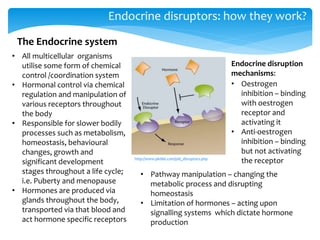
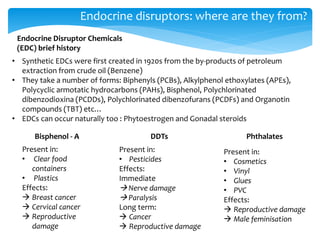
This document discusses endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and their effects. It provides background on how EDCs impact the endocrine system and examples of common EDCs such as bisphenol A, DDT, and phthalates. Sources of EDCs are identified as agriculture, landfills, littering, waterways, and oceans. Case studies demonstrate the bioaccumulation of EDCs in polar bears and sea birds, leading to health effects. Implications for human health are discussed, including concerns about the "cocktail effect" of simultaneous exposure to multiple EDCs and bioaccumulation over a lifetime.