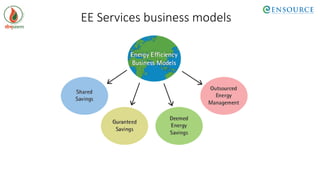
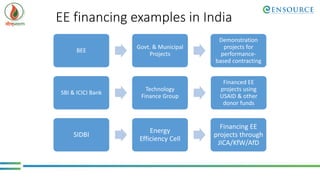
The document outlines energy efficiency (EE) projects, which range from simple retrofits to complex technology upgrades, focusing on their characteristics, financing models, and barriers. It highlights the National Mission for Enhanced Energy Efficiency (NMEEE) initiative, which aims to facilitate finance and promote awareness of EE benefits, as well as various financing instruments like the Partial Risk Guarantee Fund and Venture Capital Fund for energy efficiency. Additionally, it discusses the necessary steps for banks and financial institutions to enhance their EE financing capabilities and examples of successful projects in India.