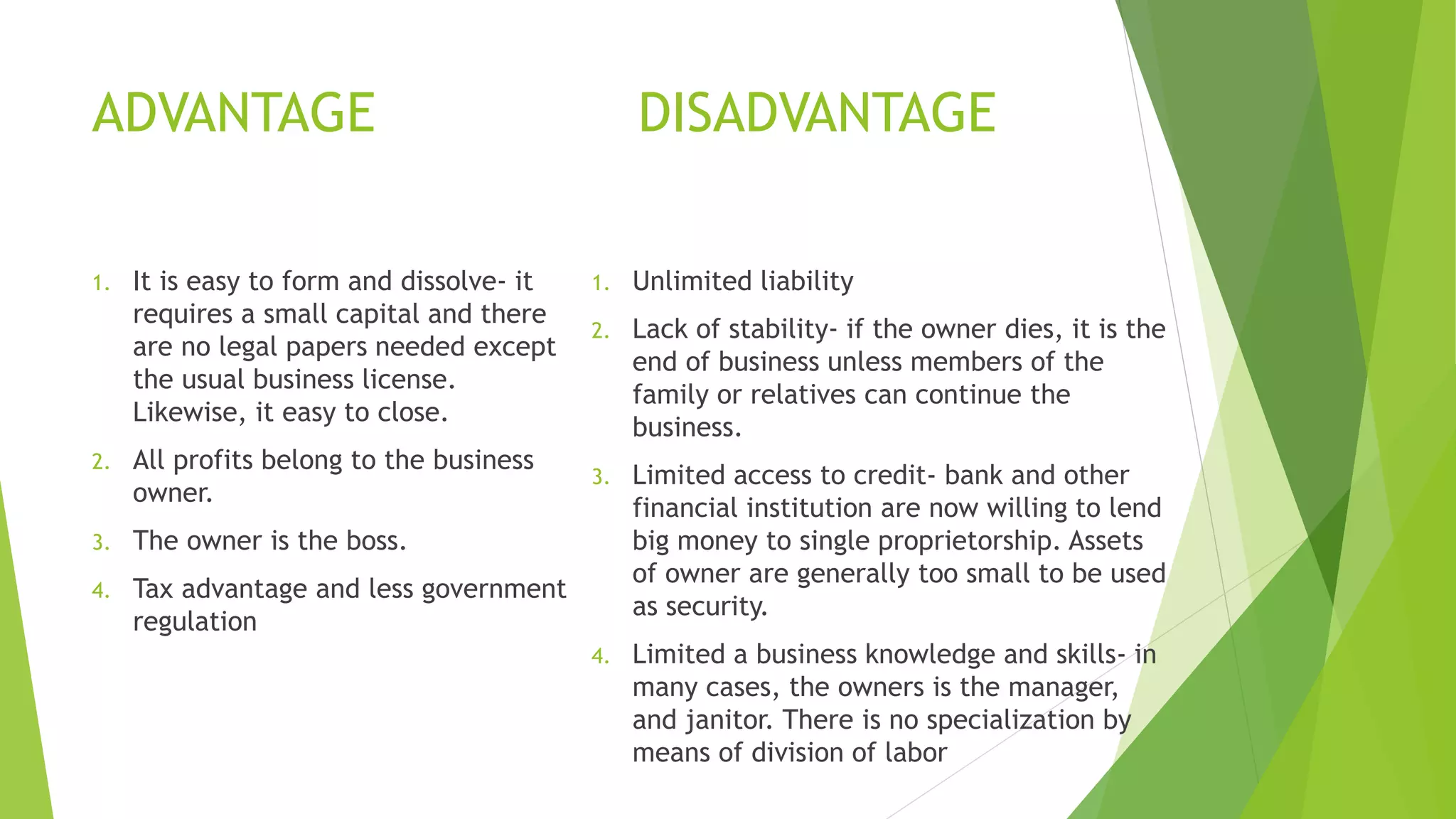
The document defines entrepreneurship and discusses various views on what constitutes an entrepreneur. It provides definitions that describe entrepreneurs as individuals who start new businesses, identify opportunities to improve their environment, and take risks to implement ideas. The document also outlines the benefits of entrepreneurship such as job creation, economic growth, and improved quality of life. It discusses different forms of business organization including sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations, as well as their advantages and disadvantages. Finally, it touches on environmental scanning as important for developing long-term business strategies.