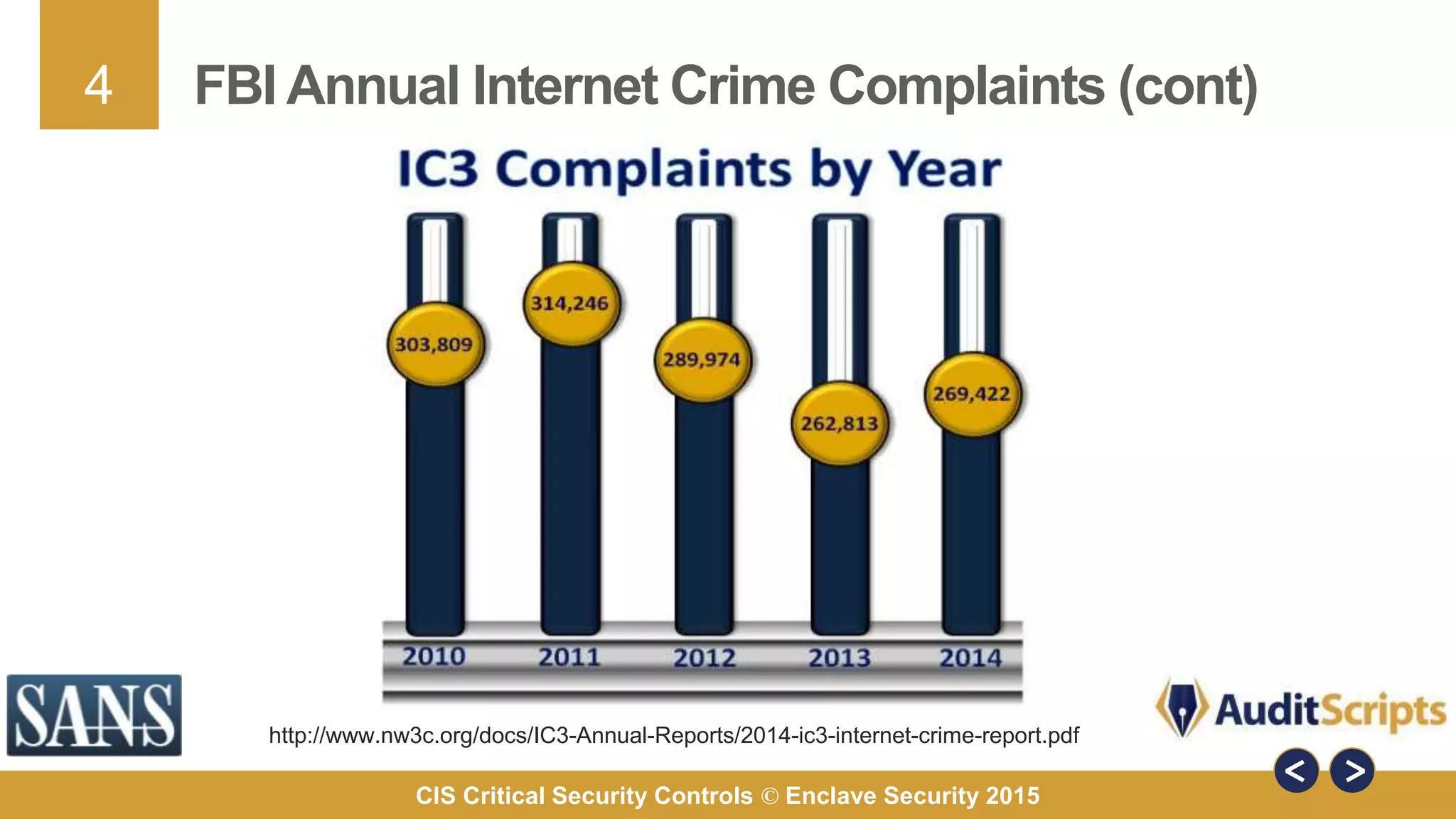
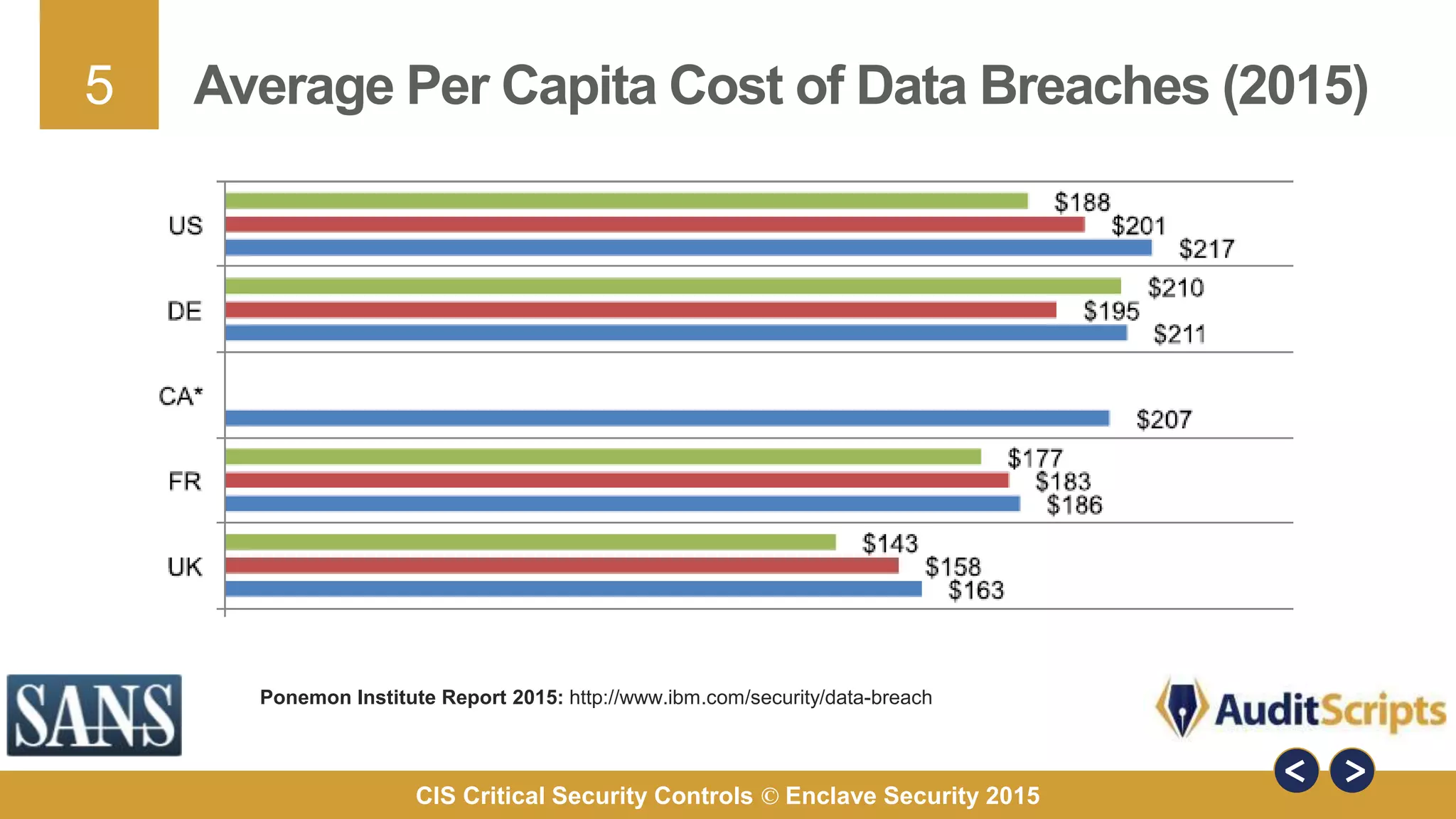
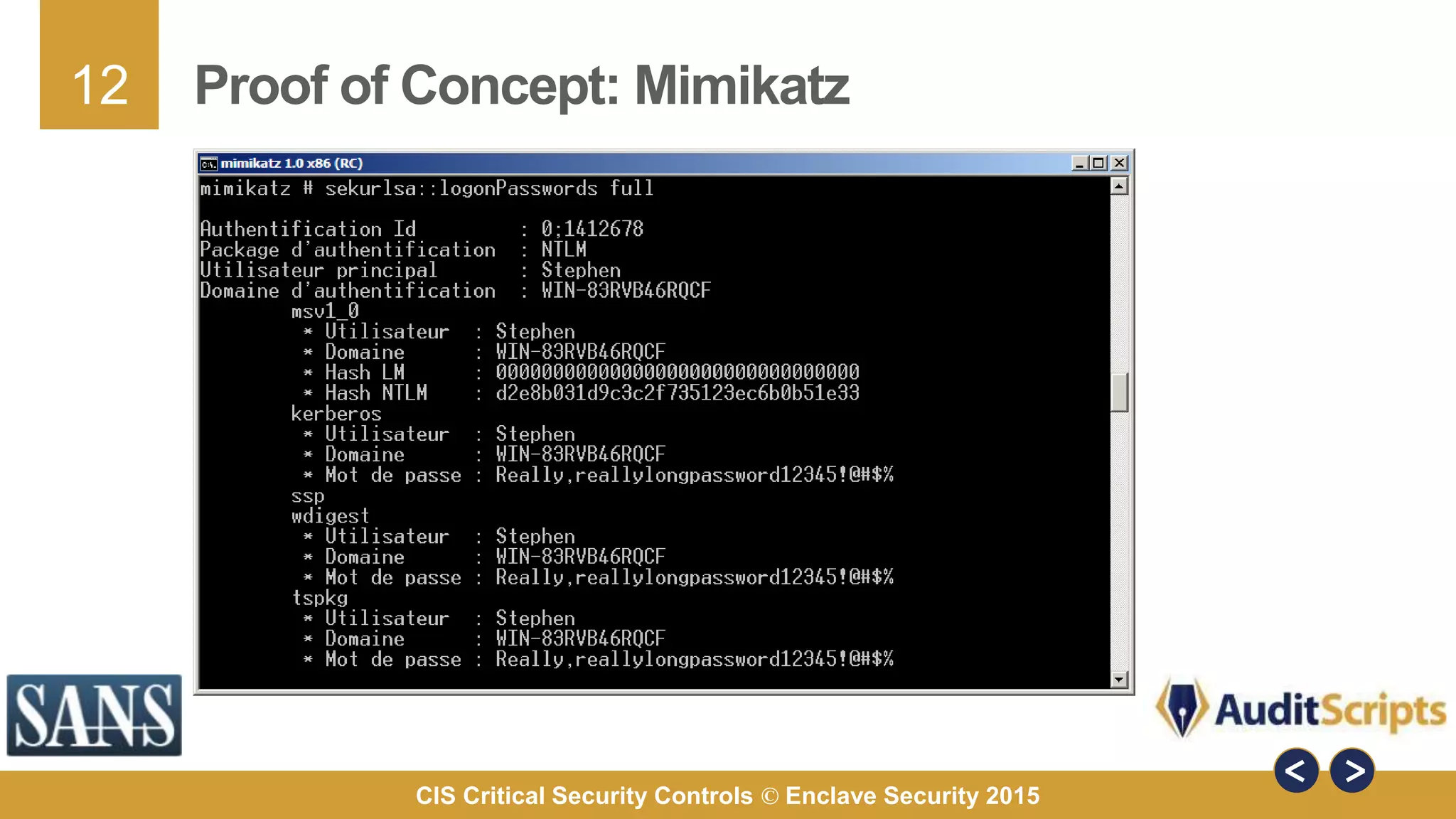
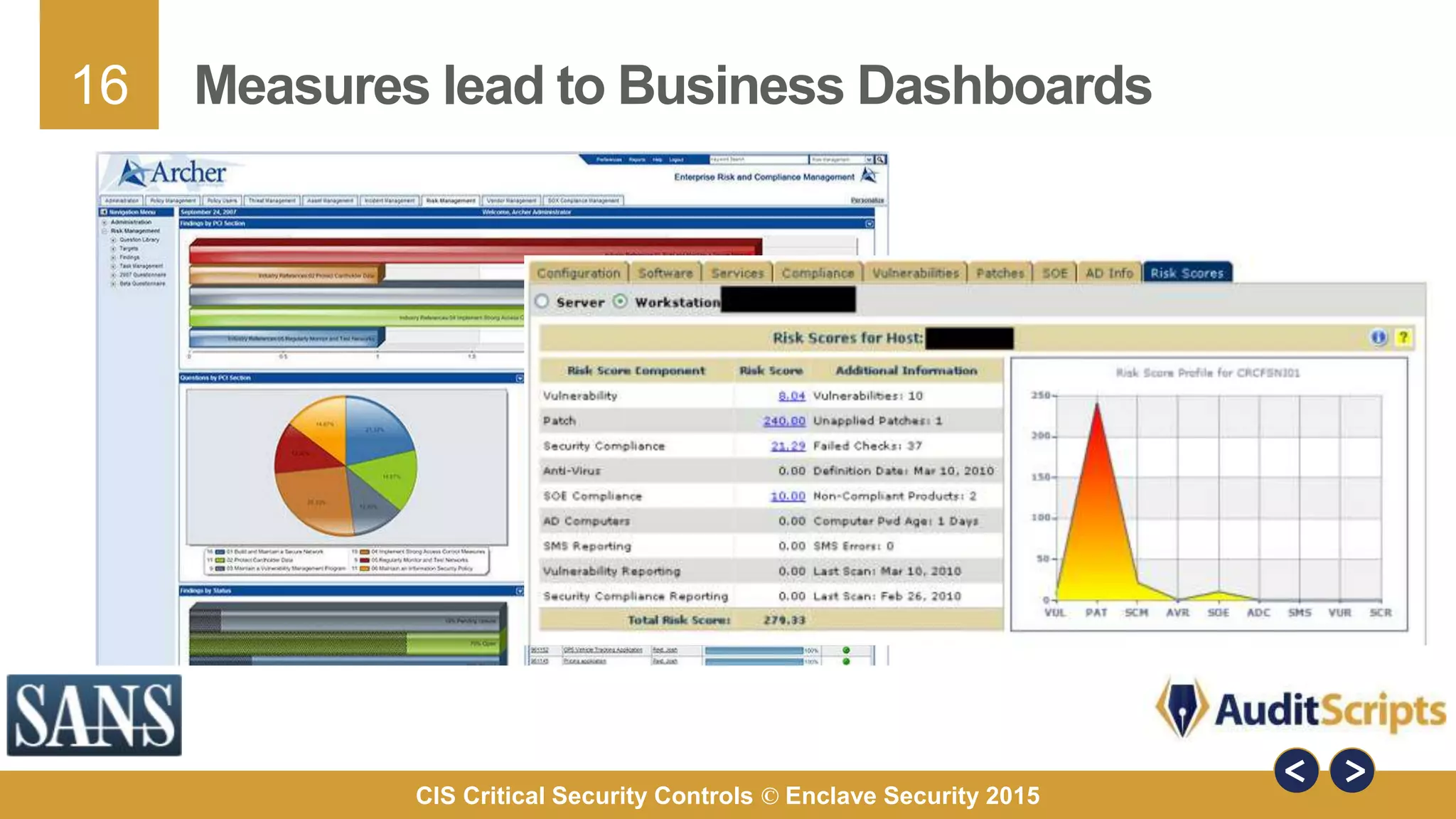
The document discusses why organizations are implementing the Critical Security Controls (CSCs). It provides 7 key reasons: 1) organizations are experiencing breaches, 2) the CSCs were developed by hundreds of cybersecurity experts, 3) the CSCs provide comprehensive and practical guidance, 4) the CSCs can stop known attack techniques, 5) the CSCs define specific measures for assessing risk, 6) the CSCs are based on known current threats, and 7) implementing the CSCs helps organizations achieve compliance with other standards. The document uses a 2013 Java vulnerability as a case study to demonstrate how the CSCs could have prevented the attacks.