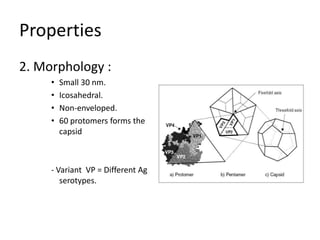
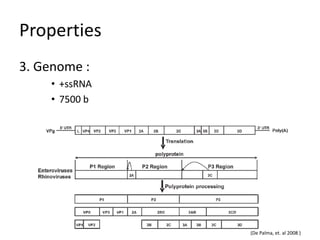
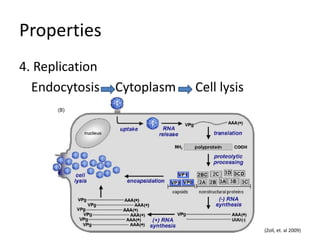
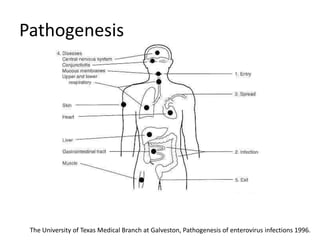
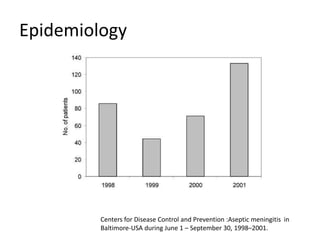
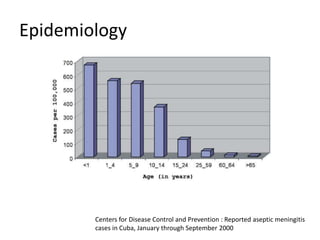
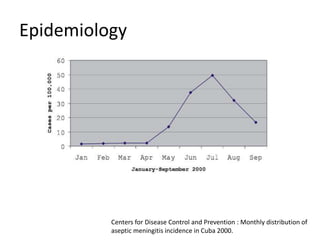
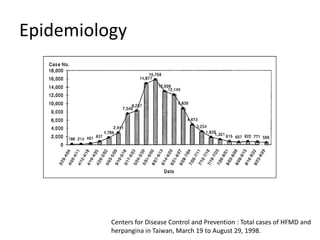
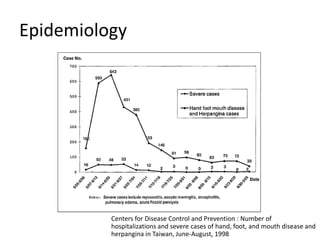
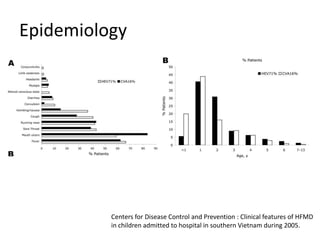
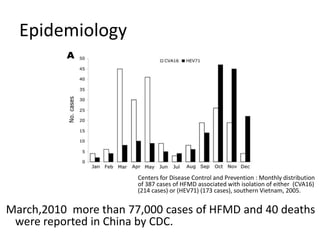
This document provides an overview of enteroviruses, including their properties, clinical aspects, pathogenesis, treatment and epidemiology. It describes enteroviruses as common human pathogens that usually cause mild fever but can rarely lead to severe disease. Key points include that enteroviruses are small, non-enveloped viruses that replicate in the cytoplasm and can cause illnesses like aseptic meningitis, hand foot and mouth disease, and herpangina. While good hygiene helps prevent transmission, there are currently no vaccines or specific antiviral treatments.