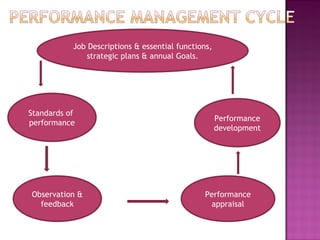
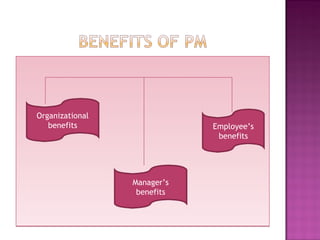
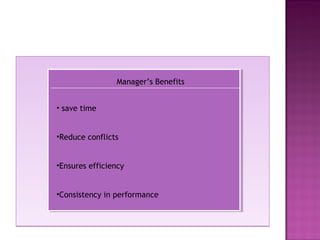
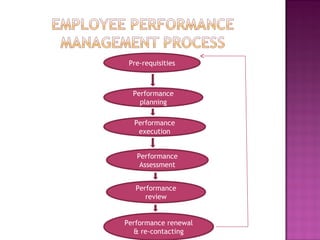
Performance management is a subset of human resource management that focuses on facilitating employee development and organizational goals. The performance management cycle begins with establishing job descriptions and performance standards, then involves ongoing observation, feedback, and development. The goals of performance management are to assess and develop employee performance in order to meet organizational objectives, identify performance gaps, and provide continuous learning opportunities to improve employee capabilities. An effective performance management system communicates organizational vision and strategies, sets measurable individual and departmental goals, provides formal reviews, and links performance to rewards and career development.