Embed presentation
Download to read offline

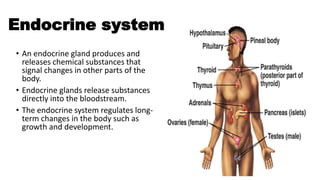




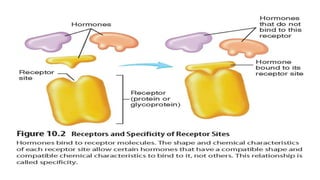
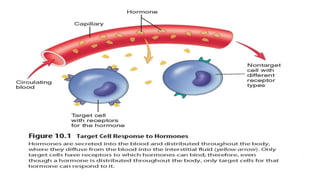

The endocrine system regulates long-term changes in the body through glands that release chemical substances called hormones directly into the bloodstream. Hormones control homeostasis, metabolism and growth, reproductive functions, water balance, heart rate and blood pressure, immune function, and more. Hormones are either steroid hormones that diffuse through cell membranes or nonsteroid hormones that bind to receptors on cell surfaces or inside cells. The endocrine glands include the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pituitary, pancreas, ovaries, testes, and placenta.







