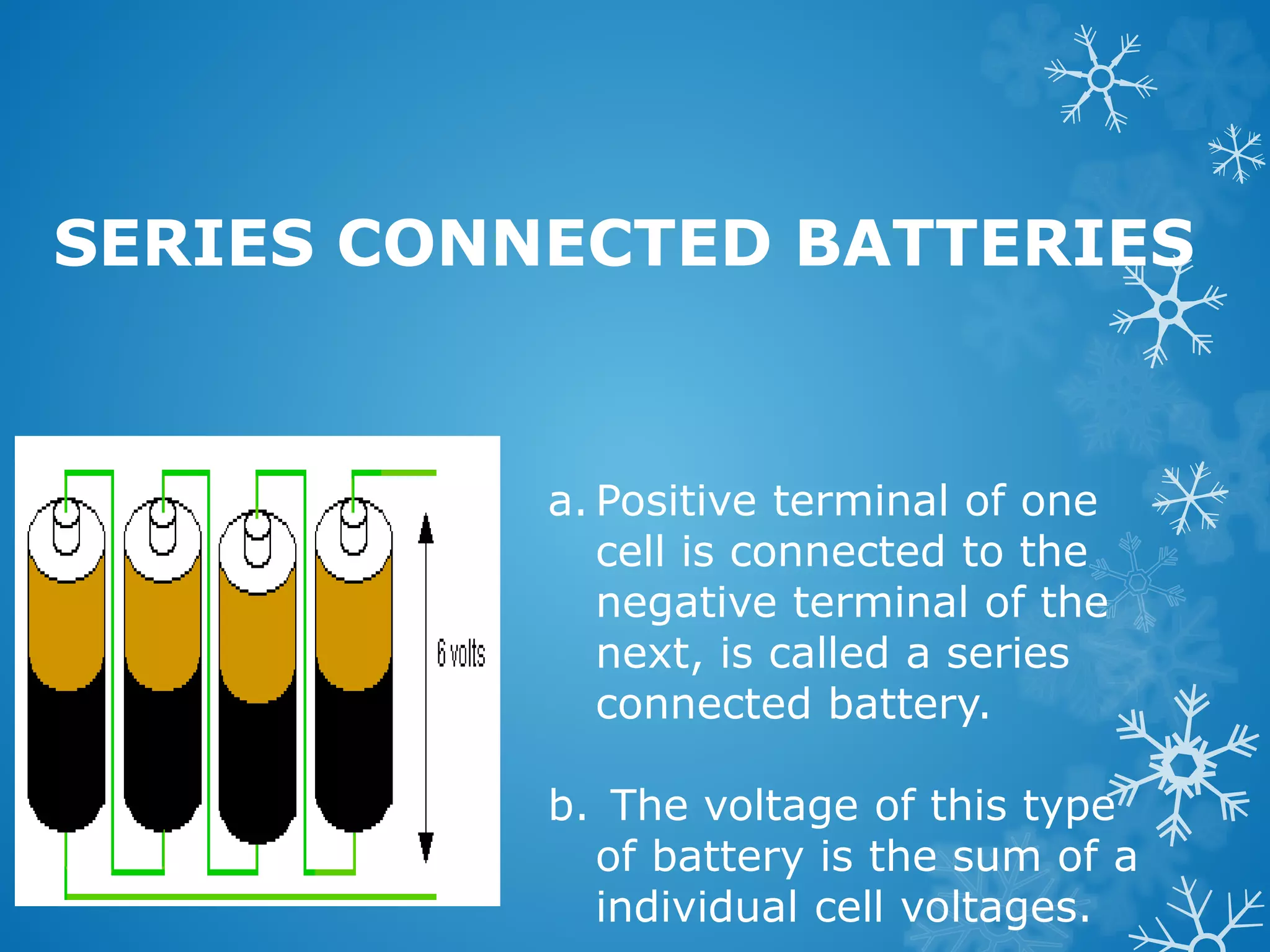
The document discusses different types of batteries, including primary batteries that are not rechargeable and secondary batteries that are rechargeable. It provides examples of the lead acid battery, a secondary battery, and dry cells, a primary battery. It describes the basic components of cells, including electrodes, electrolyte, and separators. It also covers how batteries can be connected in series or parallel configurations and the chemical reactions that occur during charging and discharging of batteries. The document discusses new types of flexible paper batteries and applications of lithium batteries in wearable electronics and other innovative devices.