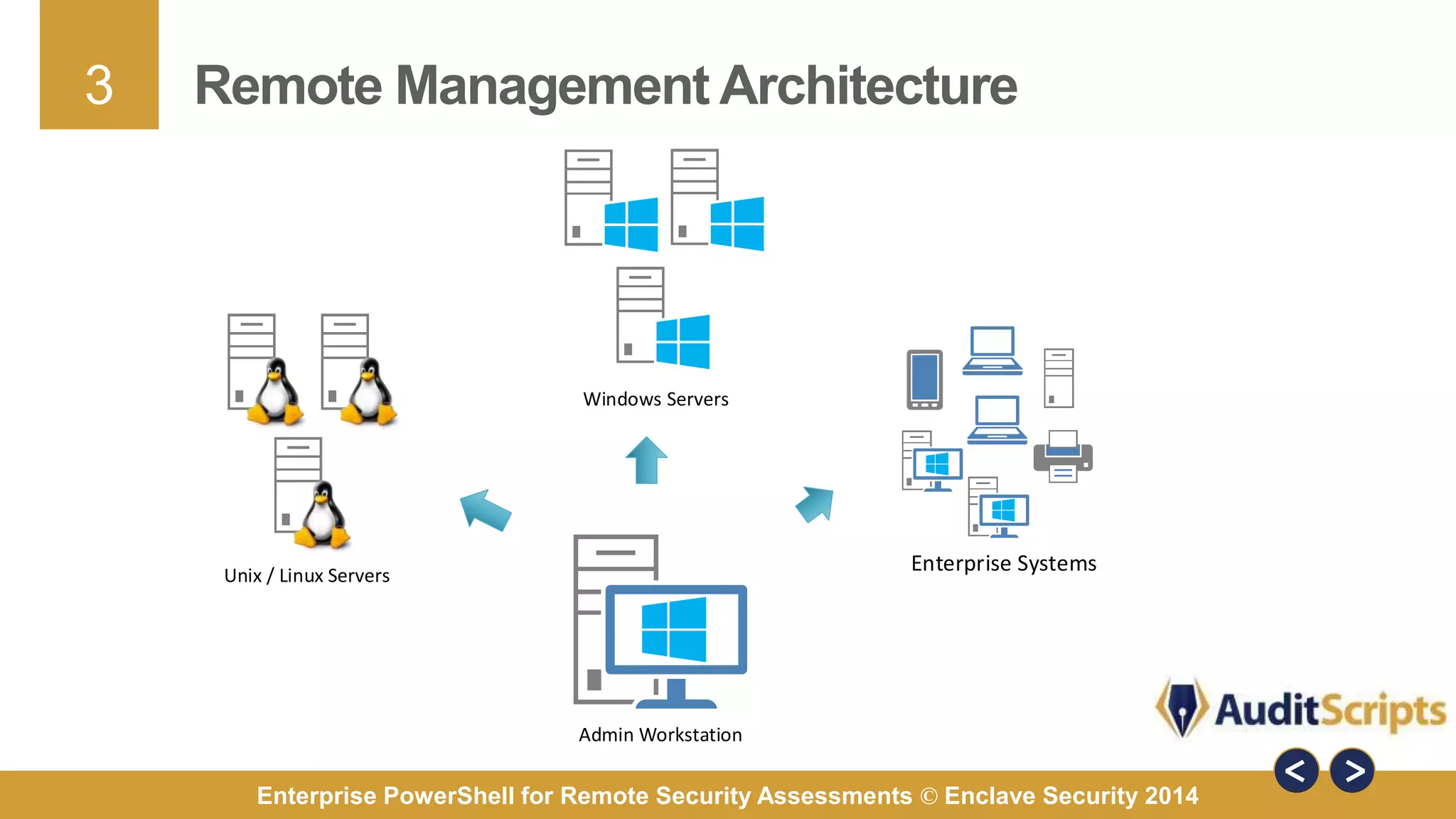
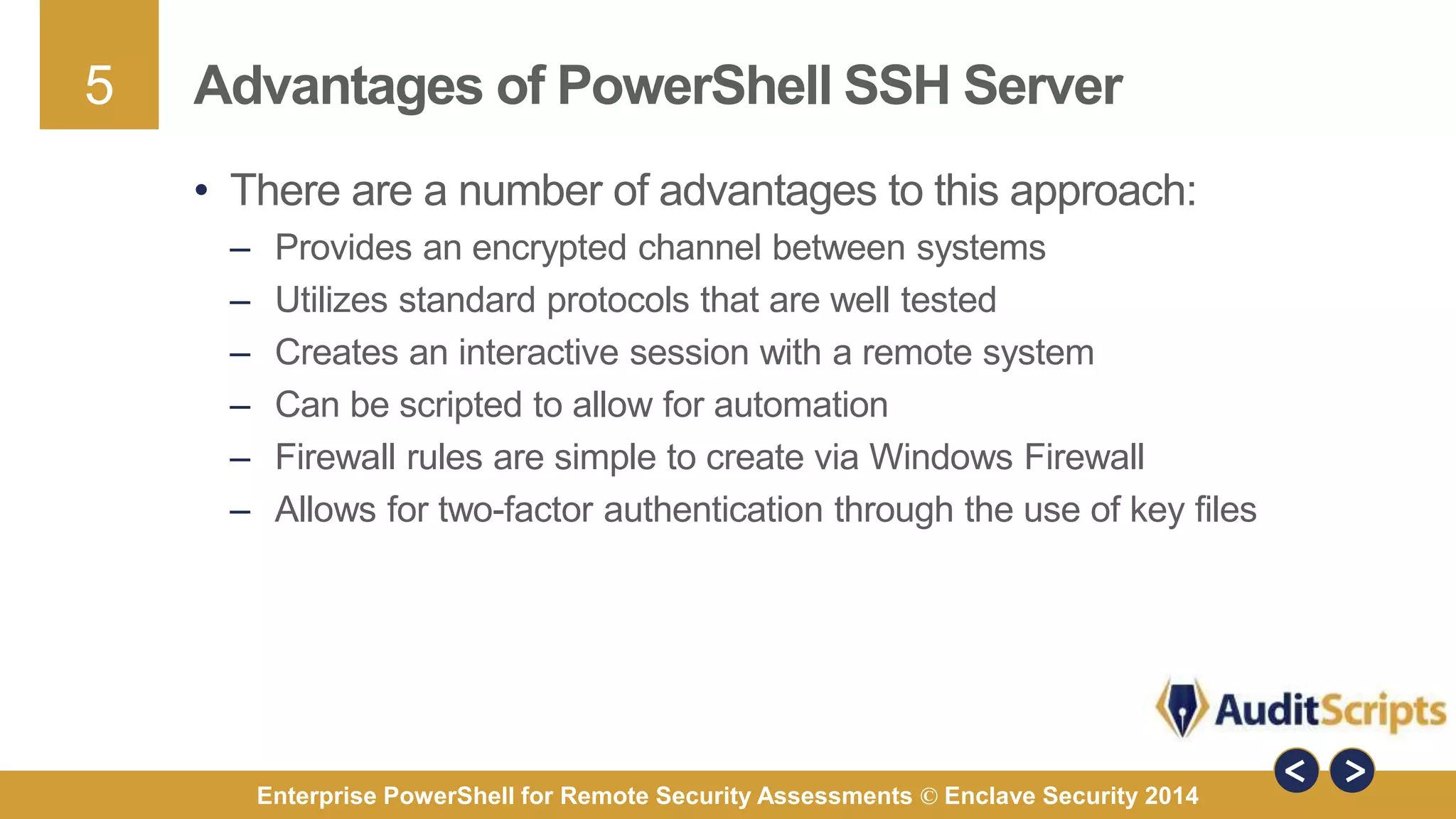
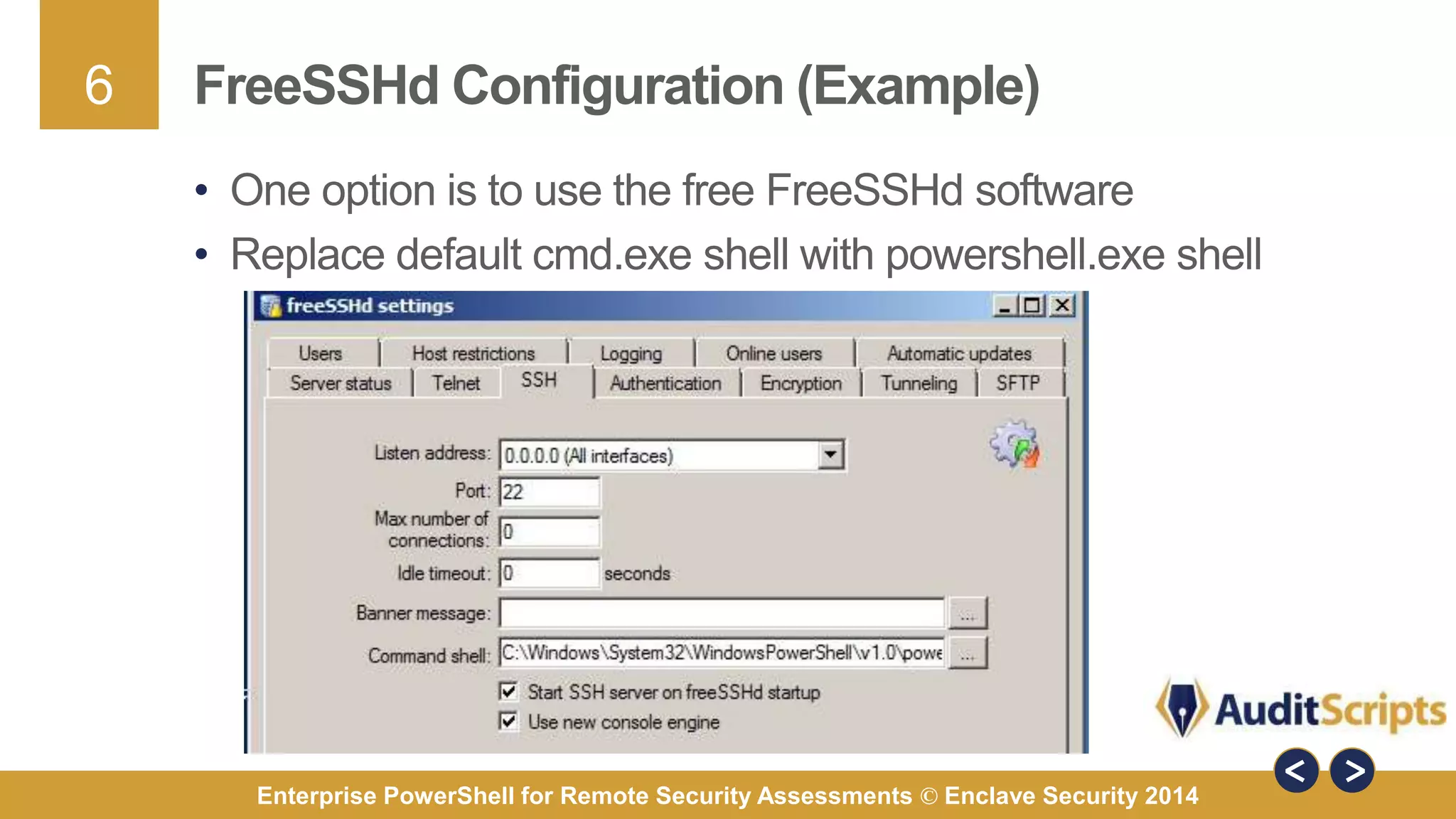
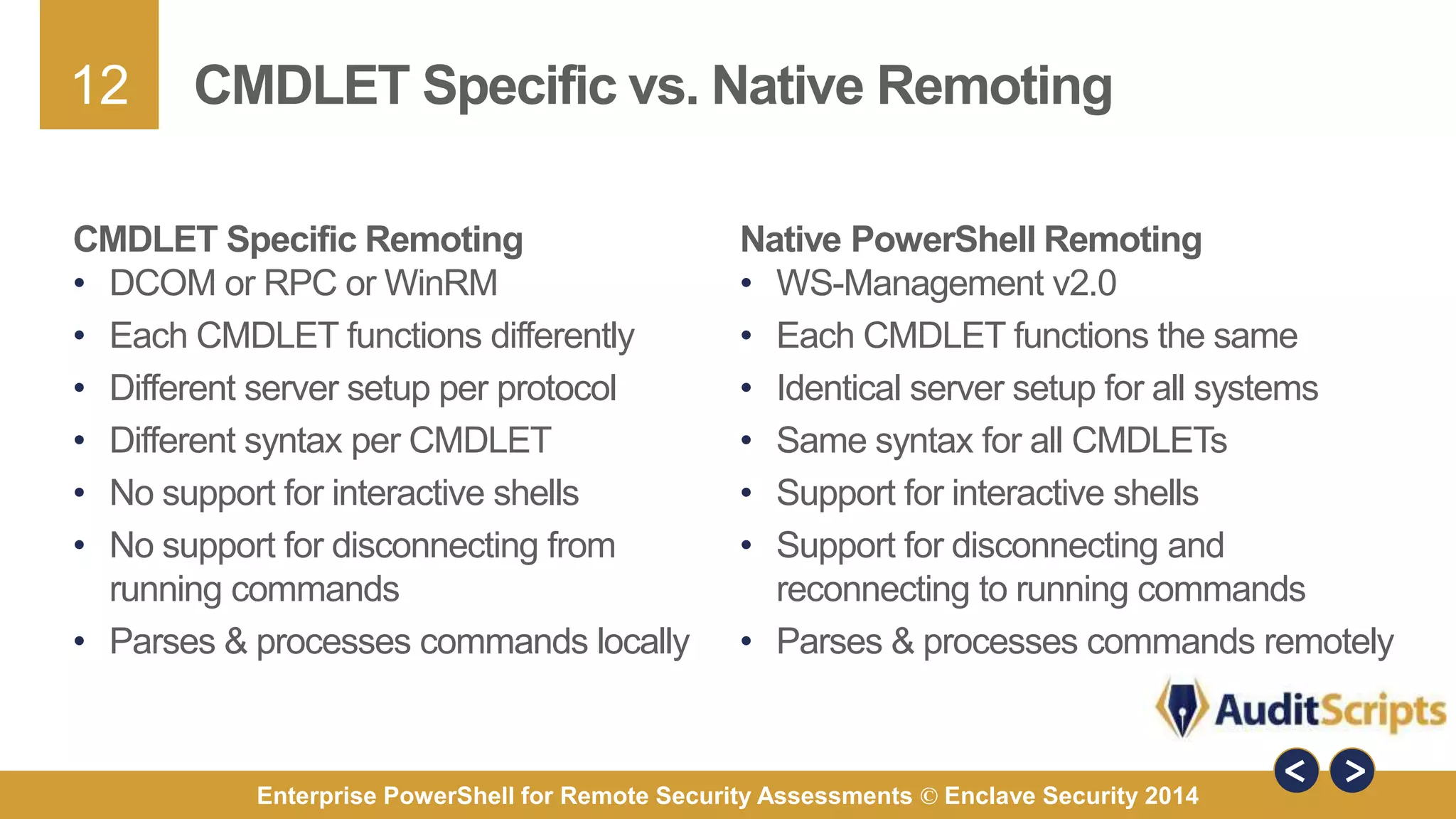
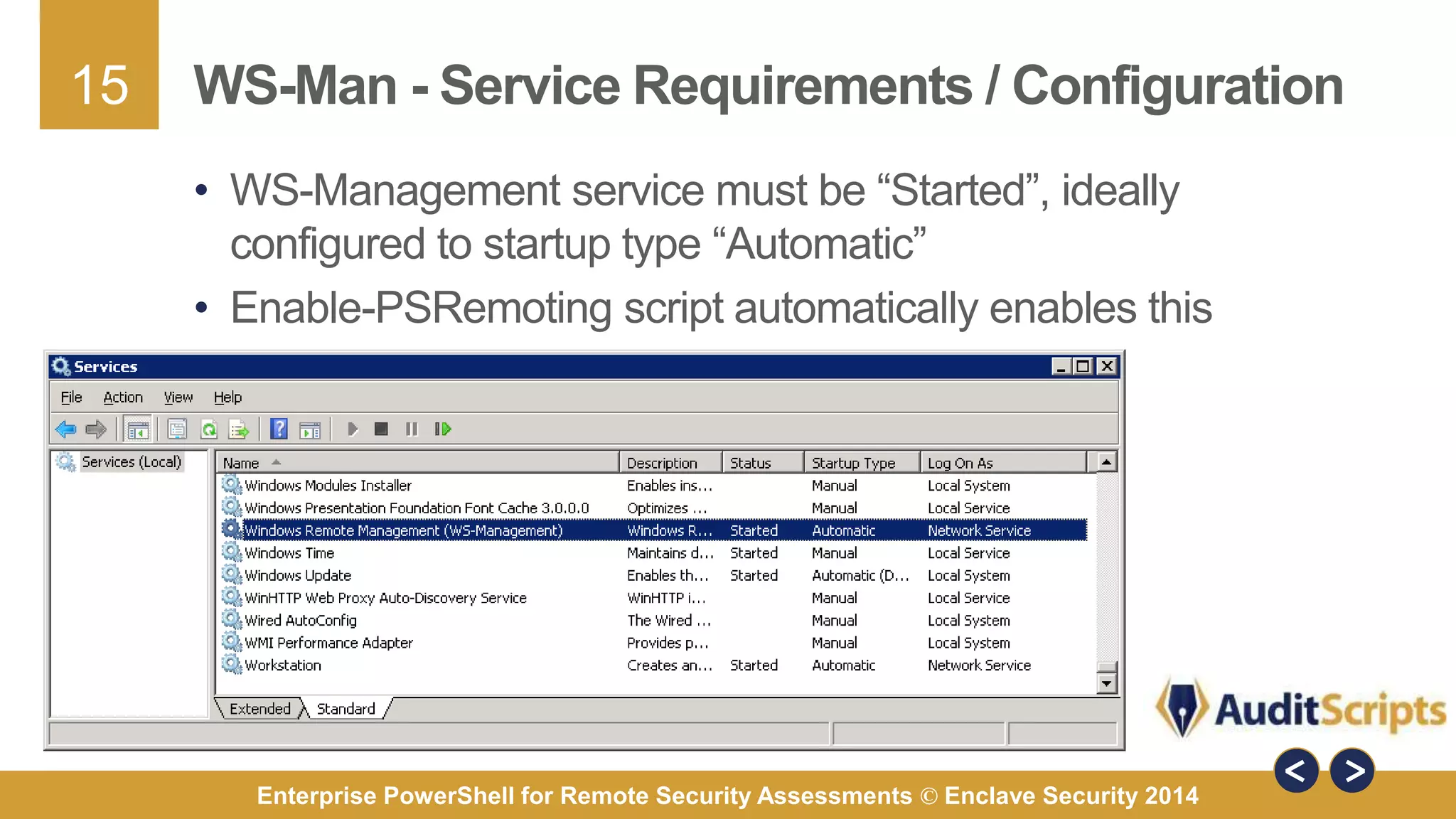
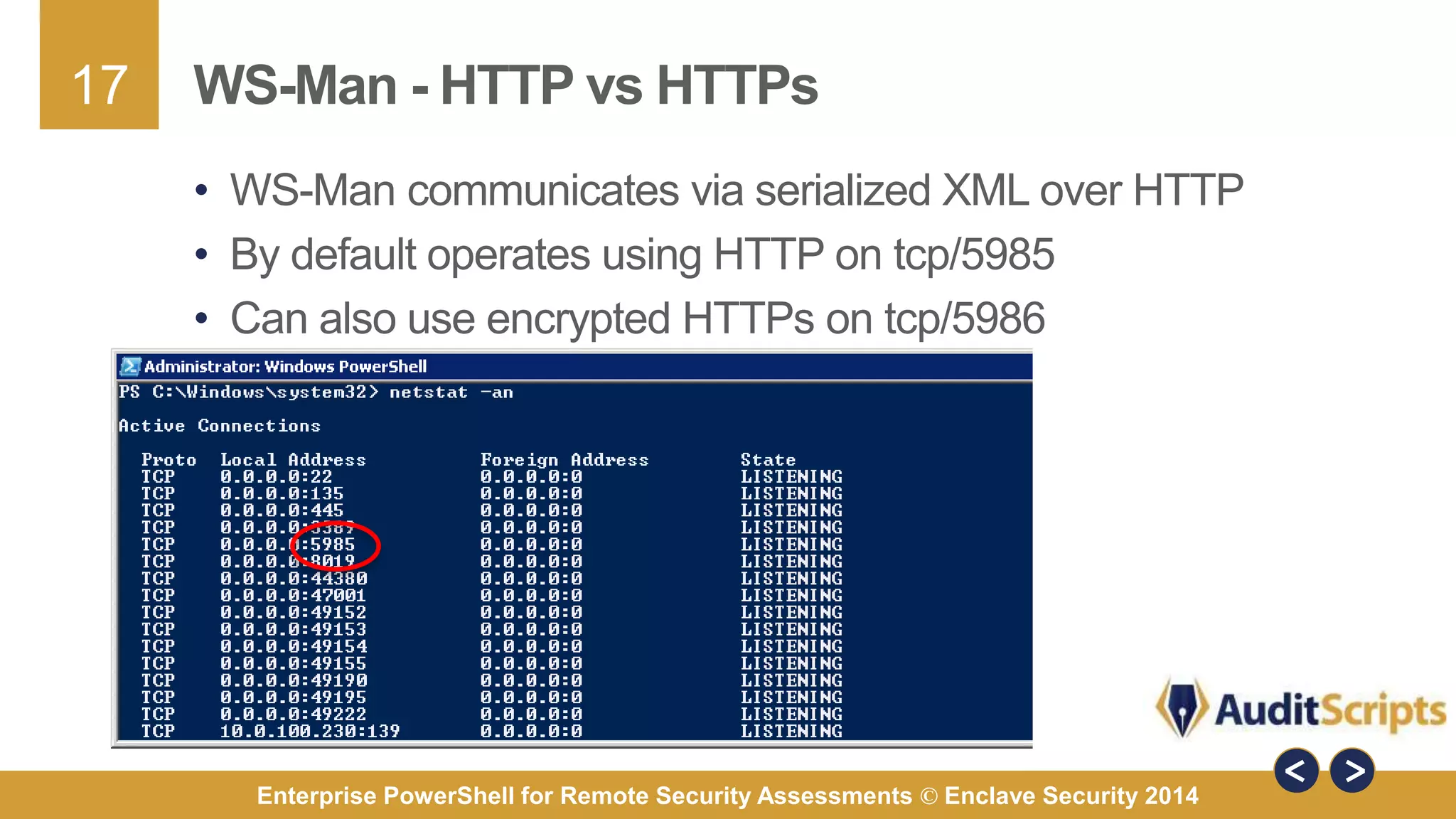
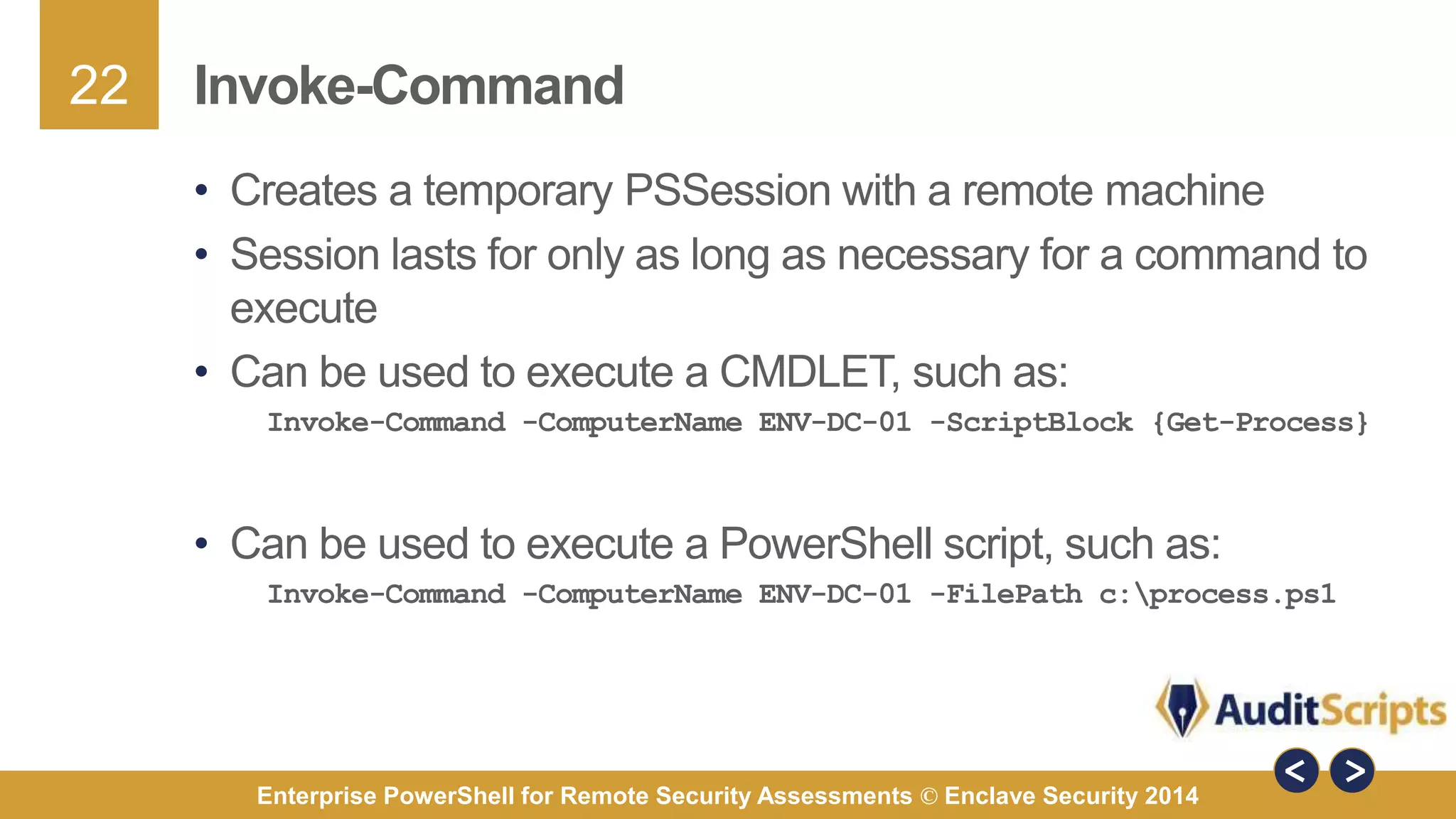
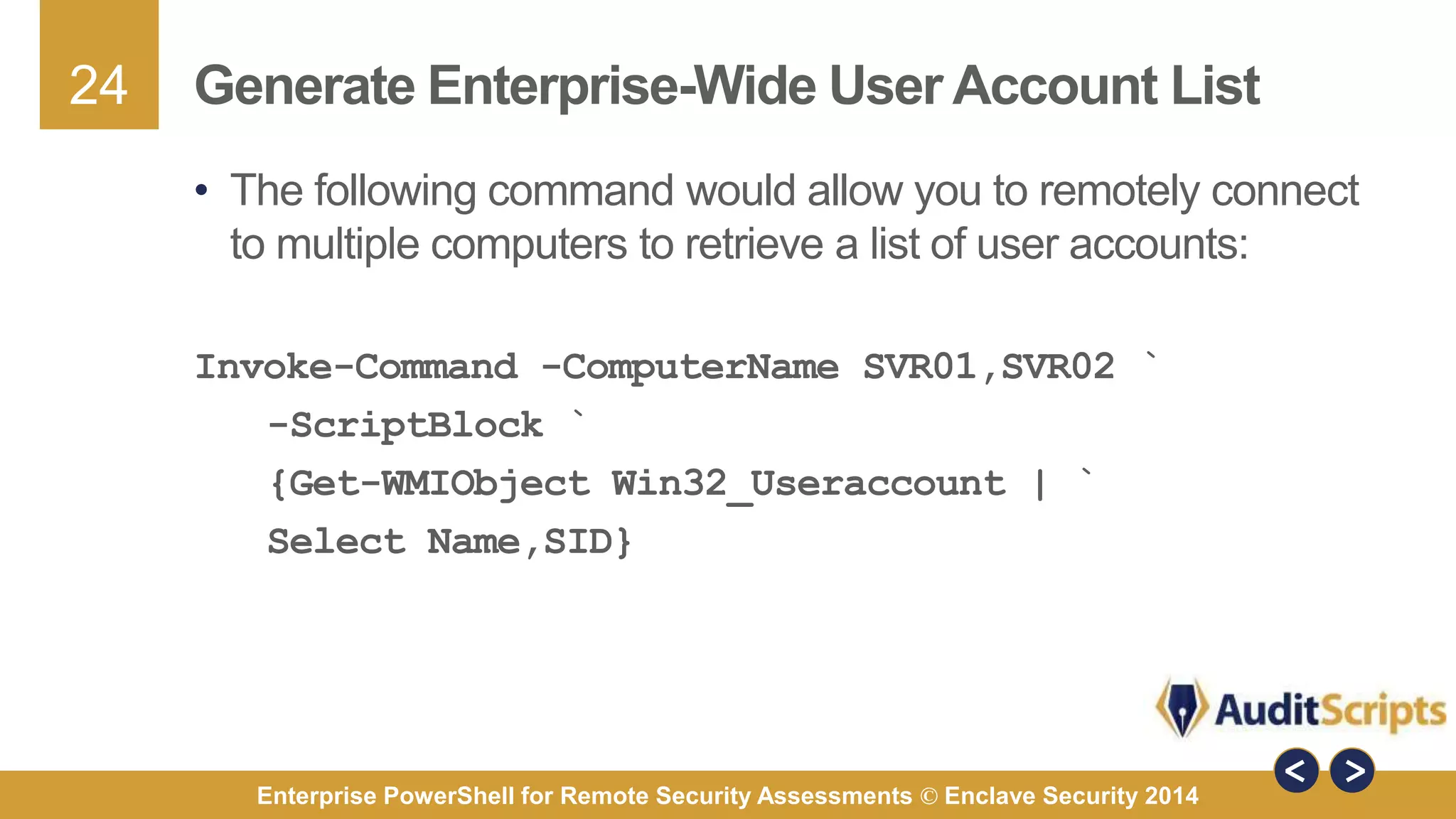
The document discusses using PowerShell for remote security assessments. It describes using SSH with PowerShell to remotely manage Windows and Unix machines. A better solution is to use Windows Remote Management (WinRM) and WS-Management to create PowerShell sessions on remote machines, allowing administrators to run commands and scripts remotely with the same syntax. Examples are provided for using PowerShell to generate user lists, scan for malicious processes, kill processes, and parse event logs across multiple remote machines.