Embed presentation
Download to read offline




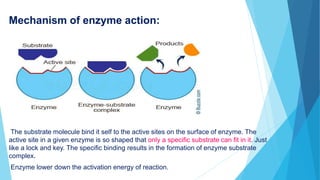




Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts for biochemical reactions by binding to specific substrate molecules. Enzymes have an active site that allows only particular substrates to bind via a "lock and key" mechanism. This binding forms an enzyme-substrate complex and lowers the activation energy needed for the reaction, accelerating the production of products. For example, the activation energy of acid hydrolysis of sucrose is 6.22 kj/mol, but only 2.15 kj/mol in the presence of the sucrose enzyme. The enzyme then changes shape after producing products and can no longer bind substrates.








