Westlund 2001. 2 Fasanella et al 2008; Bennett et al 1996. 3 Herman et al 2006. 4 Szallasi and Blumberg 1996. 5 Kawasaki et al 1988; Holzer 1991, 1995, Escott et al, 1995; Khalil and Helme 1996; Croom et al 1997; Wu et al 2006 . 6 Khalil et al 1997. 7 Oh-hashi et al 2001. 8 Holzer et al 1995a. 9 Sima and Kamiy 2006. 10 D ’Luzansky 2000; Cook 1973. 11 Wu et al 2008. 12 Mehri et al 1998; Escott et al 1995; Santicioli et al 1992. 13 Willis, 1999. 14 Wardle et al 1997. Figure 3. EMG signal at 100 microvolts threshold criteria. Once reached, amplitude was adjusted to 80% to threshold levels. RTX Treated (n=5) Algesic substances applied to the skin and transcutaneous electrical stimulation provoke a neurogenic vasodilatory response due to excitation of the SSNF pathways involving dorsal root reflexes (DRRs) 3 . These capsaicin-sensitive pathways express TRPV1. Likewise, SCS elicits a neurogenic vasodilatory response by activating the DRR 13 inducing antidromic excitation of the SSNFs innervating microvessels of the target tissue. In this study we examined whether the beta cells of the pancreas are disturbed in two experimental conditions associated with diminished neurogenic vasodilatation and TRPV1 innervation- obesity and RTX-treatment. The following observations were made: (1) SCS caused higher abdominal skin BF at 5 Hz rather than 100 Hz (Fig. 5). This can be ascribed to NA sympathetic over activity in the presence of a 100 Hz signal; a similar pattern was observed with stimulation of peripheral sensory nerves 6 . This is further inferred by the observation that RTX-treatment did not alter negative flow; (2) ZF rats did not exhibit negative BF suggesting impairment of sympathetic nerve fibers. The magnitude of BF in the obese rats was only minimally decreased, perhaps due to the relatively young age of the rats and/or to residual vasodilatory molecules released by SCS. The morphological studies revealed marked disruption of the ISLETS in the ZF rat (Fig. 4E) with some evidence of changes in neuronal innervation (not illustrated); (3) RTX-treatment deletes most of the TRPV1 neurons at the dose used in this study caused both a marked decrease in vasodilatation and a disruption of the ISLETS (Fig. 4C, 5). The shift to a higher threshold of current to elicit a MT and a neurogenic vasodilatation would be caused by the suppressive action of RTX on both central and peripheral TRPV1 pathways. 14 (4) SCS treatment elicits an insulin action from the beta cell after treatments of 45 minute duration (Fig 6). The studies revealed that C-fiber ISLET neuropathy causing beta-cell stress can be addressed therapeutically by SCS at frequencies modulating ISLET function and insulin production through similar pathways used for vasodilatation of the pancreatic and visceral tissue in obese animals. Figure 5. Abdominal BF analyzed by measuring the area under the curve (AUC) of 90 sec 5 Hz (exciting) and 100 Hz (blocking) stimulation of ZL (n=6) and ZF (n=9) and RTX treated (n=5) rats at 0.2 ms or 1 ms pulse duration. Decreased BF at 100 Hz can be attributed to the negative BF (see upper right panel) which appears before positive flow occurs. Negative flow is not observed in ZF rats..) At the pre-treatment MT, RTX abolishes BF. However, when current intensity increases by 2-4x pre-treatment threshold, a new MT threshold value is observed but the BF responses are substantially attenuated. The negative BF responses at 100 Hz are not altered by RTX-treatment. 4A 4B 4C 4D 4E ZL (n=6) and ZF (n=9) Figure 1. A SSNF containing TRPV1 neurons (e.g. C-fibers) is modulated by SCS acting on the DRG through volume conduction from a DC placement of an electrode lead. The neurotransmitter CGRP is released stimulating insulin action within the beta cell. SCS treated animals show a marked effect on insulin production. 5 Hz Conclusion Figure 6. Representative islets from a ZL control rat, a ZL SCS treated rat, a ZF control rat, and a ZF SCS treated rat. Notice the more obvious staining for glucagon and PGP 9.5 after SCS in the ZL animals, the healthier appearance of the islet as a whole and the more obvious staining for insulin after SCS . This data suggests that SCS results in greater PGP9.5 and glucagon staining in the islets of ZL rats and greater insulin staining in the islets of ZF pre‐diabetic rats . Green: insulin (beta cells); White: glucagon (alpha cells); Red: PGP9.5 (neurons); Scale bar: 75 um. 4E Control “Healthy” Islets RTX Acute RTX Three Day