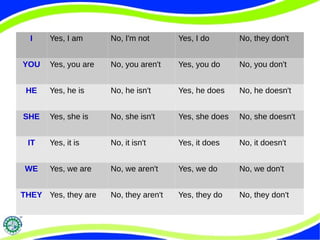
The document discusses various English grammar topics including the simple present tense, pronouns, and future plans expressed with "be going to". It explains that the simple present is used for regular actions, facts, future schedules, and present thoughts/feelings. It also discusses subject and object pronouns, questions formed with "be" and "do", short answers, the uses of "would", and using the present continuous form to talk about future plans with time expressions like "tonight".