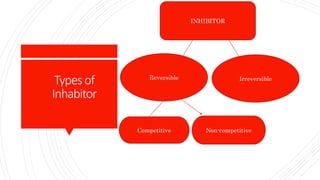
This document provides information about enzymes and key related concepts. It defines enzymes as substances produced by living organisms that act as catalysts for biochemical reactions in cells. It discusses cofactors, prosthetic groups, and coenzymes that assist enzymes. It also describes apoenzymes and holoenzymes, and characteristics of enzymes like being globular proteins that lower activation energy. The document outlines mechanisms of enzyme action through enzyme-substrate complexes and discusses factors affecting enzymes like temperature and pH. It also introduces the lock-and-key and induced fit models of enzyme-substrate binding and different types of inhibitors.