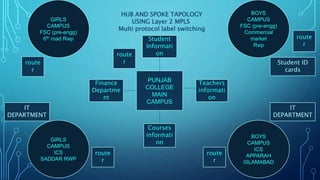
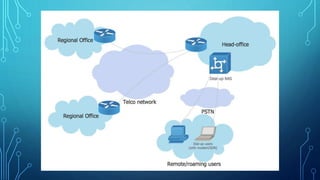
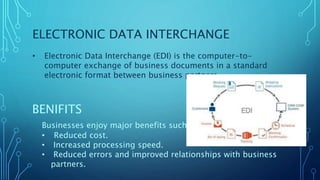
An enterprise private network is a computer network controlled by a single organization that connects multiple offices and locations. It allows resources like student information, teacher information, and finance systems to be securely shared across locations. Enterprise private networks first emerged in the 1970s and were built over telecom networks, but now often use virtual private network technology and encryption over public internet infrastructure. For example, one organization describes its use of a Layer 2 MPLS network with hub and spoke topology to connect various campuses and departments.