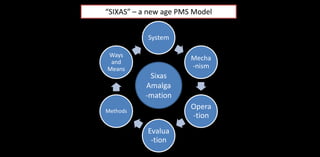
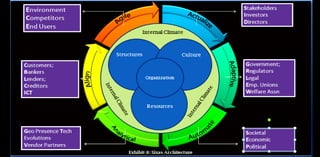
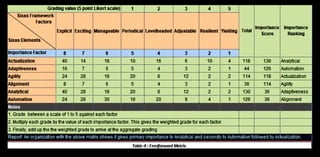
The document provides an overview of performance management systems (PMS) evolution, critical factors for adopting electronic performance management systems (e-PMS), and best practices such as OKRs for goal management. It highlights the continuous communication process aimed at aligning individual and organizational objectives, as well as the need for adaptable and resilient practices post-COVID-19. The discussion includes various evaluation methods, integration of technology, and emerging workforce trends that impact organizational effectiveness.

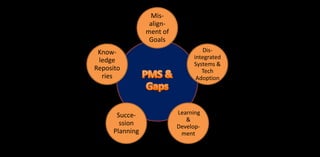

![People Factors
Tech Factors
Org. Factors
- Top management support,
- User acceptance,
- Effective communication
-Skills in HR and cultural factors.
- Extent of customization
- Modifying plug n play model
- Manageable complexity of ePMS
-Data Integrity | System usefulness
- Integration with 3rd party software
- Size of the organization
- Characteristics of organization
- Capacities & capabilities [training]
-Geographical distribution of
business & data integrity [ Sales &
Marketing ]
Adoption
Factors of
ePMS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/epmsppt26-aug-2020-200828122254/85/Enterprise-Performance-Management-System-or-ePMS-or-e-PMS-6-320.jpg)





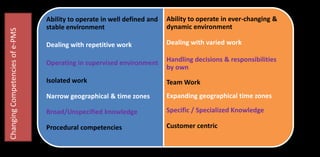
![Cloud based apps are
integrated with SNS;
automation;
administrative efficiency
Social Media Connect
Multiple evaluations;
helpful for developmental
purposes [not rewards];
anytime access to data
360-D Feedback
Favourable towards
electronic feedback ;
image management; less
time on processes & more
time on performance
management;
Feedback
Streamlines process
sometimes feedback is
harsh & negative and does
not give. addl Inuts; not
always captures relevant
aspects of performance;
Looks Good to Systems
rather displaying
performance related
behaviours;
Misunderstanding;
Distruct
Communication
Interpersonal distance
Tightly monitoring
behaviour; lower level
satisfaction; Systems
are not secure
Privacy violation
Merits
Demerits
Evaluation of
ePMS
Cuts costs; Decreases
time & effort; increases
efficiency; administrative
capablities; closely
replicates pen & paper;
Employee & Manager
relationships are strained;
Heavily rely on
comp.data than fact-
finding interactions;
biased, polit.,
Mechanical](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/epmsppt26-aug-2020-200828122254/85/Enterprise-Performance-Management-System-or-ePMS-or-e-PMS-13-320.jpg)

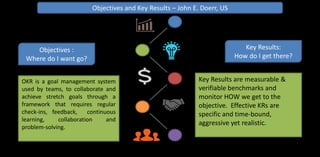


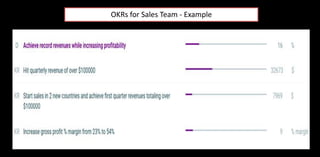

![Weekly check-
ins for tracking
results
Quarterly
tactical
OKRs for the
teams
High Level strategic OKRs
for the company [low
prices, fast delivery, vast
selection – Amazon, Jeff
Bezos]
OKRs -Nested Cadences](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/epmsppt26-aug-2020-200828122254/85/Enterprise-Performance-Management-System-or-ePMS-or-e-PMS-20-320.jpg)